Tutorial
Physical Layer
Data Link layer
Network Layer
Routing Algorithm
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Network Security
Misc
- Router
- OSI vs TCP/IP
- TCP vs UDP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP port
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- ARP Packet Format
- ARP Table
- Working of ARP
- FTP Client
- FTP Commands
- FTP Server
- I2C Protocol
- Sliding Window Protocol
- SPI Protocol
- IP
- ARP Commands
- ARP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP and its types
- TCP Retransmission
- CAN protocol
- HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- RIP Protocol
- UDP Protocol
- ICMP Protocol
- MQTT protocol
- OSPF Protocol
- Stop and Wait Protocol
- IMAP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- CIFS
- DAS
- DIMM
- iSCSI
- NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- NFS
- NVMe
- SAN
- Border Gateway Protocol
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- RJ Cable
- Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Service
- CDMA vs. GSM
- What is MAC Address
- Modem vs. Router
- Switch Vs. Router
- USB 2.0 vs 3.0
- Difference between CSMA CA and CSMA CD
- Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
- URI vs URL
- IMAP vs. POP3
- SSH Meaning| SSH Protocol
- UTP vs STP
- Status Code 400
- MIME Protocol
- IP address
- proxy server
- How to set up and use a proxy server
- network security
- WWW is based on which model
- Proxy Server List
- Fundamentals of Computer Networking
- IP Address Format and Table
- Bus topology and Ring topology
- Bus topology and Star topology
- Circuit Switching and Packet switching?
- Difference between star and ring topology
- Difference between Router and Bridge
- TCP Connection Termination
- Image Steganography
- Network Neutrality
- Onion Routing
- Adaptive security appliance (ASA) features
- Relabel-to-front Algorithm
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Access Lists (ACL)
- What is a proxy server and how does it work
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Operating system based Virtualization
- Context based Access Control (CBAC)
- Cristian's Algorithm
- Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)
- Extended Access List
- Li-fi vs. Wi-fi
- Reflexive Access List
- Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
- Wifi protected access (WPA)
- Wifi Protected Setup (WPS)
- Standard Access List
- Time Access List
- What is 3D Internet
- 4G Mobile Communication Technology
- Types of Wireless Transmission Media
- Best Computer Networking Courses
- Data Representation
- Network Criteria
- Classful vs Classless addressing
- Difference between BOOTP and RARP in Computer Networking
- What is AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- External IP Address
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Types of Authentication Protocols
- What is a CISCO Packet Tracer
- BOOTP work
- Subnetting in Computer Networks
- Mesh Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ring Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Star Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Zigbee Technology-The smart home protocol
- Network Layer in OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer in OSI Model
- Internet explorer shortcut keys
- Network Layer Security | SSL Protocols
- Presentation Layer in OSI Model
- Session Layer in OSI Model
- SUBNET MASK
- Transport Layer Security | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and SSL Architecture
- Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Layer
- Protocols in Noiseless and Noisy Channel
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
- Count to Infinity Problem in Distance Vector Routing
- Difference Between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat Protocol
- Difference between Stop and Wait, GoBackN, and Selective Repeat
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): transforming Network Architecture with Virtualized Functions
- Network-Layer Security | IPSec Modes
- Next - Prev Network-Layer Security | IPSec Protocols and Services
- Ping vs Traceroute
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): Benefits and Challenges of Network Virtualization
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) vs. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- Virtual Circuits vs Datagram Networks
- BlueSmack Attack in Wireless Networks
- Bluesnarfing Attack in Wireless Networks
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Warchalking in Wireless Networks
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- Wireless security encryption
- Wireless Security in an Enterprise
- Quantum Networking
- Network Automation
- Difference between MSS and MTU
- What is MTU
- Mesh Networks: A decentralized and Self-Organizing Approach to Networking
- What is Autonomous System
- What is MSS
- Cyber security & Software security
- Information security & Network security.
- Security Engineer & Security Architect
- Protection Methods for Network Security
- Trusted Systems in Network Security
- What are Authentication Tokens in Network security
- Cookies in Network Security
- Intruders in Network Security
- Network Security Toolkit (NST) in virtual box
- Pivoting-Moving Inside a Network
- Security Environment in Computer Networks
- Voice Biometric technique in Network Security
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Testing
- Difference between Kerberos and LDAP
- Cyber security and Information Security
- GraphQL Attacks and Security
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Applications of Remote Sensing
- Seven Layers of IT Security
- What is Ad Hoc TCP
- What is Server Name Indication(SNI)
What is a proxy server and how does it work
Every computer that is connected to the network has an IP (Internet Protocol) address that identifies the device uniquely. Similarly, the proxy server is a computer on the network that has its own IP address. But sometimes, we want to access those websites or servers that are restricted and we do not want to show our identity (IP address). In such a scenario, the proxy server comes into existence. We can achieve the same by using the proxy server. It provides varying levels of functionality, security, and privacy that depend on the use case, needs, or policies of the company. In this section, we will discuss what is a proxy server, its types, advantages, need, and working of proxy servers.
Proxy Server
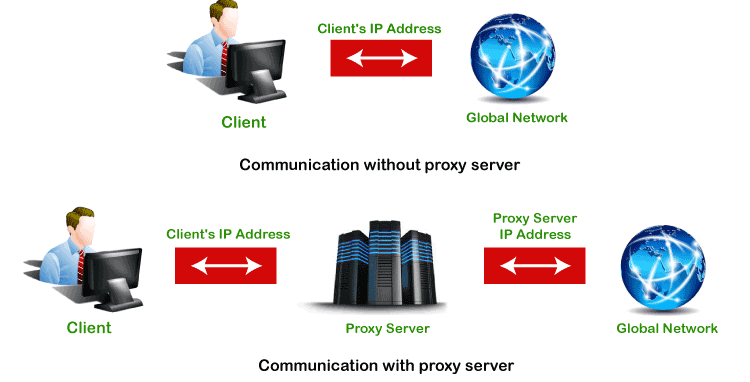
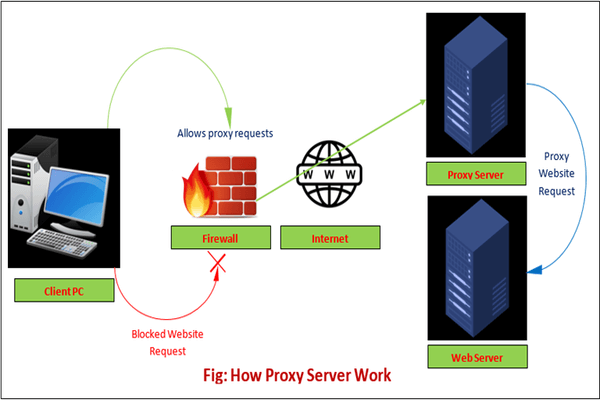
The proxy server is a computer on the internet that accepts the incoming requests from the client and forwards those requests to the destination server. It works as a gateway between the end-user and the internet. It has its own IP address. It separates the client system and web server from the global network.
In other words, we can say that the proxy server allows us to access any websites with a different IP address. It plays an intermediary role between users and targeted websites or servers. It collects and provides information related to user requests. The most important point about a proxy server is that it does not encrypt traffic.
There are two main purposes of proxy server:
- To keep the system behind it anonymous.
- To speed up access to a resource through caching.
Mechanism of Proxy Server
The following figure depicts the mechanism of the proxy server.
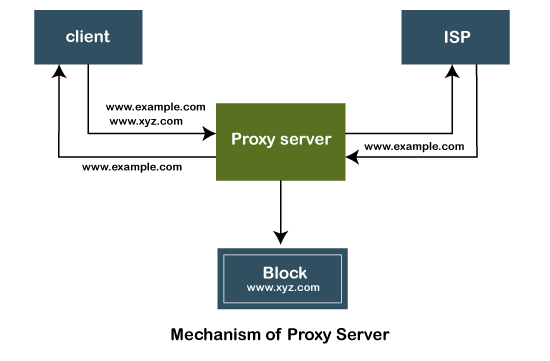
The proxy server accepts the request from the client and produces a response based on the following conditions:
- If the requested data or page already exists in the local cache, the proxy server itself provides the required retrieval to the client.
- If the requested data or page does not exist in the local cache, the proxy server forwards that request to the destination server.
- The proxy servers transfer the replies to the client and also being cached to them.
Therefore, it can be said that the proxy server acts as a client as well as the server.
Types of Proxy Servers
There are many types of proxy servers available. The two most common types of proxy servers are forward and reverse proxy servers. The other proxy server has its own feature and advantages. Let's discuss each in detail.
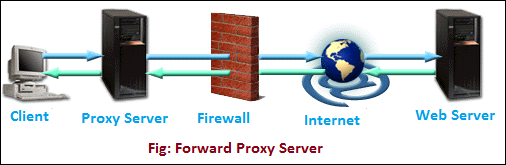
- Open or Forward Proxy Server: It is the most widely recognized type of intermediary worker that is gotten to by the customer. An open or forward proxy server refers to those sorts of intermediaries that get demands from web clients and afterward peruse destinations to gather the mentioned information. After collecting the data from the sites, it forwards the data to the internet users directly. It bypasses the firewall made by authorities. The following image shows forward proxy configuration.
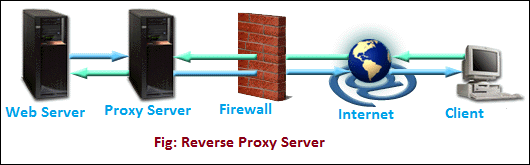
- Reverse Proxy Server: It is a proxy server that is installed in the neighborhood of multiple other internal resources. It validated and processes a transaction in such a way that the clients do not communicate directly. The most popular reverse proxies are Varnish and Squid. The following image shows the reverse proxy configuration.
- Split Proxy Server: It is implemented as two programs installed on two different computers.
- Transparent Proxy: It is a proxy server that does not modify the request or response beyond what is required for proxy authentication and identification. It works on port 80.
- Non-Transparent Proxy: It is an intermediary that alters the solicitation reaction to offer some extra types of assistance to the client. Web demands are straightforwardly shipped off the intermediary paying little mind to the worker from where they started.
- Hostile Proxy: It is used to eavesdrop upon the data flow between the client machine and the web.
- Intercepting Proxy Server: It combines the proxy server with a gateway. It is commonly used in businesses to prevent avoidance of acceptable use policy and ease of administration.
- Forced Proxy Server: It is a combination of Intercepting and non-intercepting policies.
- Caching Proxy Server: Caching is servicing the request of clients with the help of saved contents from previous requests, without communicating with the specified server.
- Web Proxy Server: The proxy that is targeted to the world wide web is known as a web proxy server.
- Anonymous Proxy: The server tries to anonymizing the web surfing.
- Socks Proxy: It is an ITEF (Internet Engineering Task Force) standard. It is just like a proxy system that supports proxy-aware applications. It does not allow the external network components to collects the information of the client that had generated the request. It consists of the following components:
- A dient library for the SOCK.
- A dient program such as FTP, telnet, or internet browser.
- A SOCK server for the specified operating system.
- High Anonymity Proxy: The proxy server that doesn't contain the proxy server type and the client IP address in a request header. Clients using the proxy can't be tracked.
- Rotating Proxy: It assigns a unique IP address to each client who is connected to it. It is ideal for users who do a lot of continuous web scrapping. It allows us to return the same website again and again. So, using the rotating proxy requires more attention.
- SSL Proxy Server: It decrypts the data between the client and the server. It means data is encrypted in both directions. Since proxy hides its existence from both the client and the server. It is best suited for organizations that enhance protection against threats. In SSL proxy, the content encrypted is not cached.
- Shared Proxy: A shared proxy server is used by more than one user at a time. It provides an IP address to the client that can be shared with other clients. It also allows users to select the location from where the user wants to search. It is ideal for users who do not want to spend a lot of money on a fast connection. Low cost is an advantage of it. The disadvantage of it is that a user can be get blamed for someone else's mischievous activity. For this reason, the user can be blocked from the site.
- Public Proxy: A public proxy is available free of cost. It is perfect for the user for whom cost is a major concern while security and speed are not. Its speed is usually slow. Using a public proxy puts the user at high risk because information can be accessed by others on the internet.
- Residential Proxy: It assigns an IP address to a specific device. All requests made by the client channeled through that device. It is ideal for the users who want to verify ads that display on their websites. Using the residential proxy server, we can block unwanted and suspicious ads from competitors. In comparison to other proxy servers, the residential proxy server is more reliable.
- Distorting Proxy: It is different from others because it identifies itself as a proxy to a website but hides its own identity. The actual IP address is changed by providing an incorrect one. It is perfect for clients who do not want to disclose their location during surfing.
- Data Center Proxy: It is a special type of proxy that is not affiliated with the ISP. It is provided by other corporations through a data center. These servers can be found in physical data centers. It is ideal for clients who want quick responses. It does not provide high-level anonymity. For this reason, it can put client information at high risk.
- HTTP Proxy: HTTP proxies are those proxy servers that are used to save cache files of the browsed websites. It saves time and enhances the speed because cached files reside in the local memory. If the user again wants to access the same file proxy itself provides the same file without actually browsing the pages.
Advantages of Proxy Server
There are the following benefits of using the proxy server:
- It improves the security and enhances the privacy of the user.
- It hides the identity (IP address) of the user.
- It controls the traffic and prevents crashes.
- Also, saves bandwidth by caching files and compressing incoming traffic.
- Protect our network from malware.
- Allows access to the restricted content.
Need of Proxy Server
- It reduces the chances of data breaches.
- It adds a subsidiary layer of security between server and outside traffic.
- It also protects from hackers.
- It filters the requests.
Working of Proxy Server
As we have discussed above, the proxy server has its own IP address and it works as a gateway between the client and the internet. The client's computer knows the IP address of the proxy server. When the client sends a request on the internet, the request is re-routed to the proxy. After that, the proxy server gets the response from the destination or targeted server/site and forwards the data from the page to the client's browser (Chrome, Safari, etc.).
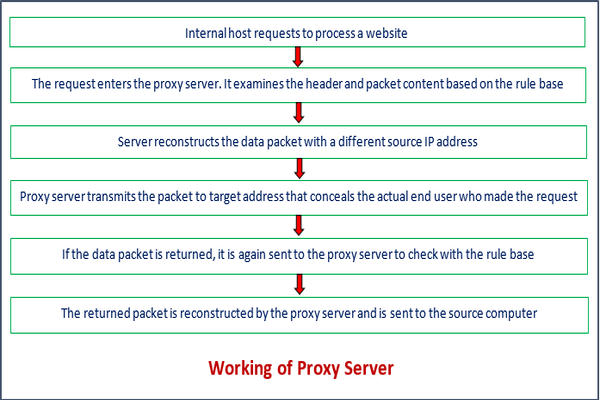
Overall, it can be said that the proxy server accesses the targeted site, on behalf of the client, and collects all the requested information, and forwards them to the user (client). The following figure clearly depicts the working of the proxy server.
Proxy Server Vs. VPN
Proxy server and VPN (Virtual Private Network) are quite similar. Both allow clients to hide their IP addresses, location and allows access to the restricted websites. The only difference is that the proxy server does not encrypt the traffic while VPN does the same. Another difference is that no one can track the activity of the VPN user while the activity of the proxy server user can be tracked.
The following table describes the key differences between the proxy server and VPN.
| Basis of Comparison | Proxy Server | VPN |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | It does not encrypt the traffic. | It encrypts the traffic. |
| Software | It does not have its own software. | It has its own software. |
| Speed | It is faster than VPN. | It is slower in comparison to the proxy server. |
| Cache | It uses cache. | It does not use cache. |
| IP Address | It hides the IP address but the proxy owner can see the client's IP address. | The IP address is completely hidden. |
| Connection | It is unstable. | It is seamless. |
| Pricing | It is mostly free. | It is chargeable. |
| Reliability | Its connection drops more frequently. | Its connection is more reliable. |
| Level of Working | It works on the application level. | It works on the operating system level. |
| Security | It is less secure. | It provides greater security. |


