Tutorial
Physical Layer
Data Link layer
Network Layer
Routing Algorithm
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Network Security
Misc
- Router
- OSI vs TCP/IP
- TCP vs UDP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP port
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- ARP Packet Format
- ARP Table
- Working of ARP
- FTP Client
- FTP Commands
- FTP Server
- I2C Protocol
- Sliding Window Protocol
- SPI Protocol
- IP
- ARP Commands
- ARP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP and its types
- TCP Retransmission
- CAN protocol
- HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- RIP Protocol
- UDP Protocol
- ICMP Protocol
- MQTT protocol
- OSPF Protocol
- Stop and Wait Protocol
- IMAP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- CIFS
- DAS
- DIMM
- iSCSI
- NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- NFS
- NVMe
- SAN
- Border Gateway Protocol
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- RJ Cable
- Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Service
- CDMA vs. GSM
- What is MAC Address
- Modem vs. Router
- Switch Vs. Router
- USB 2.0 vs 3.0
- Difference between CSMA CA and CSMA CD
- Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
- URI vs URL
- IMAP vs. POP3
- SSH Meaning| SSH Protocol
- UTP vs STP
- Status Code 400
- MIME Protocol
- IP address
- proxy server
- How to set up and use a proxy server
- network security
- WWW is based on which model
- Proxy Server List
- Fundamentals of Computer Networking
- IP Address Format and Table
- Bus topology and Ring topology
- Bus topology and Star topology
- Circuit Switching and Packet switching?
- Difference between star and ring topology
- Difference between Router and Bridge
- TCP Connection Termination
- Image Steganography
- Network Neutrality
- Onion Routing
- Adaptive security appliance (ASA) features
- Relabel-to-front Algorithm
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Access Lists (ACL)
- What is a proxy server and how does it work
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Operating system based Virtualization
- Context based Access Control (CBAC)
- Cristian's Algorithm
- Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)
- Extended Access List
- Li-fi vs. Wi-fi
- Reflexive Access List
- Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
- Wifi protected access (WPA)
- Wifi Protected Setup (WPS)
- Standard Access List
- Time Access List
- What is 3D Internet
- 4G Mobile Communication Technology
- Types of Wireless Transmission Media
- Best Computer Networking Courses
- Data Representation
- Network Criteria
- Classful vs Classless addressing
- Difference between BOOTP and RARP in Computer Networking
- What is AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- External IP Address
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Types of Authentication Protocols
- What is a CISCO Packet Tracer
- BOOTP work
- Subnetting in Computer Networks
- Mesh Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ring Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Star Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Zigbee Technology-The smart home protocol
- Network Layer in OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer in OSI Model
- Internet explorer shortcut keys
- Network Layer Security | SSL Protocols
- Presentation Layer in OSI Model
- Session Layer in OSI Model
- SUBNET MASK
- Transport Layer Security | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and SSL Architecture
- Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Layer
- Protocols in Noiseless and Noisy Channel
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
- Count to Infinity Problem in Distance Vector Routing
- Difference Between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat Protocol
- Difference between Stop and Wait, GoBackN, and Selective Repeat
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): transforming Network Architecture with Virtualized Functions
- Network-Layer Security | IPSec Modes
- Next - Prev Network-Layer Security | IPSec Protocols and Services
- Ping vs Traceroute
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): Benefits and Challenges of Network Virtualization
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) vs. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- Virtual Circuits vs Datagram Networks
- BlueSmack Attack in Wireless Networks
- Bluesnarfing Attack in Wireless Networks
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Warchalking in Wireless Networks
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- Wireless security encryption
- Wireless Security in an Enterprise
- Quantum Networking
- Network Automation
- Difference between MSS and MTU
- What is MTU
- Mesh Networks: A decentralized and Self-Organizing Approach to Networking
- What is Autonomous System
- What is MSS
- Cyber security & Software security
- Information security & Network security.
- Security Engineer & Security Architect
- Protection Methods for Network Security
- Trusted Systems in Network Security
- What are Authentication Tokens in Network security
- Cookies in Network Security
- Intruders in Network Security
- Network Security Toolkit (NST) in virtual box
- Pivoting-Moving Inside a Network
- Security Environment in Computer Networks
- Voice Biometric technique in Network Security
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Testing
- Difference between Kerberos and LDAP
- Cyber security and Information Security
- GraphQL Attacks and Security
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Applications of Remote Sensing
- Seven Layers of IT Security
- What is Ad Hoc TCP
- What is Server Name Indication(SNI)
RJ Cable
RJ abbreviated for the Registered Jack. It used as a medium in telecommunications or network interface. It enables network devices to connect voice and data equipment. It is mainly used to connect different types of data equipment and telecommunication media to take services offered by the local services provider to exchange data for longer distances and shorter exchange carriers. These RJ cables are categorised on the basis of structure and functions, such as size, PIN number, and their reliability on different devices.
Types of RJ
There are following types of RJ cable used in telephone line and to connect and share data among the connected systems.
- RJ11
- RJ11-W
- RJ14
- RJ21RJ25
- RJ45
- RJ48
- RJ61
RJ11
It stands for the Registered Jack11, containing a four-wire or six-wire telephone-type connector to connect telephones to wall plates. However, it supports up to six-wire; most of the old wired telephone lines use twisted-pair cables with four wires to connect to ISPs (Internet Service providers).
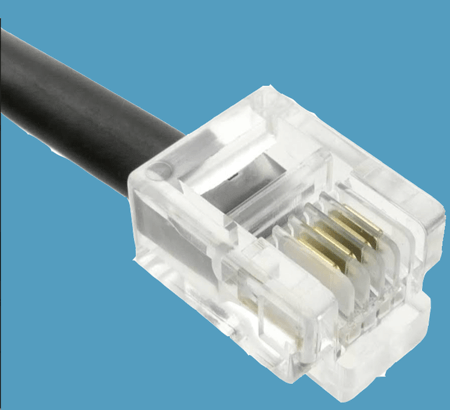
RJ11-W
It is the RJ11-W, where the W denotes the wall mount. It is an extended version of the RJ11. It is used to create bridge connections to the telephone lines with various wall mount functionalities.
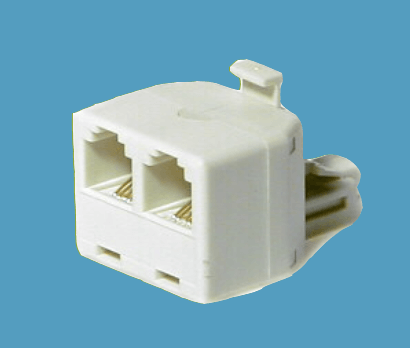
RJ14
It is a standard connector that uses 6P4C, i.e., six positions, four contacts modular connector. It is similar to RJ11 except that it uses two telephone cable lines and can be used as a modem connector in a computer.

RJ21
It is a registered jack 21 designed with 50 conductors in such a way that it can handle 25 telephone lines simultaneously. It is mostly used in wide networks to operate in an organization with multiple switches and devices.
RJ25
It is a standard connector RJ25 that uses a 6P6C, six positions, six contacts modular connector. These modular plugs are used to connect three lines of telephone cable connectors.
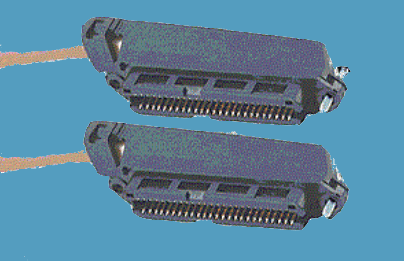
RJ45
It is a widely used type of registered jack connector in Ethernet cables or network devices. It is similar to the telephone jack or connector for sharing the data over the local area network. The shape of RJ45 cable or Ethernet cable is wider than the telephone jack or RJ11, 14, 21 and 25. It is used to create a connection with both shielded twisted pair (STP) and unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cabling in the star topology of the Ethernet network. RJ45 connectors are usually with 8P8C that means eight positions, eight contacts modular connectors with separate twisted pair for connecting computer and telephone lines, wall plates, patch panels and other networking devices.

RJ48
It is a type of registered jack connector that uses a twisted wire pair of cables and an eight-pin modular jack for data communication interfaces. The RJ48 uses the same type of plug and socket as we used in the RJ45 connector, but the RJ48 uses a different type of pin-out, where one pair of pins is used to transmit the signal, another pair of pins is used for receiving the signal, another pair of pins is used for draining the signal, and one more pair of pins is left unused. The RJ48 cable is divided into three parts such as the RJ48-C, used for a surface mount like T1 lines and requires 1, 2, 4, and 5 pins. The RJ48-S uses 56 kbps for digital lines of wall mount that use pins 1, 2, 7, and 8. The RJ48-X is used for complex troubleshooting jack requiring 1, 2, 4 and 5 pins.
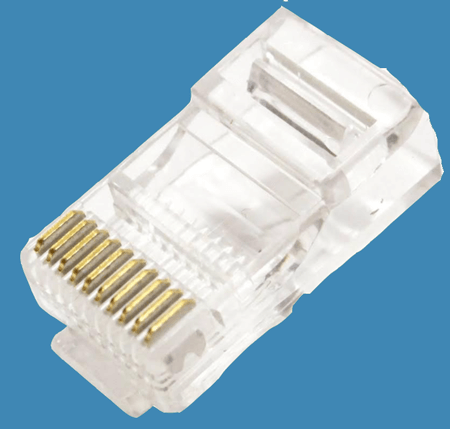
RJ61
It is the same as RJ11, but it uses 8P8C connector that means it has eight positions and eight conductors modular to connect with twisted-pair cables in the network devices.
Difference between RJ45 and RJ11
| Key Differences | RJ45 | RJ11 |
|---|---|---|
| Size | The size of the RJ45 cable is wider. | The size of the RJ11 is smaller. |
| Connected wires | It has eight separate wires. | It has four connected wires. |
| Usage | It is used with Ethernet cable as well as telephone lines. | It is used in the telephone cable lines such as single, double or triple. |
| Supported Bandwidth | The transferring speed of data up to 10 Gbps over the Ethernet cable. | The transferring speed of the data in RJ11 is up to 24 Mbps. |
| Connector | It uses an 8P8C connector, where eight positions eight contacts modular. | It uses a 6P4C connector, where six positions four contacts modular. |
Characteristics of the RJ Cable:
- It can work with configuring mounting surfaces for connecting voice and data equipment.
- It is used with different telephone lines to share data over the registered jack connector.
- There are many institutional academies, large organization, offices use RJ11, RJ12, RJ25, etc., because it can connect multiple telephone lines simultaneously.
- It is also used to connect multiple computers using the Ethernet cable to share data over the local area network.
- It can connect to cross-connections for more than two systems.
Advantages of the RJ Cable:
- It is easy to install and configured with different devices.
- It is a reliable cable, and the connection speed with the telecommunication interface is high.
Disadvantage of the RJ Cable:
- It is only used for the shortest distance to connect with telecommunication devices.
- Today most devices are wireless, so the use of registered jacks is becoming obsolete.
- It has the limited mobility of the wire.


