Tutorial
Physical Layer
Data Link layer
Network Layer
Routing Algorithm
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Network Security
Misc
- Router
- OSI vs TCP/IP
- TCP vs UDP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP port
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- ARP Packet Format
- ARP Table
- Working of ARP
- FTP Client
- FTP Commands
- FTP Server
- I2C Protocol
- Sliding Window Protocol
- SPI Protocol
- IP
- ARP Commands
- ARP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP and its types
- TCP Retransmission
- CAN protocol
- HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- RIP Protocol
- UDP Protocol
- ICMP Protocol
- MQTT protocol
- OSPF Protocol
- Stop and Wait Protocol
- IMAP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- CIFS
- DAS
- DIMM
- iSCSI
- NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- NFS
- NVMe
- SAN
- Border Gateway Protocol
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- RJ Cable
- Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Service
- CDMA vs. GSM
- What is MAC Address
- Modem vs. Router
- Switch Vs. Router
- USB 2.0 vs 3.0
- Difference between CSMA CA and CSMA CD
- Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
- URI vs URL
- IMAP vs. POP3
- SSH Meaning| SSH Protocol
- UTP vs STP
- Status Code 400
- MIME Protocol
- IP address
- proxy server
- How to set up and use a proxy server
- network security
- WWW is based on which model
- Proxy Server List
- Fundamentals of Computer Networking
- IP Address Format and Table
- Bus topology and Ring topology
- Bus topology and Star topology
- Circuit Switching and Packet switching?
- Difference between star and ring topology
- Difference between Router and Bridge
- TCP Connection Termination
- Image Steganography
- Network Neutrality
- Onion Routing
- Adaptive security appliance (ASA) features
- Relabel-to-front Algorithm
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Access Lists (ACL)
- What is a proxy server and how does it work
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Operating system based Virtualization
- Context based Access Control (CBAC)
- Cristian's Algorithm
- Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)
- Extended Access List
- Li-fi vs. Wi-fi
- Reflexive Access List
- Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
- Wifi protected access (WPA)
- Wifi Protected Setup (WPS)
- Standard Access List
- Time Access List
- What is 3D Internet
- 4G Mobile Communication Technology
- Types of Wireless Transmission Media
- Best Computer Networking Courses
- Data Representation
- Network Criteria
- Classful vs Classless addressing
- Difference between BOOTP and RARP in Computer Networking
- What is AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- External IP Address
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Types of Authentication Protocols
- What is a CISCO Packet Tracer
- BOOTP work
- Subnetting in Computer Networks
- Mesh Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ring Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Star Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Zigbee Technology-The smart home protocol
- Network Layer in OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer in OSI Model
- Internet explorer shortcut keys
- Network Layer Security | SSL Protocols
- Presentation Layer in OSI Model
- Session Layer in OSI Model
- SUBNET MASK
- Transport Layer Security | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and SSL Architecture
- Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Layer
- Protocols in Noiseless and Noisy Channel
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
- Count to Infinity Problem in Distance Vector Routing
- Difference Between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat Protocol
- Difference between Stop and Wait, GoBackN, and Selective Repeat
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): transforming Network Architecture with Virtualized Functions
- Network-Layer Security | IPSec Modes
- Next - Prev Network-Layer Security | IPSec Protocols and Services
- Ping vs Traceroute
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): Benefits and Challenges of Network Virtualization
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) vs. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- Virtual Circuits vs Datagram Networks
- BlueSmack Attack in Wireless Networks
- Bluesnarfing Attack in Wireless Networks
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Warchalking in Wireless Networks
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- Wireless security encryption
- Wireless Security in an Enterprise
- Quantum Networking
- Network Automation
- Difference between MSS and MTU
- What is MTU
- Mesh Networks: A decentralized and Self-Organizing Approach to Networking
- What is Autonomous System
- What is MSS
- Cyber security & Software security
- Information security & Network security.
- Security Engineer & Security Architect
- Protection Methods for Network Security
- Trusted Systems in Network Security
- What are Authentication Tokens in Network security
- Cookies in Network Security
- Intruders in Network Security
- Network Security Toolkit (NST) in virtual box
- Pivoting-Moving Inside a Network
- Security Environment in Computer Networks
- Voice Biometric technique in Network Security
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Testing
- Difference between Kerberos and LDAP
- Cyber security and Information Security
- GraphQL Attacks and Security
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Applications of Remote Sensing
- Seven Layers of IT Security
- What is Ad Hoc TCP
- What is Server Name Indication(SNI)
IP address

An IP address represents a unique address that distinguishes any device on the internet or any network from another. IP or Internet Protocol defines the set of commands directing the setup of data transferred through the internet or any other local network.
An IP address is the identifier that enables your device to send or receive data packets across the internet. It holds information related to your location and therefore making devices available for two-way communication. The internet requires a process to distinguish between different networks, routers, and websites. Therefore, IP addresses provide the mechanism of doing so, and it forms an indispensable part in the working of the internet. You will notice that most of the IP addresses are essentially numerical. Still, as the world is witnessing a colossal growth of network users, the network developers had to add letters and some addresses as internet usage grows.
An IP address is represented by a series of numbers segregated by periods(.). They are expressed in the form of four pairs - an example address might be 255.255.255.255 wherein each set can range from 0 to 255.
IP addresses are not produced randomly. They are generated mathematically and are further assigned by the IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority), a department of the ICANN.
ICANN stands for Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers. It is a non-profit corporation founded in the US back in 1998 with an aim to manage Internet security and enable it to be available by all.
How do IP addresses work?
Sometimes your device doesn't connect to your network the way you expect it to be, or you wish to troubleshoot why your network is not operating correctly. To answer the above questions, it is vital to learn the process with which IP addresses work.
Internet Protocol or IP runs the same manner as other languages, i.e., applying the set guidelines to communicate the information. All devices obtain, send, and pass information with other associated devices with the help of this protocol only. By using the same language, the computers placed anywhere can communicate with one another.
The process of IP address works in the following way:
- Your computer, smartphone, or any other Wi-Fi-enabled device firstly connects to a network that is further connected to the internet. The network is responsible for giving your device access to the internet.
- While working from home, your device would be probably using that network provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). In a professional environment, your device uses your company network.
- Your ISP is responsible to generate the IP address for your device.
- Your internet request penetrates through the ISP, and they place the requested data back to your device using your IP address. Since they provide you access to the internet, ISP's are responsible for allocating an IP address to your computer or respective device.
- Your IP address is never consistent and can change if there occurs any changes in its internal environment. For instance, if you turn your modem or router on or off, it will change your IP address. Or the user can also connect the ISP to change their IP address.
- When you are out of your home or office, mainly if you travel and carry your device with you, your computer won't be accessing your home IP address anymore. This is because you will be accessing the different networks (your phone hotspot, Wi-Fi at a cafe, resort, or airport, etc.) to connect the device with the internet. Therefore, your device will be allocated a different (temporary) IP address by the ISP of the hotel or cafe.
Types of IP addresses
There are various classifications of IP addresses, and each category further contains some types.
Consumer IP addresses
Every individual or firm with an active internet service system pursues two types of IP addresses, i.e., Private IP (Internet Protocol) addresses and public IP (Internet Protocol) addresses. The public and private correlate to the network area. Therefore, a private IP address is practiced inside a network, whereas the other (public IP address) is practiced outside a network.
1. Private IP addresses
All the devices that are linked with your internet network are allocated a private IP address. It holds computers, desktops, laptops, smartphones, tablets, or even Wi-Fi-enabled gadgets such as speakers, printers, or smart Televisions. With the expansion of IoT (internet of things), the demand for private IP addresses at individual homes is also seemingly growing. However, the router requires a method to identify these things distinctly. Therefore, your router produces unique private IP addresses that act as an identifier for every device using your internet network. Thus, differentiating them from one another on the network.
2. Public IP addresses
A public IP address or primary address represents the whole network of devices associated with it. Every device included within with your primary address contains their own private IP address. ISP is responsible to provide your public IP address to your router. Typically, ISPs contains the bulk stock of IP addresses that they dispense to their clients. Your public IP address is practiced by every device to identify your network that is residing outside your internet network.
Public IP addresses are further classified into two categories- dynamic and static.
- Dynamic IP addresses
As the name suggests, Dynamic IP addresses change automatically and frequently. With this types of IP address, ISPs already purchase a bulk stock of IP addresses and allocate them in some order to their customers. Periodically, they re-allocate the IP addresses and place the used ones back into the IP addresses pool so they can be used later for another client. The foundation for this method is to make cost savings profits for the ISP. - Static IP addresses
In comparison to dynamic IP addresses, static addresses are constant in nature. The network assigns the IP address to the device only once and, it remains consistent. Though most firms or individuals do not prefer to have a static IP address, it is essential to have a static IP address for an organization that wants to host its network server. It protects websites and email addresses linked with it with a constant IP address.
Types of website IP addresses
The following classification is segregated into the two types of website IP addresses i.e., shared and dedicated.
1. Shared IP addresses
Many startups or individual website makers or various SME websites who don't want to invest initially in dedicated IP addresses can opt for shared hosting plans. Various web hosting providers are there in the market providing shared hosting services where two or more websites are hosted on the same server. Shared hosting is only feasible for websites that receive average traffic, the volumes are manageable, and the websites themselves are confined in terms of the webpages, etc.
2. Dedicated IP addresses
Web hosting providers also provide the option to acquire a dedicated IP address. Undoubtedly dedicated IP addresses are more secure, and they permit the users to run their File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server. Therefore, it is easier to share and transfer data with many people within a business, and it also provides the option of anonymous FTP sharing. Another advantage of a dedicated IP addresses it the user can easily access the website using the IP address rather than typing the full domain name.
How to search for IP addresses
The easiest method to find the public IP address of your router is to type "What is my IP address?" on Google.com. Google will immediately display the results on the screen.
There are some third-party websites available on the internet that also provides the same information. Those websites can access your public IP address because your router has requested to access their information by visiting their website.
Below are the steps to find your private IP address in two commonly used platforms:
In Windows:
- Open the command prompt by typing the term 'cmd' (no quote marks) in the Windows search panel.
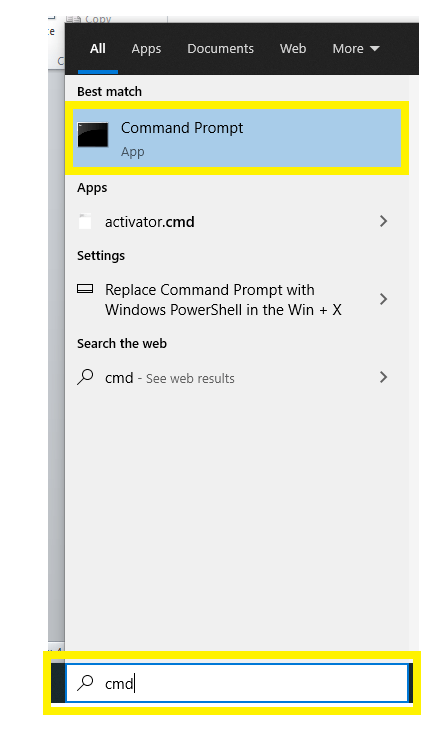
- The following window will appear. Type "ipconfig" (without the quotes) to access the private IP address information.
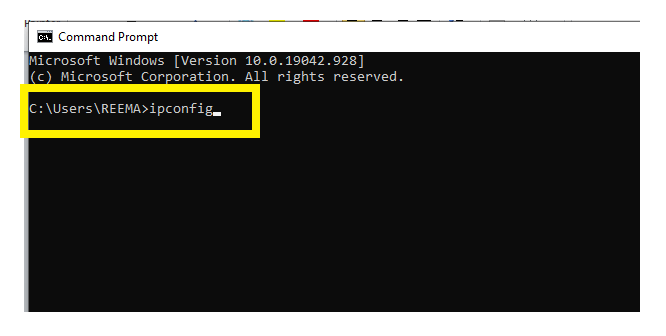
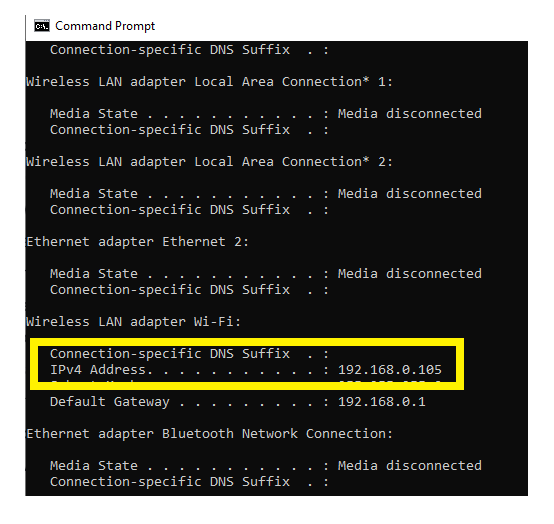
- It will display the following information.
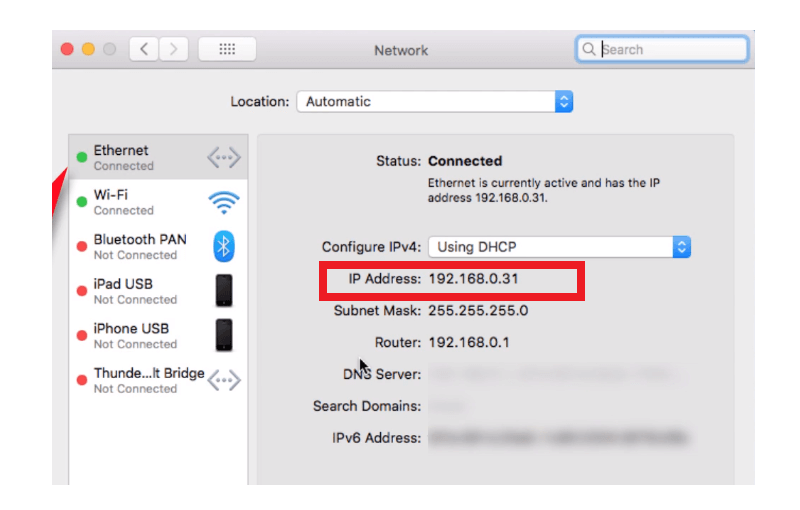
On a Mac:
- Go to System Preferences
- Click on the network option.

- It will display the information regarding your private IP address.
IP address security threats
Cybercriminals or digital crackers various ways to hack your IP address. The two commonly used techniques include social engineering and online stalking.
Social engineering
Hackers can practice social engineering techniques to trick you into disclosing your device's IP address. For example, they will connect you through email, Skype, or a similar instantaneous messaging app, that accepts IP addresses to communicate and pass information. If you chat with these anonymous people using these messaging applications, it is essential to note that they can get your IP address. Cybercriminals can use a third-party tool named Skype Resolver, with the help of which they can locate your IP address using your username.
Online stalking
Attackers can get crack your IP address by simply tracking your online activities. Any online activity can disclose your IP address, i.e., from using an instant messaging app to playing online games to discussing a topic on any digital websites and forums. Once they gain access to your IP address, criminals can visit an IP address tracking website (whatismyipaddress.com), they will enter your IP address there, and in no seconds, they can track your current location. They won't stop till this; they can further cross-check it with other available information to verify whether the IP address is connected with you particularly. Social networking sites such as instagram, LinkedIn, facebook are used to verify the information of your location gathered by the attacker.


