Tutorial
Physical Layer
Data Link layer
Network Layer
Routing Algorithm
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Network Security
Misc
- Router
- OSI vs TCP/IP
- TCP vs UDP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP port
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- ARP Packet Format
- ARP Table
- Working of ARP
- FTP Client
- FTP Commands
- FTP Server
- I2C Protocol
- Sliding Window Protocol
- SPI Protocol
- IP
- ARP Commands
- ARP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP and its types
- TCP Retransmission
- CAN protocol
- HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- RIP Protocol
- UDP Protocol
- ICMP Protocol
- MQTT protocol
- OSPF Protocol
- Stop and Wait Protocol
- IMAP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- CIFS
- DAS
- DIMM
- iSCSI
- NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- NFS
- NVMe
- SAN
- Border Gateway Protocol
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- RJ Cable
- Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Service
- CDMA vs. GSM
- What is MAC Address
- Modem vs. Router
- Switch Vs. Router
- USB 2.0 vs 3.0
- Difference between CSMA CA and CSMA CD
- Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
- URI vs URL
- IMAP vs. POP3
- SSH Meaning| SSH Protocol
- UTP vs STP
- Status Code 400
- MIME Protocol
- IP address
- proxy server
- How to set up and use a proxy server
- network security
- WWW is based on which model
- Proxy Server List
- Fundamentals of Computer Networking
- IP Address Format and Table
- Bus topology and Ring topology
- Bus topology and Star topology
- Circuit Switching and Packet switching?
- Difference between star and ring topology
- Difference between Router and Bridge
- TCP Connection Termination
- Image Steganography
- Network Neutrality
- Onion Routing
- Adaptive security appliance (ASA) features
- Relabel-to-front Algorithm
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Access Lists (ACL)
- What is a proxy server and how does it work
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Operating system based Virtualization
- Context based Access Control (CBAC)
- Cristian's Algorithm
- Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)
- Extended Access List
- Li-fi vs. Wi-fi
- Reflexive Access List
- Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
- Wifi protected access (WPA)
- Wifi Protected Setup (WPS)
- Standard Access List
- Time Access List
- What is 3D Internet
- 4G Mobile Communication Technology
- Types of Wireless Transmission Media
- Best Computer Networking Courses
- Data Representation
- Network Criteria
- Classful vs Classless addressing
- Difference between BOOTP and RARP in Computer Networking
- What is AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- External IP Address
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Types of Authentication Protocols
- What is a CISCO Packet Tracer
- BOOTP work
- Subnetting in Computer Networks
- Mesh Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ring Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Star Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Zigbee Technology-The smart home protocol
- Network Layer in OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer in OSI Model
- Internet explorer shortcut keys
- Network Layer Security | SSL Protocols
- Presentation Layer in OSI Model
- Session Layer in OSI Model
- SUBNET MASK
- Transport Layer Security | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and SSL Architecture
- Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Layer
- Protocols in Noiseless and Noisy Channel
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
- Count to Infinity Problem in Distance Vector Routing
- Difference Between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat Protocol
- Difference between Stop and Wait, GoBackN, and Selective Repeat
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): transforming Network Architecture with Virtualized Functions
- Network-Layer Security | IPSec Modes
- Next - Prev Network-Layer Security | IPSec Protocols and Services
- Ping vs Traceroute
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): Benefits and Challenges of Network Virtualization
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) vs. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- Virtual Circuits vs Datagram Networks
- BlueSmack Attack in Wireless Networks
- Bluesnarfing Attack in Wireless Networks
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Warchalking in Wireless Networks
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- Wireless security encryption
- Wireless Security in an Enterprise
- Quantum Networking
- Network Automation
- Difference between MSS and MTU
- What is MTU
- Mesh Networks: A decentralized and Self-Organizing Approach to Networking
- What is Autonomous System
- What is MSS
- Cyber security & Software security
- Information security & Network security.
- Security Engineer & Security Architect
- Protection Methods for Network Security
- Trusted Systems in Network Security
- What are Authentication Tokens in Network security
- Cookies in Network Security
- Intruders in Network Security
- Network Security Toolkit (NST) in virtual box
- Pivoting-Moving Inside a Network
- Security Environment in Computer Networks
- Voice Biometric technique in Network Security
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Testing
- Difference between Kerberos and LDAP
- Cyber security and Information Security
- GraphQL Attacks and Security
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Applications of Remote Sensing
- Seven Layers of IT Security
- What is Ad Hoc TCP
- What is Server Name Indication(SNI)
Transmission modes
- The way in which data is transmitted from one device to another device is known as transmission mode.
- The transmission mode is also known as the communication mode.
- Each communication channel has a direction associated with it, and transmission media provide the direction. Therefore, the transmission mode is also known as a directional mode.
- The transmission mode is defined in the physical layer.
The Transmission mode is divided into three categories:
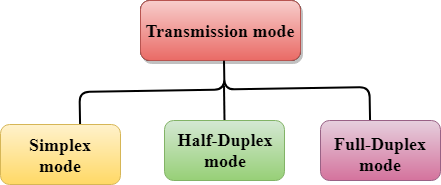
- Simplex mode
- Half-duplex mode
- Full-duplex mode
Simplex mode
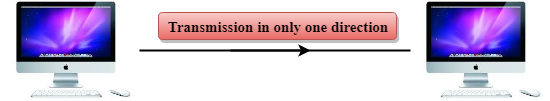
- In Simplex mode, the communication is unidirectional, i.e., the data flow in one direction.
- A device can only send the data but cannot receive it or it can receive the data but cannot send the data.
- This transmission mode is not very popular as mainly communications require the two-way exchange of data. The simplex mode is used in the business field as in sales that do not require any corresponding reply.
- The radio station is a simplex channel as it transmits the signal to the listeners but never allows them to transmit back.
- Keyboard and Monitor are the examples of the simplex mode as a keyboard can only accept the data from the user and monitor can only be used to display the data on the screen.
- The main advantage of the simplex mode is that the full capacity of the communication channel can be utilized during transmission.
Advantage of Simplex mode:
- In simplex mode, the station can utilize the entire bandwidth of the communication channel, so that more data can be transmitted at a time.
Disadvantage of Simplex mode:
- Communication is unidirectional, so it has no inter-communication between devices.
Half-Duplex mode
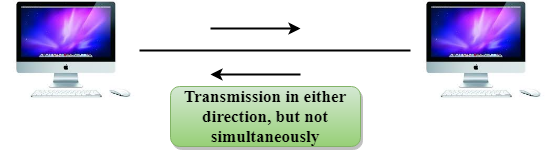
- In a Half-duplex channel, direction can be reversed, i.e., the station can transmit and receive the data as well.
- Messages flow in both the directions, but not at the same time.
- The entire bandwidth of the communication channel is utilized in one direction at a time.
- In half-duplex mode, it is possible to perform the error detection, and if any error occurs, then the receiver requests the sender to retransmit the data.
- A Walkie-talkie is an example of the Half-duplex mode. In Walkie-talkie, one party speaks, and another party listens. After a pause, the other speaks and first party listens. Speaking simultaneously will create the distorted sound which cannot be understood.
Advantage of Half-duplex mode:
- In half-duplex mode, both the devices can send and receive the data and also can utilize the entire bandwidth of the communication channel during the transmission of data.
Disadvantage of Half-Duplex mode:
- In half-duplex mode, when one device is sending the data, then another has to wait, this causes the delay in sending the data at the right time.
Full-duplex mode
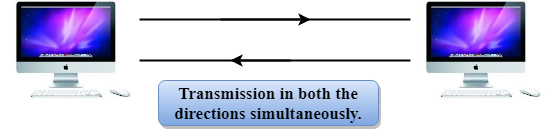
- In Full duplex mode, the communication is bi-directional, i.e., the data flow in both the directions.
- Both the stations can send and receive the message simultaneously.
- Full-duplex mode has two simplex channels. One channel has traffic moving in one direction, and another channel has traffic flowing in the opposite direction.
- The Full-duplex mode is the fastest mode of communication between devices.
- The most common example of the full-duplex mode is a telephone network. When two people are communicating with each other by a telephone line, both can talk and listen at the same time.
Advantage of Full-duplex mode:
- Both the stations can send and receive the data at the same time.
Disadvantage of Full-duplex mode:
- If there is no dedicated path exists between the devices, then the capacity of the communication channel is divided into two parts.
Differences b/w Simplex, Half-duplex and Full-duplex mode
| Basis for comparison | Simplex mode | Half-duplex mode | Full-duplex mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direction of communication | In simplex mode, the communication is unidirectional. | In half-duplex mode, the communication is bidirectional, but one at a time. | In full-duplex mode, the communication is bidirectional. |
| Send/Receive | A device can only send the data but cannot receive it or it can only receive the data but cannot send it. | Both the devices can send and receive the data, but one at a time. | Both the devices can send and receive the data simultaneously. |
| Performance | The performance of half-duplex mode is better than the simplex mode. | The performance of full-duplex mode is better than the half-duplex mode. | The Full-duplex mode has better performance among simplex and half-duplex mode as it doubles the utilization of the capacity of the communication channel. |
| Example | Examples of Simplex mode are radio, keyboard, and monitor. | Example of half-duplex is Walkie-Talkies. | Example of the Full-duplex mode is a telephone network. |


