Tutorial
Physical Layer
Data Link layer
Network Layer
Routing Algorithm
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Network Security
Misc
- Router
- OSI vs TCP/IP
- TCP vs UDP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP port
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- ARP Packet Format
- ARP Table
- Working of ARP
- FTP Client
- FTP Commands
- FTP Server
- I2C Protocol
- Sliding Window Protocol
- SPI Protocol
- IP
- ARP Commands
- ARP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP and its types
- TCP Retransmission
- CAN protocol
- HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- RIP Protocol
- UDP Protocol
- ICMP Protocol
- MQTT protocol
- OSPF Protocol
- Stop and Wait Protocol
- IMAP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- CIFS
- DAS
- DIMM
- iSCSI
- NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- NFS
- NVMe
- SAN
- Border Gateway Protocol
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- RJ Cable
- Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Service
- CDMA vs. GSM
- What is MAC Address
- Modem vs. Router
- Switch Vs. Router
- USB 2.0 vs 3.0
- Difference between CSMA CA and CSMA CD
- Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
- URI vs URL
- IMAP vs. POP3
- SSH Meaning| SSH Protocol
- UTP vs STP
- Status Code 400
- MIME Protocol
- IP address
- proxy server
- How to set up and use a proxy server
- network security
- WWW is based on which model
- Proxy Server List
- Fundamentals of Computer Networking
- IP Address Format and Table
- Bus topology and Ring topology
- Bus topology and Star topology
- Circuit Switching and Packet switching?
- Difference between star and ring topology
- Difference between Router and Bridge
- TCP Connection Termination
- Image Steganography
- Network Neutrality
- Onion Routing
- Adaptive security appliance (ASA) features
- Relabel-to-front Algorithm
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Access Lists (ACL)
- What is a proxy server and how does it work
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Operating system based Virtualization
- Context based Access Control (CBAC)
- Cristian's Algorithm
- Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)
- Extended Access List
- Li-fi vs. Wi-fi
- Reflexive Access List
- Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
- Wifi protected access (WPA)
- Wifi Protected Setup (WPS)
- Standard Access List
- Time Access List
- What is 3D Internet
- 4G Mobile Communication Technology
- Types of Wireless Transmission Media
- Best Computer Networking Courses
- Data Representation
- Network Criteria
- Classful vs Classless addressing
- Difference between BOOTP and RARP in Computer Networking
- What is AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- External IP Address
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Types of Authentication Protocols
- What is a CISCO Packet Tracer
- BOOTP work
- Subnetting in Computer Networks
- Mesh Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ring Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Star Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Zigbee Technology-The smart home protocol
- Network Layer in OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer in OSI Model
- Internet explorer shortcut keys
- Network Layer Security | SSL Protocols
- Presentation Layer in OSI Model
- Session Layer in OSI Model
- SUBNET MASK
- Transport Layer Security | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and SSL Architecture
- Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Layer
- Protocols in Noiseless and Noisy Channel
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
- Count to Infinity Problem in Distance Vector Routing
- Difference Between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat Protocol
- Difference between Stop and Wait, GoBackN, and Selective Repeat
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): transforming Network Architecture with Virtualized Functions
- Network-Layer Security | IPSec Modes
- Next - Prev Network-Layer Security | IPSec Protocols and Services
- Ping vs Traceroute
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): Benefits and Challenges of Network Virtualization
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) vs. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- Virtual Circuits vs Datagram Networks
- BlueSmack Attack in Wireless Networks
- Bluesnarfing Attack in Wireless Networks
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Warchalking in Wireless Networks
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- Wireless security encryption
- Wireless Security in an Enterprise
- Quantum Networking
- Network Automation
- Difference between MSS and MTU
- What is MTU
- Mesh Networks: A decentralized and Self-Organizing Approach to Networking
- What is Autonomous System
- What is MSS
- Cyber security & Software security
- Information security & Network security.
- Security Engineer & Security Architect
- Protection Methods for Network Security
- Trusted Systems in Network Security
- What are Authentication Tokens in Network security
- Cookies in Network Security
- Intruders in Network Security
- Network Security Toolkit (NST) in virtual box
- Pivoting-Moving Inside a Network
- Security Environment in Computer Networks
- Voice Biometric technique in Network Security
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Testing
- Difference between Kerberos and LDAP
- Cyber security and Information Security
- GraphQL Attacks and Security
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Applications of Remote Sensing
- Seven Layers of IT Security
- What is Ad Hoc TCP
- What is Server Name Indication(SNI)
network security
includes crucial organization information, clients' personal data, and legal files that, if leaked out, could lead to a big problem and data breach for the company. The security of data is only made achievable by executing beneficial network security policies and techniques.
Definition of network security
Network security is the security designed to protect the integrity of the network from unauthorized access and threats. The network administrators are responsible for adopting various defensive measures to guard their networks from possible security risks.
Computer networks are linked in daily transactions and communication within the government, private, or corporates that needs security. The most common and straightforward strategy of protecting network support is allocating it with a unique name and a corresponding password. The network security consists of:
- Protection: The user should be able to configure their devices and networks accurately.
- Detection: The user must detect whether the configuration has changed or get a notification if there is any problem in the network traffic.
- Reaction: After detecting the problems, the user must respond to them and must return to a protected position as quickly as possible.
How does network security work?
Network security works with multiple layers of protection at the edge and in between the network. All the security layers execute some strategies and follow specified policies. Only the authorized users will obtain access to the network resources, and the illegitimate users will be blocked from conducting exploits and malicious activities.
There are different layers to analyze while addressing any network security for an association. Though the attacks can occur at any layer in the network security model, all the network's constituent devices, unlike hardware, software, and policies, must be composed in sync to approach each division.
The network security model is composed of three different controls: physical, technical, and administrative. Let's cover the brief analysis of network security and will learn how each control works.
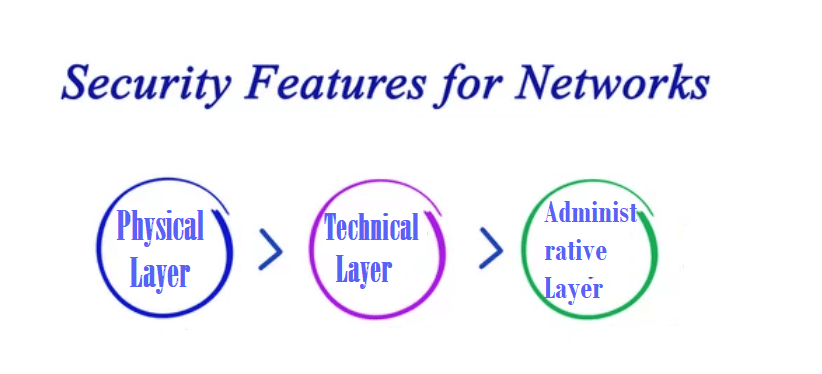
1. Physical Network Security
Physical security networks are developed to restrict unauthorized users from accessing various physical network devices, unlike routers, cabling cupboards, and so on. Every organization also requires checking the controlled access, unlike locks, biometric passwords, and other components.
2. Technical Network Security
Technical security controls, safeguard the information, put on the network or transferred over, into, or out of the network. Protection is duplex; it requires protecting information and devices from the unofficial group, and it also needs to guard against unofficial exercises from workers.
3. Administrative Network Security
Administrative network security controls end-user behavior, including their authentication, level of access, and how the IT staff of any organization implements reforms to its infrastructure. Administration security includes various security policies and processes to its functioning.
Types of network security
Below given are some of the different methods that are commonly used in our day-to-day life to secure computer networks:
1. Active Devices
Active security gadgets tackle the surplus traffic. For example, Firewalls, antivirus scanning tools, and content filtering appliances are the most commonly used active devices.
2. Passive Devices
Passive devices are used to recognize and block unwanted traffic, such as invasion detection devices.
3. Preventative Devices
Preventative devices are used to scan the networks and detect possible security threats. Penetration testing appliances and vulnerability assessment devices are the common examples of Preventative devices.
4. Unified Threat Management (UTM)
UTM devices act as all-in-one security tools. Firewalls, content filtering, web caching are the common examples of Unified Threat Management.
5. NAC or Network Access Control
NAC is a technique for applying computer security networks at the most fundamental level. For instance, the user could allow administrators full access to the network but deny access to particular confidential files or restrict their system from connecting any network. It is a method that attempts to unite endpoint security technology that supports network security enforcement.
6. Antivirus and Antimalware Software
Antivirus software's are designed to protect the system from a range of malware and malicious software, including viruses, worms, ransomware, and Trojans. The best software scans the malware, quarantines it and stops it before it causes any damage to the system.
7. Firewall Protection
A firewall acts as a defense barrier between your trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks such as viruses, worms, Trojans, brute force attacks. A firewall could be of any form, i.e., software or hardware, unlike a router. Though both the method performs the same function, scanning incoming network traffic to make sure it doesn't contain blacklisted data.
8. Virtual Private Networks
VPN supports the user in creating a secure and reliable private connection between the networks used by his computer or device to another network across the Internet. It handles the encryption process and uses other technologies to keep all your Internet activity safe and secure from attackers or cybercriminals who may be sneaking around when you connect your device with any public Wi-Fi. For instance, users working from home usually connect to the company's network via a VPN.
9. Content Filtering
Content filtering devices are used to filter offensive and nasty emails or web pages. This technique is implemented as a part of firewalls as well as in computers in companies. The content filtering devices generate the denial pop-up message displaying "Access Denied" if any unauthorized user attempts to access any official web page or email.
Content placed on the web is usually screened for obscene content or the content that spreads violence- or may contain hate-oriented information. Some organizations also screen and eliminate shopping and job-related content.
Content filtering can be classified in the below-given divisions: -
- Web filtering
- Scanning of Web sites or web pages
- E-mail filtering
- Screening of spam mails
- Various objectionable content
- INS or Intrusion Detection Systems
10. Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion Detection Systems or Intrusion Detection or Prevention Systems are the devices or the applications that actively monitor the network for malicious activities, log information about those activities, alert the company if the system detects an attack, and take steps to prevent them.
Intrusion detection systems keep a list of malware signatures and compares incoming threats to the list. It instantly blocks any attack and resends the packets whose configuration matches the list, and reset the connection to protect the IP address from any blockage. The various other actions performed by Intrusion detection systems are as follows:
- It checks the CRC (Correct Cyclic Redundancy Check) errors.
- It helps to prevent the various TCP sequencing problems.
- It cleans up the unwanted transport and network layer options.
Network security and the cloud
Cloud is the need of the hour. Every organization wants to extend its data storage capabilities that can be easily maintained, shared, and accessed between their employees. Physical storage mediums are hard to manage and conk out after a while. Therefore more and more enterprises are shifting their data and computing requirements to cloud service providers. Cloud providers build hybrid infrastructures where their internal network can operate securely with third-party servers. To manage network security, various cloud providers have implemented centralized security control strategies on their platforms.


