Tutorial
Physical Layer
Data Link layer
Network Layer
Routing Algorithm
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Network Security
Misc
- Router
- OSI vs TCP/IP
- TCP vs UDP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP port
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- ARP Packet Format
- ARP Table
- Working of ARP
- FTP Client
- FTP Commands
- FTP Server
- I2C Protocol
- Sliding Window Protocol
- SPI Protocol
- IP
- ARP Commands
- ARP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP and its types
- TCP Retransmission
- CAN protocol
- HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- RIP Protocol
- UDP Protocol
- ICMP Protocol
- MQTT protocol
- OSPF Protocol
- Stop and Wait Protocol
- IMAP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- CIFS
- DAS
- DIMM
- iSCSI
- NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- NFS
- NVMe
- SAN
- Border Gateway Protocol
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- RJ Cable
- Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Service
- CDMA vs. GSM
- What is MAC Address
- Modem vs. Router
- Switch Vs. Router
- USB 2.0 vs 3.0
- Difference between CSMA CA and CSMA CD
- Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
- URI vs URL
- IMAP vs. POP3
- SSH Meaning| SSH Protocol
- UTP vs STP
- Status Code 400
- MIME Protocol
- IP address
- proxy server
- How to set up and use a proxy server
- network security
- WWW is based on which model
- Proxy Server List
- Fundamentals of Computer Networking
- IP Address Format and Table
- Bus topology and Ring topology
- Bus topology and Star topology
- Circuit Switching and Packet switching?
- Difference between star and ring topology
- Difference between Router and Bridge
- TCP Connection Termination
- Image Steganography
- Network Neutrality
- Onion Routing
- Adaptive security appliance (ASA) features
- Relabel-to-front Algorithm
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Access Lists (ACL)
- What is a proxy server and how does it work
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Operating system based Virtualization
- Context based Access Control (CBAC)
- Cristian's Algorithm
- Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)
- Extended Access List
- Li-fi vs. Wi-fi
- Reflexive Access List
- Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
- Wifi protected access (WPA)
- Wifi Protected Setup (WPS)
- Standard Access List
- Time Access List
- What is 3D Internet
- 4G Mobile Communication Technology
- Types of Wireless Transmission Media
- Best Computer Networking Courses
- Data Representation
- Network Criteria
- Classful vs Classless addressing
- Difference between BOOTP and RARP in Computer Networking
- What is AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- External IP Address
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Types of Authentication Protocols
- What is a CISCO Packet Tracer
- BOOTP work
- Subnetting in Computer Networks
- Mesh Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ring Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Star Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Zigbee Technology-The smart home protocol
- Network Layer in OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer in OSI Model
- Internet explorer shortcut keys
- Network Layer Security | SSL Protocols
- Presentation Layer in OSI Model
- Session Layer in OSI Model
- SUBNET MASK
- Transport Layer Security | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and SSL Architecture
- Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Layer
- Protocols in Noiseless and Noisy Channel
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
- Count to Infinity Problem in Distance Vector Routing
- Difference Between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat Protocol
- Difference between Stop and Wait, GoBackN, and Selective Repeat
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): transforming Network Architecture with Virtualized Functions
- Network-Layer Security | IPSec Modes
- Next - Prev Network-Layer Security | IPSec Protocols and Services
- Ping vs Traceroute
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): Benefits and Challenges of Network Virtualization
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) vs. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- Virtual Circuits vs Datagram Networks
- BlueSmack Attack in Wireless Networks
- Bluesnarfing Attack in Wireless Networks
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Warchalking in Wireless Networks
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- Wireless security encryption
- Wireless Security in an Enterprise
- Quantum Networking
- Network Automation
- Difference between MSS and MTU
- What is MTU
- Mesh Networks: A decentralized and Self-Organizing Approach to Networking
- What is Autonomous System
- What is MSS
- Cyber security & Software security
- Information security & Network security.
- Security Engineer & Security Architect
- Protection Methods for Network Security
- Trusted Systems in Network Security
- What are Authentication Tokens in Network security
- Cookies in Network Security
- Intruders in Network Security
- Network Security Toolkit (NST) in virtual box
- Pivoting-Moving Inside a Network
- Security Environment in Computer Networks
- Voice Biometric technique in Network Security
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Testing
- Difference between Kerberos and LDAP
- Cyber security and Information Security
- GraphQL Attacks and Security
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Applications of Remote Sensing
- Seven Layers of IT Security
- What is Ad Hoc TCP
- What is Server Name Indication(SNI)
Status Code 400
An HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Bad) State code 400 represents a user error. Whenever any user sends an invalid request to the server, the server immediately reports it and generates an HTTP based 400 bad request error. This error usually occurs if the user has entered an incorrect URL.
In the broad majority of likely situations, the status code 400 error occurs due to a client-side problem caused by the submitted request to the server or local caching causes. Hence, in this tutorial, we will cover various easy methods that anyone can implement even if the user is not tech-savvy. Following the given methods, you should be successfully able to make your website working!
What is a 400 bad Request error?
Status Code 400 or 400 Bad Request, or 400 error or HTTP error 400, is recognized by the server as a general user error. The server throws the 400 bad error if the server decides that the resulting error doesn't come under any other status code classifications.
The 400 status code (Bad Request) represents that the server cannot process the request due to some user error. In return for an invalid request, the server should dispense the specific 4xx status code in the case of a failed request.
Common Causes of 400 error
A 400 Bad Request error is mostly the consequence of typing the incorrect URL in the browser window or making errors in an address link while linking it from a web page to another.
1. URL String Syntax Error
The primary reason for the HTTP error 400 to occur is an incorrectly typed URL (Uniform Resource Locator), deformed syntax, or a URL that contains some illegal characters.
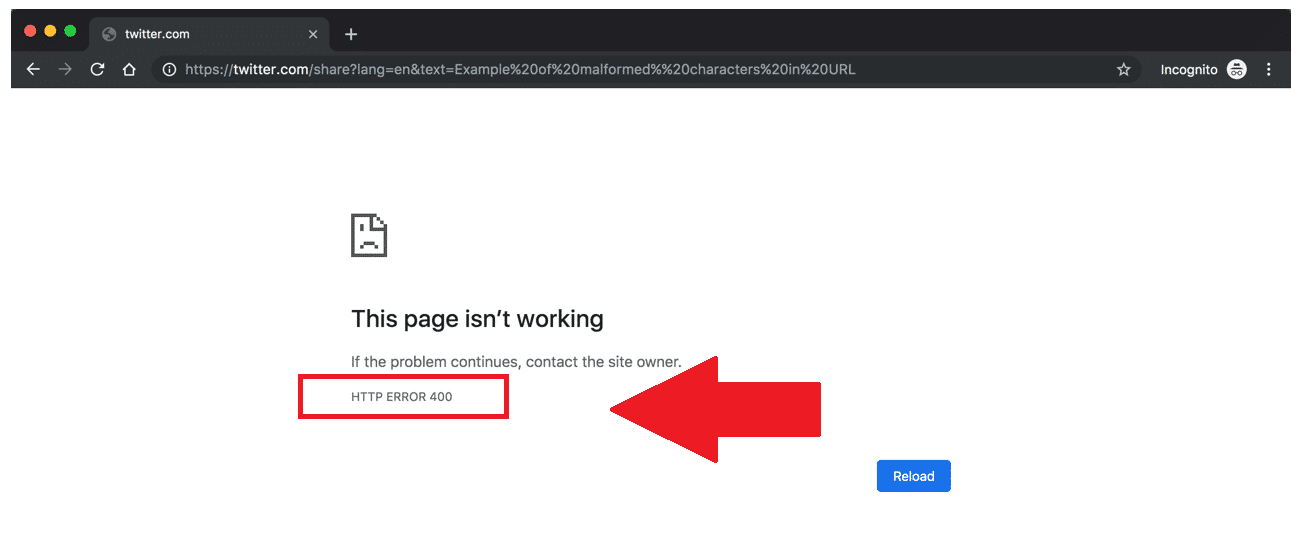
Though the user can mistakenly type the wrong URL, it can sometimes happen if the URL encoding has been performed incorrectly. The below-given link is an example of an incorrect URL that the server won't process, and therefore, it will trigger a 400 HTTP error.
https://twitter.com/share?lang=en&text=Example%20of%20malformed%%20characters%20in%20URL
2. Corrupted Browser Cache & Cookies
URL typo error is not the only case where the server triggers the 400 bad error. Even if the passed URL is 100% accurate, the server can still throw a 400 Bad Request error because it detects the presence of any corrupted files in the browser cache memory or other issues such as expired or damaged cookies.
The user can also encounter a 400 Bad Request error if he/she tries to gain access to their WordPress admin area after some time of their last log-in session. The reason why it occurred because the process following which the cookie was managing the login authentication information may have gotten expired, and it cannot further authenticate the same valid user with admin rights. And it eventually results in the connection being declined and therefore passes 400 Bad Request error.
3. DNS Lookup Cache
The 400 Bad Request can occur if the local DNS data stored is not in sync with registered DNS (Domain Name server) data. All the domain names available on the internet are the art of IP address. You can compare the IP address of your phone number as it connects to a particular "calling number" you wish to dial.
4. File Size Too Large
A 400 Bad Request can also trigger if the files uploaded by the user on a website are too heavy for the upload request to be met. This is strictly associated with the server's file size limit and will change based on its setup.
5. Generic Server Error
The 400 bad request error can also occur if there is any technical issue on the server-side. Though, a 400 status code will display a generic problem with the server, server or network glitch, or any other undefined volatile issues.
Suppose it triggers when the user tries to connect to a third-party website, in that the user cannot control it. At that time, he/she can try to refresh the browser and monitor at frequent intervals whether the website developers have resolved the issue or not. Just in case you want to confirm whether the specific error is a server-side issue or not, try to load the website on various browsers, or you can also test it on a different machine/device to eliminate the system-specific problems.
If the same issue occurs with other browsers, systems are also confirmed to be a server-side problem. If the site content is important for you, you directly communicate to the website owner and give all the details related to Operating System, browser, system, and versions you were using when you experienced the 400 bad error issue.
How to fix 400 Errors
The various ways to fix the bad 400 errors are explained below:
1. Check the Submitted URL
One of the most common reasons for the 400 Bad Request error is the obvious URL string itself. One can easily make mistakes by manually typing unwanted characters in the URL in the web browser.
Re-check the spelling of the domain name or the particular web page you want to access and make sure that they are typed accurately and are separated with forwarding slashes. If the URL includes any special characters, make sure they are encoded properly with valid URL characters.
If you find it hard to check the URL spelling and encoding process repeatedly, you can opt for the online URL encoder/decoder. It is very useful for long URLs and less error-prone. These kinds of software help the user to identify various illegal characters in the URL automatically.
Once you have entered the correct URL, it's time to run it again in the browser. Still, if you face the 400 Bad Request error, try with other fixing methods given below.
2. Clear Browser Cache
While accessing specific website content, the user receives a 400 Bad Request error if any website files stored locally have been corrupted.
It consists of all sorts of files that a website demands for its proper functioning, unlike:
- HTML, PHP
- JavaScript
- Text/config files
- CSS coding
- Digital Media, unlike photos, videos, audio, etc.
- Data files such as XML, JSON, etc.
Whenever any user visits any website, all the above files are stored locally on your computer's browser. Therefore to fix this problem, one should clear the browser's cache memory. Follow the below-given steps to clear the computer cache:
- Open your browser (in our case, we have opened Google chrome), click on the three-dotted icon located on the top right-hand corner of the screen. It will throw a popup menu window (as shown in the given screenshot) -> select the More Tools
- The following menu will appear, select the Clear Browsing Data option.
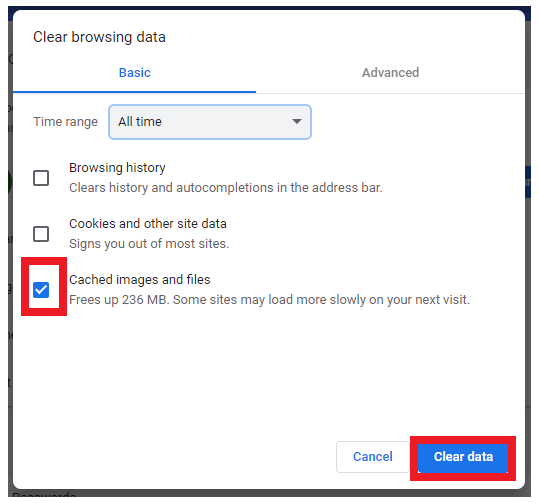
- It will direct you to the Clear browsing data window. Make sure to tick on the checkbox for the third option (Cached images and files), and once done, click on the Clear data button located at the bottom.
- It will clear the cache memory of your browser.
Note: Google provides you the option to delete only the recent files for a particular time range with the help of the Time range dropdown. However, to ensure all possibly corrupted files are eliminated, we suggest removing all stored files locally by selecting the All-time option.
- Once done, reload the website again. Hopefully your website will run successfully this time!
3. Clear Browser Cookies
If you are still facing the 400 error even after clearing your browser cache, in that case, your browser cookies are also corrupted. Whenever you open any website on your browser, it uses different cookies. If any one of the used cookies gets expired or corrupted, then it can trigger the 400 Bad Request error.
To clear your cookies in web browser (Chrome in our case) follow the below given steps:
- Open your browser (in our case, we have opened Google chrome), click on the three-dotted icon located on the top right-hand corner of the screen. It will throw a popup menu window (as shown in the given screenshot) -> select the More Tools
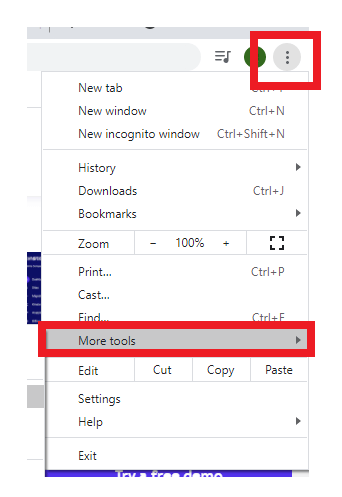
- The following menu will appear, select the Clear Browsing Data option.
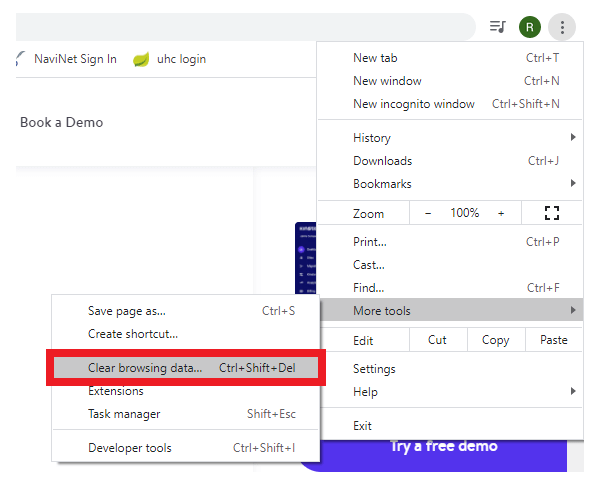
- Tick on the checkbox for Cookies and other site data.
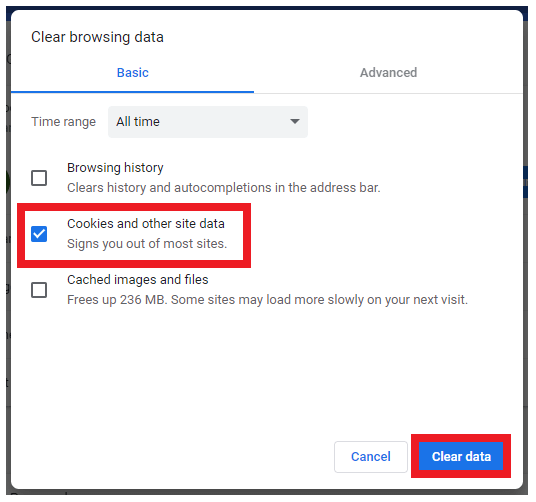
- NOTE: Make sure to select the All-time option for the time range for the top as it will give option to delete all current website cookies.
- Once done, reload the website again. Hopefully, your website will run successfully this time!
4. File Upload Exceeds Server Limit
While uploading a file, we often forget about the server size limit and exceed its maximum limit. Eventually, you confront a 400 Bad Request error.
Try to upload a file again, and this time upload a smaller file. If it gets uploaded successfully, then the likely error occurred because the initial file was too large, and before uploading the file again, either you need to trim the file size or need to find some way.
5. Clear DNS Cache
The 400 Bad request can be triggered if the DNS data stored locally gets corrupted or out-of-date.
Note: The local DNS data are not stored by the browser but on the OS (operating system).
6. eactivate Browser Extensions
Today, we install various extensions to our browser. Some extensions might affect your website cookies which could trigger the 400 bad request error. To find out the real culprit, temporarily disable them and check whether it makes a difference by running the website again.


