Tutorial
Physical Layer
Data Link layer
Network Layer
Routing Algorithm
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Network Security
Misc
- Router
- OSI vs TCP/IP
- TCP vs UDP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP port
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- ARP Packet Format
- ARP Table
- Working of ARP
- FTP Client
- FTP Commands
- FTP Server
- I2C Protocol
- Sliding Window Protocol
- SPI Protocol
- IP
- ARP Commands
- ARP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP and its types
- TCP Retransmission
- CAN protocol
- HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- RIP Protocol
- UDP Protocol
- ICMP Protocol
- MQTT protocol
- OSPF Protocol
- Stop and Wait Protocol
- IMAP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- CIFS
- DAS
- DIMM
- iSCSI
- NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- NFS
- NVMe
- SAN
- Border Gateway Protocol
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- RJ Cable
- Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Service
- CDMA vs. GSM
- What is MAC Address
- Modem vs. Router
- Switch Vs. Router
- USB 2.0 vs 3.0
- Difference between CSMA CA and CSMA CD
- Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
- URI vs URL
- IMAP vs. POP3
- SSH Meaning| SSH Protocol
- UTP vs STP
- Status Code 400
- MIME Protocol
- IP address
- proxy server
- How to set up and use a proxy server
- network security
- WWW is based on which model
- Proxy Server List
- Fundamentals of Computer Networking
- IP Address Format and Table
- Bus topology and Ring topology
- Bus topology and Star topology
- Circuit Switching and Packet switching?
- Difference between star and ring topology
- Difference between Router and Bridge
- TCP Connection Termination
- Image Steganography
- Network Neutrality
- Onion Routing
- Adaptive security appliance (ASA) features
- Relabel-to-front Algorithm
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Access Lists (ACL)
- What is a proxy server and how does it work
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Operating system based Virtualization
- Context based Access Control (CBAC)
- Cristian's Algorithm
- Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)
- Extended Access List
- Li-fi vs. Wi-fi
- Reflexive Access List
- Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
- Wifi protected access (WPA)
- Wifi Protected Setup (WPS)
- Standard Access List
- Time Access List
- What is 3D Internet
- 4G Mobile Communication Technology
- Types of Wireless Transmission Media
- Best Computer Networking Courses
- Data Representation
- Network Criteria
- Classful vs Classless addressing
- Difference between BOOTP and RARP in Computer Networking
- What is AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- External IP Address
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Types of Authentication Protocols
- What is a CISCO Packet Tracer
- BOOTP work
- Subnetting in Computer Networks
- Mesh Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ring Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Star Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Zigbee Technology-The smart home protocol
- Network Layer in OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer in OSI Model
- Internet explorer shortcut keys
- Network Layer Security | SSL Protocols
- Presentation Layer in OSI Model
- Session Layer in OSI Model
- SUBNET MASK
- Transport Layer Security | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and SSL Architecture
- Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Layer
- Protocols in Noiseless and Noisy Channel
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
- Count to Infinity Problem in Distance Vector Routing
- Difference Between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat Protocol
- Difference between Stop and Wait, GoBackN, and Selective Repeat
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): transforming Network Architecture with Virtualized Functions
- Network-Layer Security | IPSec Modes
- Next - Prev Network-Layer Security | IPSec Protocols and Services
- Ping vs Traceroute
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): Benefits and Challenges of Network Virtualization
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) vs. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- Virtual Circuits vs Datagram Networks
- BlueSmack Attack in Wireless Networks
- Bluesnarfing Attack in Wireless Networks
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Warchalking in Wireless Networks
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- Wireless security encryption
- Wireless Security in an Enterprise
- Quantum Networking
- Network Automation
- Difference between MSS and MTU
- What is MTU
- Mesh Networks: A decentralized and Self-Organizing Approach to Networking
- What is Autonomous System
- What is MSS
- Cyber security & Software security
- Information security & Network security.
- Security Engineer & Security Architect
- Protection Methods for Network Security
- Trusted Systems in Network Security
- What are Authentication Tokens in Network security
- Cookies in Network Security
- Intruders in Network Security
- Network Security Toolkit (NST) in virtual box
- Pivoting-Moving Inside a Network
- Security Environment in Computer Networks
- Voice Biometric technique in Network Security
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Testing
- Difference between Kerberos and LDAP
- Cyber security and Information Security
- GraphQL Attacks and Security
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Applications of Remote Sensing
- Seven Layers of IT Security
- What is Ad Hoc TCP
- What is Server Name Indication(SNI)
Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
To understand the advantages and disadvantages, first we have to know about the what is Tree Topology? So, let's begin with introduction.
What is Tree Topology?
Bus-star topology is also known as tree topology. In tree topology, it incorporates the elements of both a bus topology as well as a star topology. Tree topology is not a commonly used network, but when a combined hierarchical or scalability setup is required between two networks, this topology comes into work. Since it appears like a tree, the structure of a tree topology is quite different from others.
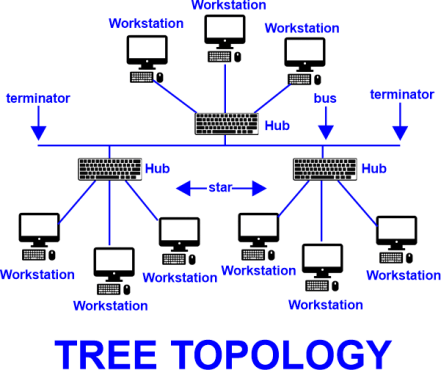
The central node of this topology acts as a strength for the network used, and it has some nodes extending outwards, just like branches of a tree. In tree topology, Only the root is seen in between any two nodes on the network. The connection pattern looks like a tree whose branches spread from only one route.
Tree topology is a hybrid of bus topology and star topology. In a bus topology, all the other nodes are connected by a central node known as the bus.
Each and every node in a star topology is connected through hubs. For that reason, tree topology is an expansion of these two topologies, which is easily called an expanded star topology.
In this topology, only one connection exists Between any two connected nodes. There is a mutual relationship exists between the two nodes. So a parent and child hierarchy is created in a tree topology. In this topology, for forming a hierarchical structure, all the nodes of this network are connected through a central node. Hence it is also known as hierarchical topology.
It is one of the simplest approaches among all the topologies. Tree topologies are flexible and reliable. One has to connect extra cables and a hub for the expansion of this network.
Tree topology networks can also be connected in large areas. One can click as many servers as they go through the network. When any data is transmitted through your computer, it will get broadcasted in the hub, and then the message will be conveyed by the hub to the designated computer.
Advantages of Tree Topology:
1. Detection of error:
Error detection in a tree topology becomes more accessible. In this tree topology, the central node connects all the nodes present in it. The error in this node can be easily detected by the hub since all the information transmitted through the node passes through the hub. By replacing the faulty node in this network, we can easily replace the node which has a mistake in it.
2. Sturdiness:
If a single node gets defective in the tree topology, it will not affect the other nodes. The tree topology network is created based on the main backbone cable. Hence, the failure of 1 node would not affect the other nodes, and the other nodes will regularly continue to function. The performance of the network would not be affected by the removal of any node in it.
3. Easy expansion:
The expansion of a tree topology is a straightforward method. Though this topology has no space, it can be expanded. In this topology, without any issue, many secondary nodes can be attached to it since this topology follows a hierarchy pattern. As long as enough cables and hubs are present, the expansion won't be a problem.
4. Every support:
A tree topology is the best considerable option at the time of the addition of new devices. Due to its hybrid approach, various manufacturers support this type of network. For maintenance and other work, he allowed the manufacturers to access the devices connected to the network easily.
5. Low cable requirement:
Any cables are not required at the time of installation of a tree topology. The single cable in this type of topology acts like the backbone of the network, and it runs joint for all the network segments. every tree network is presented with a point to point wiring. This type of point-to-point wiring in this network ensures high bandwidth and low latency.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology:
1. Tree topology installation:
Due to its difficulty during the installation process, the uses of tree topology are very limited. Both bus and star topology functions are included in the tree topology. Hence the cabling requirement of a tree topology is massive. For that reason, the installation process of this topology becomes difficult to handle and expensive.
2. Security:
Extremely weak security is present in a tree topology. All the computers in this topology are interconnected with each other. As a result, any computer within this network can access the data that can pass through the network. So, if a hacker tries to take over a single workstation, they can easily and quickly access all the data; hence, the whole network is compromised.
3. Reliability:
The backbone cable of the tree topology is the main cable on which the entire network depends. If the backbone cable gets defective and fails, then the whole network will collapse. The point where the failure occurs also decides the level of loss. If the damage is restricted before a specific branch, all the segments related to that branch will face problems while functioning. On the other hand, the components which are not associated with it will continue to work usually.
4. Cost:
The cable length of a tree topology is also an essential factor. While creating the point-to-point connection in tree topology, the cable length is limited to a certain point by default. This limitation later causes trouble since it makes it challenging to get wired. Regardless of this, there will be high wiring requirements if the network needs expansion, which will increase the total cost.
5. Maintenance:
Maintenance and configuration of tree topology become difficult due to its large size. A lot of time is taken up for managing point-to-point connections, individual star networks, and the identification of errors. This is amongst one of the major reasons why large organizations less prefer tree topology.
Comparison Table for Advantages and Disadvantages of Tree Topology
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| 1. Easier detection of error. | 1. Difficulty in maintenance and configuration. |
| 2. Failure of a solo node will not disturb the other nodes. | 2. Difficult to install a tree topology network. |
| 3. Tree topology does not require any particular type of cable. | 3. The cable length of a tree topology is minimal. If we expand the topology, the excess cable is required, which results in increasing overall expense. |
| 4. We can expand tree topology easily. | 4. Tree topology poses high-security threats. |
| 5. Tree topology is one of the finest choices while adding new devices due to its hybrid approach. | 5. If the main cable of the topology collapses, the whole network will also collapse. |


