Tutorial
Physical Layer
Data Link layer
Network Layer
Routing Algorithm
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Network Security
Misc
- Router
- OSI vs TCP/IP
- TCP vs UDP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP port
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- ARP Packet Format
- ARP Table
- Working of ARP
- FTP Client
- FTP Commands
- FTP Server
- I2C Protocol
- Sliding Window Protocol
- SPI Protocol
- IP
- ARP Commands
- ARP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP and its types
- TCP Retransmission
- CAN protocol
- HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- RIP Protocol
- UDP Protocol
- ICMP Protocol
- MQTT protocol
- OSPF Protocol
- Stop and Wait Protocol
- IMAP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- CIFS
- DAS
- DIMM
- iSCSI
- NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- NFS
- NVMe
- SAN
- Border Gateway Protocol
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- RJ Cable
- Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Service
- CDMA vs. GSM
- What is MAC Address
- Modem vs. Router
- Switch Vs. Router
- USB 2.0 vs 3.0
- Difference between CSMA CA and CSMA CD
- Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
- URI vs URL
- IMAP vs. POP3
- SSH Meaning| SSH Protocol
- UTP vs STP
- Status Code 400
- MIME Protocol
- IP address
- proxy server
- How to set up and use a proxy server
- network security
- WWW is based on which model
- Proxy Server List
- Fundamentals of Computer Networking
- IP Address Format and Table
- Bus topology and Ring topology
- Bus topology and Star topology
- Circuit Switching and Packet switching?
- Difference between star and ring topology
- Difference between Router and Bridge
- TCP Connection Termination
- Image Steganography
- Network Neutrality
- Onion Routing
- Adaptive security appliance (ASA) features
- Relabel-to-front Algorithm
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Access Lists (ACL)
- What is a proxy server and how does it work
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Operating system based Virtualization
- Context based Access Control (CBAC)
- Cristian's Algorithm
- Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)
- Extended Access List
- Li-fi vs. Wi-fi
- Reflexive Access List
- Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
- Wifi protected access (WPA)
- Wifi Protected Setup (WPS)
- Standard Access List
- Time Access List
- What is 3D Internet
- 4G Mobile Communication Technology
- Types of Wireless Transmission Media
- Best Computer Networking Courses
- Data Representation
- Network Criteria
- Classful vs Classless addressing
- Difference between BOOTP and RARP in Computer Networking
- What is AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- External IP Address
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Types of Authentication Protocols
- What is a CISCO Packet Tracer
- BOOTP work
- Subnetting in Computer Networks
- Mesh Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ring Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Star Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Zigbee Technology-The smart home protocol
- Network Layer in OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer in OSI Model
- Internet explorer shortcut keys
- Network Layer Security | SSL Protocols
- Presentation Layer in OSI Model
- Session Layer in OSI Model
- SUBNET MASK
- Transport Layer Security | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and SSL Architecture
- Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Layer
- Protocols in Noiseless and Noisy Channel
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
- Count to Infinity Problem in Distance Vector Routing
- Difference Between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat Protocol
- Difference between Stop and Wait, GoBackN, and Selective Repeat
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): transforming Network Architecture with Virtualized Functions
- Network-Layer Security | IPSec Modes
- Next - Prev Network-Layer Security | IPSec Protocols and Services
- Ping vs Traceroute
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): Benefits and Challenges of Network Virtualization
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) vs. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- Virtual Circuits vs Datagram Networks
- BlueSmack Attack in Wireless Networks
- Bluesnarfing Attack in Wireless Networks
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Warchalking in Wireless Networks
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- Wireless security encryption
- Wireless Security in an Enterprise
- Quantum Networking
- Network Automation
- Difference between MSS and MTU
- What is MTU
- Mesh Networks: A decentralized and Self-Organizing Approach to Networking
- What is Autonomous System
- What is MSS
- Cyber security & Software security
- Information security & Network security.
- Security Engineer & Security Architect
- Protection Methods for Network Security
- Trusted Systems in Network Security
- What are Authentication Tokens in Network security
- Cookies in Network Security
- Intruders in Network Security
- Network Security Toolkit (NST) in virtual box
- Pivoting-Moving Inside a Network
- Security Environment in Computer Networks
- Voice Biometric technique in Network Security
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Testing
- Difference between Kerberos and LDAP
- Cyber security and Information Security
- GraphQL Attacks and Security
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Applications of Remote Sensing
- Seven Layers of IT Security
- What is Ad Hoc TCP
- What is Server Name Indication(SNI)
Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
What is cloud networking?
Cloud networking refers to the practice of utilizing cloud computing technologies to provide networking services, such as data storage, computing power, and network connectivity.
Organizations can use virtualized infrastructure in cloud networking to create and manage their networks rather than relying on physical hardware. Cloud networking enables businesses to easily scale their network resources up or down as needed without having to invest in additional hardware.
Some common cloud networking services include virtual private clouds (VPCs), which allow organizations to create their own private networks within a cloud environment, and software-defined wide area networks (SD-WANs), which can be used to manage network traffic across multiple locations. Cloud networking also enables remote access to network resources, allowing employees to access company data from anywhere with an internet connection securely.
Benefits of Cloud Networking
There are several benefits to using cloud networking:
- Scalability: Without needing to purchase new gear, cloud networking enables enterprises to quickly scale their network resources up or down as needed. As a result, firms find it simpler to respond to shifting customer and market expectations.
- Cost savings: With cloud networking, businesses can reduce their capital expenditure on physical hardware, as well as ongoing maintenance costs. Instead, they can pay for the network resources they need on a subscription basis, which can help reduce overall costs.
- Flexibility: Cloud networking enables remote access to network resources, allowing employees to securely access company data from anywhere with an internet connection. This makes it easier for businesses to support a mobile workforce or provide access to data for remote teams or customers.
- Security: Cloud networking companies make significant investments in security measures to safeguard the data of their clients. Because of this, companies may reap the benefits of cutting-edge security features like encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection without having to make a significant investment in their own security infrastructure.
- Reliability: Cloud networking providers offer high levels of uptime and reliability, ensuring that businesses can access their data and applications whenever they need to. For enterprises with mission-critical systems or services, this can be especially advantageous.
- Innovation: Cloud networking providers often introduce new features and services, such as AI and machine learning capabilities, that can help businesses innovate and stay competitive.
- Globalization: With cloud networking, businesses can easily expand their operations to different regions and countries, as they can access their data and applications from anywhere in the world. This might be especially useful for companies with a global clientele.
Overall, cloud networking provides businesses with greater flexibility, scalability, cost savings, security, and reliability, making it an attractive option for organizations of all sizes. By adapting cloud networking, organizations can better leverage technology to drive business success.
Types of cloud networking
There are several types of cloud networking:
- Public cloud networking: Public cloud networking involves utilizing shared cloud infrastructure provided by third-party providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These providers offer a wide range of network services, such as virtual private networks (VPNs), load balancing, and content delivery networks (CDNs), which can be accessed by businesses on a subscription basis.
- Private cloud networking: A dedicated cloud environment for a particular enterprise is created via private cloud networking. Private cloud networking is flexible and may be tailored to an organization's particular requirements. It can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider.
- Hybrid cloud networking: Using both public and private clouds simultaneously is known as hybrid cloud networking. This enables businesses to take advantage of the scalability and cost savings of public cloud networking while still maintaining control over sensitive data and applications through private cloud networking.
- Multi-cloud networking: The multi-cloud networking involves using multiple cloud providers to host different applications or services. This can help businesses avoid vendor lock-in and take advantage of the unique features and services offered by different cloud providers.
- Edge cloud networking: Edge cloud networking involves deploying cloud infrastructure at the edge of the network, closer to end-users or devices. This can help reduce latency and improve performance for applications and services that require real-time processing or low-latency connectivity.
The type of cloud networking that a business chooses to adopt will depend on its specific needs and requirements, as well as its budget and resources.
Cloud Networking Protocols
Cloud networking protocols are a set of rules and standards that govern the transfer and management of data between cloud resources. These protocols are used to ensure that data is transmitted efficiently and securely within a cloud network environment. Some common cloud networking protocols include:
- Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP): TCP/IP is a set of protocols that define how data is transmitted between devices on the internet. It is the backbone of cloud networking and is used to transfer data between cloud resources.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP): HTTP is a protocol that is used to transfer data between web servers and web clients. Cloud networking commonly uses it to transfer data between cloud resources and web clients.
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP): SNMP is a protocol that is used to manage network devices and monitor network performance. It is commonly used in cloud networking to monitor the performance of cloud resources and identify potential issues.
- Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS): SSL/TLS are protocols that are used to encrypt data transmitted over a network. They are commonly used in cloud networking to ensure that data is transmitted securely and to prevent unauthorized access to cloud resources.
- Border Gateway Protocol (BGP): BGP is a protocol that is used to exchange routing information between different networks. It is commonly used in cloud networking to manage data flow between different cloud resources and ensure that data is transmitted efficiently.
In summary, cloud networking protocols play a critical role in ensuring that data is transmitted efficiently and securely within a cloud network environment. Understanding these protocols and how they are used can help ensure that cloud resources are effectively managed and optimized for performance.
Cloud Networking Tools
Cloud networking tools are software applications and utilities that are used to manage and monitor cloud network resources. These tools are designed to simplify the management of cloud networking infrastructure and to help ensure that cloud resources are operating efficiently and securely. Some common cloud networking tools include:
- Cloud Management Platforms (CMPs): CMPs are tools that are used to manage cloud resources across multiple cloud service providers. They provide a unified interface for managing cloud infrastructure and can help automate the deployment and management of cloud resources.
- Network Management Tools: Network management tools are used to monitor network performance and identify potential issues. They can help administrators identify network bottlenecks, troubleshoot connectivity issues, and optimize network performance.
- Network Security Tools: Network security tools are used to protect cloud resources from security threats and vulnerabilities. They can include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and anti-malware software.
- Cloud Storage Management Tools: Cloud storage management tools are used to manage cloud storage resources. They can help administrators manage data backups, monitor data usage, and optimize storage performance.
- Cloud Migration Tools: Cloud migration tools are used to move applications and data from on-premises infrastructure to cloud infrastructure. They can help automate the migration process and minimize downtime.
- Cloud Monitoring Tools: Cloud monitoring tools are used to monitor the performance of cloud resources. They can help administrators identify performance bottlenecks, monitor resource utilization, and optimize cloud performance.
In summary, cloud networking tools play a critical role in simplifying the management of cloud networking infrastructure and ensuring that cloud resources are operating efficiently and securely. Choosing the right cloud networking tools can help optimize cloud performance, improve network security, and streamline the management of cloud resources.
Cloud Networking Architecture
Cloud networking architecture refers to the design, deployment, and management of network resources in a cloud computing environment. Cloud networking architecture includes various components such as virtual networks, gateways, load balancers, firewalls, and other network services required to support cloud services.
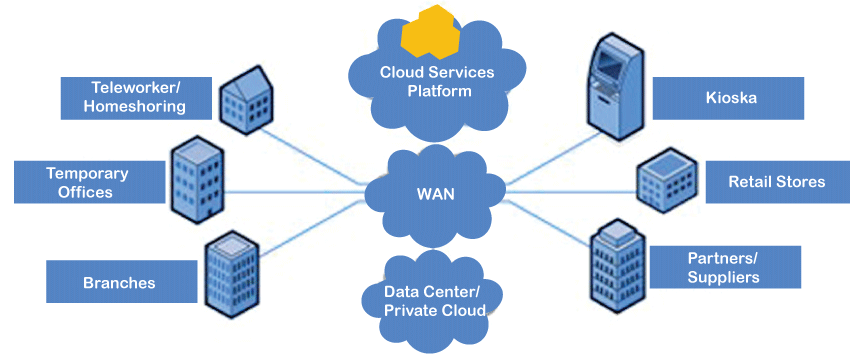
Here are some of the key components of cloud networking architecture:
- Virtual Networks: Virtual networks are a key component of cloud networking architecture. These networks are created using software-defined networking (SDN) technology, which allows network administrators to configure virtual networks and network resources from a central location. Virtual networks can be customized to meet the needs of specific cloud applications and can be scaled up or down as needed.
- Gateways: Gateways are used to connect virtual networks to the public internet or to other networks. Gateways can be used to create secure connections between cloud resources and external networks and can provide a way to manage network traffic between different cloud environments.
- Load Balancers: Load balancers are used to distribute network traffic across multiple servers or instances of an application. This helps ensure that cloud resources are utilized efficiently and can help prevent downtime or performance issues.
- Firewalls: Firewalls are used to protect cloud resources from unauthorized access and to prevent network attacks. Cloud firewalls can be configured to monitor network traffic and to block traffic from known sources of malicious activity.
- Network Services: Network services such as domain name system (DNS) servers, content delivery networks (CDNs), and intrusion detection systems (IDS) are also an important part of cloud networking architecture. These services are used to optimize cloud performance, improve security, and ensure that cloud resources are always available.
In summary, cloud networking architecture is a critical component of a cloud computing environment. It provides the networking infrastructure required to support cloud services and helps ensure that cloud resources are optimized for performance, scalability, and security. By understanding the key components of cloud networking architecture, cloud administrators can effectively design and manage cloud networks to meet the needs of their organization.


