Tutorial
Physical Layer
Data Link layer
Network Layer
Routing Algorithm
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Network Security
Misc
- Router
- OSI vs TCP/IP
- TCP vs UDP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP port
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- ARP Packet Format
- ARP Table
- Working of ARP
- FTP Client
- FTP Commands
- FTP Server
- I2C Protocol
- Sliding Window Protocol
- SPI Protocol
- IP
- ARP Commands
- ARP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP and its types
- TCP Retransmission
- CAN protocol
- HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- RIP Protocol
- UDP Protocol
- ICMP Protocol
- MQTT protocol
- OSPF Protocol
- Stop and Wait Protocol
- IMAP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- CIFS
- DAS
- DIMM
- iSCSI
- NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- NFS
- NVMe
- SAN
- Border Gateway Protocol
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- RJ Cable
- Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Service
- CDMA vs. GSM
- What is MAC Address
- Modem vs. Router
- Switch Vs. Router
- USB 2.0 vs 3.0
- Difference between CSMA CA and CSMA CD
- Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
- URI vs URL
- IMAP vs. POP3
- SSH Meaning| SSH Protocol
- UTP vs STP
- Status Code 400
- MIME Protocol
- IP address
- proxy server
- How to set up and use a proxy server
- network security
- WWW is based on which model
- Proxy Server List
- Fundamentals of Computer Networking
- IP Address Format and Table
- Bus topology and Ring topology
- Bus topology and Star topology
- Circuit Switching and Packet switching?
- Difference between star and ring topology
- Difference between Router and Bridge
- TCP Connection Termination
- Image Steganography
- Network Neutrality
- Onion Routing
- Adaptive security appliance (ASA) features
- Relabel-to-front Algorithm
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Access Lists (ACL)
- What is a proxy server and how does it work
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Operating system based Virtualization
- Context based Access Control (CBAC)
- Cristian's Algorithm
- Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)
- Extended Access List
- Li-fi vs. Wi-fi
- Reflexive Access List
- Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
- Wifi protected access (WPA)
- Wifi Protected Setup (WPS)
- Standard Access List
- Time Access List
- What is 3D Internet
- 4G Mobile Communication Technology
- Types of Wireless Transmission Media
- Best Computer Networking Courses
- Data Representation
- Network Criteria
- Classful vs Classless addressing
- Difference between BOOTP and RARP in Computer Networking
- What is AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- External IP Address
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Types of Authentication Protocols
- What is a CISCO Packet Tracer
- BOOTP work
- Subnetting in Computer Networks
- Mesh Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ring Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Star Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Zigbee Technology-The smart home protocol
- Network Layer in OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer in OSI Model
- Internet explorer shortcut keys
- Network Layer Security | SSL Protocols
- Presentation Layer in OSI Model
- Session Layer in OSI Model
- SUBNET MASK
- Transport Layer Security | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and SSL Architecture
- Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Layer
- Protocols in Noiseless and Noisy Channel
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
- Count to Infinity Problem in Distance Vector Routing
- Difference Between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat Protocol
- Difference between Stop and Wait, GoBackN, and Selective Repeat
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): transforming Network Architecture with Virtualized Functions
- Network-Layer Security | IPSec Modes
- Next - Prev Network-Layer Security | IPSec Protocols and Services
- Ping vs Traceroute
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): Benefits and Challenges of Network Virtualization
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) vs. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- Virtual Circuits vs Datagram Networks
- BlueSmack Attack in Wireless Networks
- Bluesnarfing Attack in Wireless Networks
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Warchalking in Wireless Networks
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- Wireless security encryption
- Wireless Security in an Enterprise
- Quantum Networking
- Network Automation
- Difference between MSS and MTU
- What is MTU
- Mesh Networks: A decentralized and Self-Organizing Approach to Networking
- What is Autonomous System
- What is MSS
- Cyber security & Software security
- Information security & Network security.
- Security Engineer & Security Architect
- Protection Methods for Network Security
- Trusted Systems in Network Security
- What are Authentication Tokens in Network security
- Cookies in Network Security
- Intruders in Network Security
- Network Security Toolkit (NST) in virtual box
- Pivoting-Moving Inside a Network
- Security Environment in Computer Networks
- Voice Biometric technique in Network Security
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Testing
- Difference between Kerberos and LDAP
- Cyber security and Information Security
- GraphQL Attacks and Security
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Applications of Remote Sensing
- Seven Layers of IT Security
- What is Ad Hoc TCP
- What is Server Name Indication(SNI)
Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
Data Link Layer
The data link layer is used in a computer network to transmit the data between two devices or nodes. It divides the layer into parts such as data link control and the multiple access resolution/protocol. The upper layer has the responsibility to flow control and the error control in the data link layer, and hence it is termed as logical of data link control. Whereas the lower sub-layer is used to handle and reduce the collision or multiple access on a channel. Hence it is termed as media access control or the multiple access resolutions.
Data Link Control
A data link control is a reliable channel for transmitting data over a dedicated link using various techniques such as framing, error control and flow control of data packets in the computer network.
What is a multiple access protocol?
When a sender and receiver have a dedicated link to transmit data packets, the data link control is enough to handle the channel. Suppose there is no dedicated path to communicate or transfer the data between two devices. In that case, multiple stations access the channel and simultaneously transmits the data over the channel. It may create collision and cross talk. Hence, the multiple access protocol is required to reduce the collision and avoid crosstalk between the channels.
For example, suppose that there is a classroom full of students. When a teacher asks a question, all the students (small channels) in the class start answering the question at the same time (transferring the data simultaneously). All the students respond at the same time due to which data is overlap or data lost. Therefore it is the responsibility of a teacher (multiple access protocol) to manage the students and make them one answer.
Following are the types of multiple access protocol that is subdivided into the different process as:
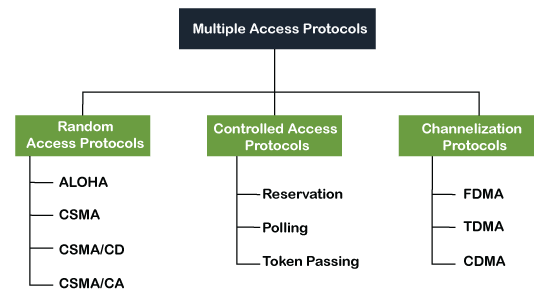
A. Random Access Protocol
In this protocol, all the station has the equal priority to send the data over a channel. In random access protocol, one or more stations cannot depend on another station nor any station control another station. Depending on the channel's state (idle or busy), each station transmits the data frame. However, if more than one station sends the data over a channel, there may be a collision or data conflict. Due to the collision, the data frame packets may be lost or changed. And hence, it does not receive by the receiver end.
Following are the different methods of random-access protocols for broadcasting frames on the channel.
- Aloha
- CSMA
- CSMA/CD
- CSMA/CA
ALOHA Random Access Protocol
It is designed for wireless LAN (Local Area Network) but can also be used in a shared medium to transmit data. Using this method, any station can transmit data across a network simultaneously when a data frameset is available for transmission.
Aloha Rules
- Any station can transmit data to a channel at any time.
- It does not require any carrier sensing.
- Collision and data frames may be lost during the transmission of data through multiple stations.
- Acknowledgment of the frames exists in Aloha. Hence, there is no collision detection.
- It requires retransmission of data after some random amount of time.

Pure Aloha
Whenever data is available for sending over a channel at stations, we use Pure Aloha. In pure Aloha, when each station transmits data to a channel without checking whether the channel is idle or not, the chances of collision may occur, and the data frame can be lost. When any station transmits the data frame to a channel, the pure Aloha waits for the receiver's acknowledgment. If it does not acknowledge the receiver end within the specified time, the station waits for a random amount of time, called the backoff time (Tb). And the station may assume the frame has been lost or destroyed. Therefore, it retransmits the frame until all the data are successfully transmitted to the receiver.
- The total vulnerable time of pure Aloha is 2 * Tfr.
- Maximum throughput occurs when G = 1/ 2 that is 18.4%.
- Successful transmission of data frame is S = G * e ^ - 2 G.
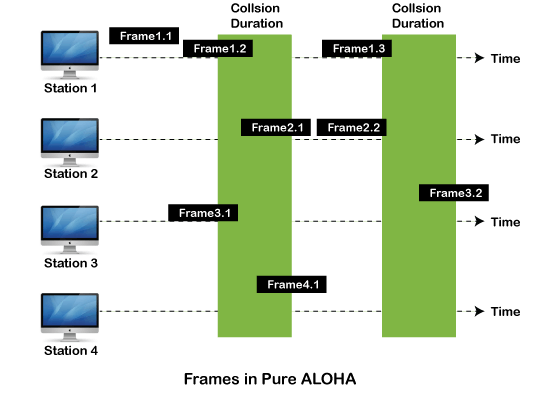
As we can see in the figure above, there are four stations for accessing a shared channel and transmitting data frames. Some frames collide because most stations send their frames at the same time. Only two frames, frame 1.1 and frame 2.2, are successfully transmitted to the receiver end. At the same time, other frames are lost or destroyed. Whenever two frames fall on a shared channel simultaneously, collisions can occur, and both will suffer damage. If the new frame's first bit enters the channel before finishing the last bit of the second frame. Both frames are completely finished, and both stations must retransmit the data frame.
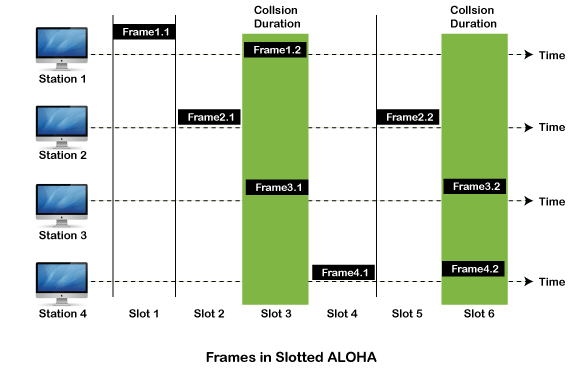
Slotted Aloha
The slotted Aloha is designed to overcome the pure Aloha's efficiency because pure Aloha has a very high possibility of frame hitting. In slotted Aloha, the shared channel is divided into a fixed time interval called slots. So that, if a station wants to send a frame to a shared channel, the frame can only be sent at the beginning of the slot, and only one frame is allowed to be sent to each slot. And if the stations are unable to send data to the beginning of the slot, the station will have to wait until the beginning of the slot for the next time. However, the possibility of a collision remains when trying to send a frame at the beginning of two or more station time slot.
- Maximum throughput occurs in the slotted Aloha when G = 1 that is 37%.
- The probability of successfully transmitting the data frame in the slotted Aloha is S = G * e ^ - 2 G.
- The total vulnerable time required in slotted Aloha is Tfr.
CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access)
It is a carrier sense multiple access based on media access protocol to sense the traffic on a channel (idle or busy) before transmitting the data. It means that if the channel is idle, the station can send data to the channel. Otherwise, it must wait until the channel becomes idle. Hence, it reduces the chances of a collision on a transmission medium.
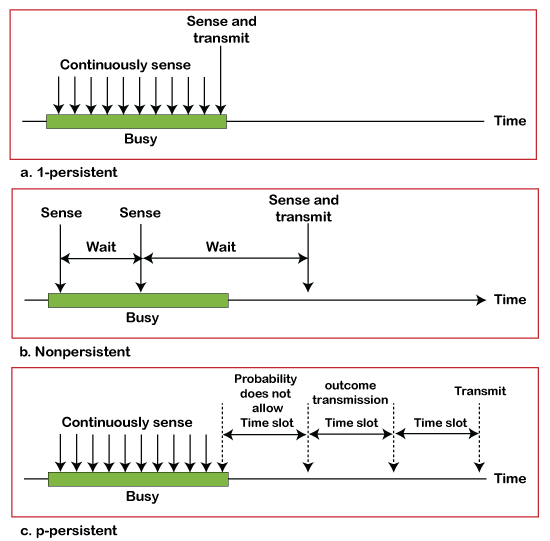
CSMA Access Modes
1-Persistent: In the 1-Persistent mode of CSMA that defines each node, first sense the shared channel and if the channel is idle, it immediately sends the data. Else it must wait and keep track of the status of the channel to be idle and broadcast the frame unconditionally as soon as the channel is idle.
Non-Persistent: It is the access mode of CSMA that defines before transmitting the data, each node must sense the channel, and if the channel is inactive, it immediately sends the data. Otherwise, the station must wait for a random time (not continuously), and when the channel is found to be idle, it transmits the frames.
P-Persistent: It is the combination of 1-Persistent and Non-persistent modes. The P-Persistent mode defines that each node senses the channel, and if the channel is inactive, it sends a frame with a P probability. If the data is not transmitted, it waits for a (q = 1-p probability) random time and resumes the frame with the next time slot.
O- Persistent: It is an O-persistent method that defines the superiority of the station before the transmission of the frame on the shared channel. If it is found that the channel is inactive, each station waits for its turn to retransmit the data.
CSMA/ CD
It is a carrier sense multiple access/ collision detection network protocol to transmit data frames. The CSMA/CD protocol works with a medium access control layer. Therefore, it first senses the shared channel before broadcasting the frames, and if the channel is idle, it transmits a frame to check whether the transmission was successful. If the frame is successfully received, the station sends another frame. If any collision is detected in the CSMA/CD, the station sends a jam/ stop signal to the shared channel to terminate data transmission. After that, it waits for a random time before sending a frame to a channel.
CSMA/ CA
It is a carrier sense multiple access/collision avoidance network protocol for carrier transmission of data frames. It is a protocol that works with a medium access control layer. When a data frame is sent to a channel, it receives an acknowledgment to check whether the channel is clear. If the station receives only a single (own) acknowledgments, that means the data frame has been successfully transmitted to the receiver. But if it gets two signals (its own and one more in which the collision of frames), a collision of the frame occurs in the shared channel. Detects the collision of the frame when a sender receives an acknowledgment signal.
Following are the methods used in the CSMA/ CA to avoid the collision:
Interframe space: In this method, the station waits for the channel to become idle, and if it gets the channel is idle, it does not immediately send the data. Instead of this, it waits for some time, and this time period is called the Interframe space or IFS. However, the IFS time is often used to define the priority of the station.
Contention window: In the Contention window, the total time is divided into different slots. When the station/ sender is ready to transmit the data frame, it chooses a random slot number of slots as wait time. If the channel is still busy, it does not restart the entire process, except that it restarts the timer only to send data packets when the channel is inactive.
Acknowledgment: In the acknowledgment method, the sender station sends the data frame to the shared channel if the acknowledgment is not received ahead of time.
B. Controlled Access Protocol
It is a method of reducing data frame collision on a shared channel. In the controlled access method, each station interacts and decides to send a data frame by a particular station approved by all other stations. It means that a single station cannot send the data frames unless all other stations are not approved. It has three types of controlled access: Reservation, Polling, and Token Passing.
C. Channelization Protocols
It is a channelization protocol that allows the total usable bandwidth in a shared channel to be shared across multiple stations based on their time, distance and codes. It can access all the stations at the same time to send the data frames to the channel.
Following are the various methods to access the channel based on their time, distance and codes:
- FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access)
- TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access)
- CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access)
FDMA
It is a frequency division multiple access (FDMA) method used to divide the available bandwidth into equal bands so that multiple users can send data through a different frequency to the subchannel. Each station is reserved with a particular band to prevent the crosstalk between the channels and interferences of stations.
TDMA
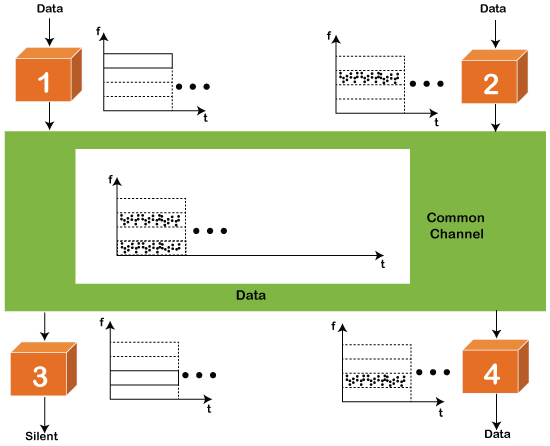
Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) is a channel access method. It allows the same frequency bandwidth to be shared across multiple stations. And to avoid collisions in the shared channel, it divides the channel into different frequency slots that allocate stations to transmit the data frames. The same frequency bandwidth into the shared channel by dividing the signal into various time slots to transmit it. However, TDMA has an overhead of synchronization that specifies each station's time slot by adding synchronization bits to each slot.
CDMA
The code division multiple access (CDMA) is a channel access method. In CDMA, all stations can simultaneously send the data over the same channel. It means that it allows each station to transmit the data frames with full frequency on the shared channel at all times. It does not require the division of bandwidth on a shared channel based on time slots. If multiple stations send data to a channel simultaneously, their data frames are separated by a unique code sequence. Each station has a different unique code for transmitting the data over a shared channel. For example, there are multiple users in a room that are continuously speaking. Data is received by the users if only two-person interact with each other using the same language. Similarly, in the network, if different stations communicate with each other simultaneously with different code language.


