Tutorial
Physical Layer
Data Link layer
Network Layer
Routing Algorithm
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Network Security
Misc
- Router
- OSI vs TCP/IP
- TCP vs UDP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP port
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- ARP Packet Format
- ARP Table
- Working of ARP
- FTP Client
- FTP Commands
- FTP Server
- I2C Protocol
- Sliding Window Protocol
- SPI Protocol
- IP
- ARP Commands
- ARP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP and its types
- TCP Retransmission
- CAN protocol
- HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- RIP Protocol
- UDP Protocol
- ICMP Protocol
- MQTT protocol
- OSPF Protocol
- Stop and Wait Protocol
- IMAP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- CIFS
- DAS
- DIMM
- iSCSI
- NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- NFS
- NVMe
- SAN
- Border Gateway Protocol
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- RJ Cable
- Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Service
- CDMA vs. GSM
- What is MAC Address
- Modem vs. Router
- Switch Vs. Router
- USB 2.0 vs 3.0
- Difference between CSMA CA and CSMA CD
- Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
- URI vs URL
- IMAP vs. POP3
- SSH Meaning| SSH Protocol
- UTP vs STP
- Status Code 400
- MIME Protocol
- IP address
- proxy server
- How to set up and use a proxy server
- network security
- WWW is based on which model
- Proxy Server List
- Fundamentals of Computer Networking
- IP Address Format and Table
- Bus topology and Ring topology
- Bus topology and Star topology
- Circuit Switching and Packet switching?
- Difference between star and ring topology
- Difference between Router and Bridge
- TCP Connection Termination
- Image Steganography
- Network Neutrality
- Onion Routing
- Adaptive security appliance (ASA) features
- Relabel-to-front Algorithm
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Access Lists (ACL)
- What is a proxy server and how does it work
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Operating system based Virtualization
- Context based Access Control (CBAC)
- Cristian's Algorithm
- Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)
- Extended Access List
- Li-fi vs. Wi-fi
- Reflexive Access List
- Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
- Wifi protected access (WPA)
- Wifi Protected Setup (WPS)
- Standard Access List
- Time Access List
- What is 3D Internet
- 4G Mobile Communication Technology
- Types of Wireless Transmission Media
- Best Computer Networking Courses
- Data Representation
- Network Criteria
- Classful vs Classless addressing
- Difference between BOOTP and RARP in Computer Networking
- What is AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- External IP Address
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Types of Authentication Protocols
- What is a CISCO Packet Tracer
- BOOTP work
- Subnetting in Computer Networks
- Mesh Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ring Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Star Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Zigbee Technology-The smart home protocol
- Network Layer in OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer in OSI Model
- Internet explorer shortcut keys
- Network Layer Security | SSL Protocols
- Presentation Layer in OSI Model
- Session Layer in OSI Model
- SUBNET MASK
- Transport Layer Security | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and SSL Architecture
- Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Layer
- Protocols in Noiseless and Noisy Channel
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
- Count to Infinity Problem in Distance Vector Routing
- Difference Between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat Protocol
- Difference between Stop and Wait, GoBackN, and Selective Repeat
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): transforming Network Architecture with Virtualized Functions
- Network-Layer Security | IPSec Modes
- Next - Prev Network-Layer Security | IPSec Protocols and Services
- Ping vs Traceroute
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): Benefits and Challenges of Network Virtualization
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) vs. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- Virtual Circuits vs Datagram Networks
- BlueSmack Attack in Wireless Networks
- Bluesnarfing Attack in Wireless Networks
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Warchalking in Wireless Networks
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- Wireless security encryption
- Wireless Security in an Enterprise
- Quantum Networking
- Network Automation
- Difference between MSS and MTU
- What is MTU
- Mesh Networks: A decentralized and Self-Organizing Approach to Networking
- What is Autonomous System
- What is MSS
- Cyber security & Software security
- Information security & Network security.
- Security Engineer & Security Architect
- Protection Methods for Network Security
- Trusted Systems in Network Security
- What are Authentication Tokens in Network security
- Cookies in Network Security
- Intruders in Network Security
- Network Security Toolkit (NST) in virtual box
- Pivoting-Moving Inside a Network
- Security Environment in Computer Networks
- Voice Biometric technique in Network Security
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Testing
- Difference between Kerberos and LDAP
- Cyber security and Information Security
- GraphQL Attacks and Security
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Applications of Remote Sensing
- Seven Layers of IT Security
- What is Ad Hoc TCP
- What is Server Name Indication(SNI)
What is 3D Internet
Technology is improving day by day, and we come up with various new technologies on a daily basis. Internet is also changing rapidly; initially, it started as just a document repository, which has now become a full-fledged resource that provides various services to us.
In our daily life, most of us are highly dependent on the internet to connect with our family & friends, get the work done, and much more. But as it is also changing, what will it look like after 50-100 years? It might give us a completely different way to approach things globally.
The internet we are using is in the form of 2D internet, but it is ready to change to 3D internet. 3D is an entirely new concept in internet technology and is also known as a virtual world. 3D Internet is about to provide 3D experiences that can replicate real life. In this topic, we will discuss in detail 3D Internet as well as how it works, the Applications of 3D Internet, and the Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Internet. So, let's start with the introduction of the 3D Internet.
Introduction of 3D Internet
3D Internet is the successor of 2D internet (existing internet), but it provides a 3D experience or a virtual world that can replicate real life. It provides a powerful new way to reach consumers or business customers by consuming various web services.
The 3D internet is mainly a combination of two factors, which are the Internet and 3D Graphics. It can provide one of the most interactive and engaging services compared to Television. One of the best examples of 3D internet is Second Life, a 3D online virtual world in which different avatars do different kinds of stuff similar to real life.
What is the need for 3D internet?
People often think that when 2D Internet is already there, which is working perfectly, then what is the need for 3D Internet? Most people worldwide are highly dependent on the internet for doing their daily work, from online shopping and communication to bill payments and many more. If we talk about the nature of the current Internet, it is of a 2D type, which means that it is just a virtual environment where people from all over the world share ideas, interact with each other and exchange information. But why restrict it just to 2D pages and hyperlinks when there are lots of things that are turning in 3D, and it can be more attractive and engaging.
In 2D internet, each website is a typical combination of a bunch of documents, 2D pages, images or videos. To navigate the websites or for web surfing, we need a search engine like Google. But we can do it in an alternate and much better way than in real life, which is our 3D world. Similarly, we can make our internet the 3D virtual world, which can replicate the real world and give us much better services and experiences than imagination. Imagine we can put our documents on the desk at home, where documents, desks, and home are "virtual" entities that are 3D representations of real-world counterparts with spatial relationships.
Applications of 3D Internet
Education
3D internet can be used as an excellent platform for Education by Schools, Colleges, and Universities. With 3D internet, students will be able to understand the concepts of some typical subjects easily that need a 3D view of things such as Chemistry, Physics, etc., rather than the traditional ways.
Religion
With the use of 3D internet, different religious organizations can organize virtual meet for different people at a specific location.
Tourism
It is always necessary to have complete information about the location where you want to visit on holidays. So, with 3D internet, tourists can get a complete 3D view of interesting locations and can decide accordingly. It will save the time invested in searching about locations, and people will have a better idea about different locations.
Entertainment
3D internet can also be widely used for entertainment purposes, including 3D Games and Movies. With the 3D internet, people can play different sports, such as Cricket, football, boxing, etc., in the 3D environment.
Embassies
Virtual embassies could be created in 3D internet, which will help the visitors to talk face-to-face with a compute generator ambassador to know about visas, trade, and other Issues.
Arts
3D internet could be employed in Arts. With it, artists will be able to create new forms of art and designs that are not possible in real life due to some physical limitations and high costs. It also enables artists to display their designs to audiences across the world with a real-life look and feel.
Social Interaction
Nowadays, people are much more active on Online social media platforms. With the help of the 3D internet, social media networking can be much more interactive and engaging, such as experiencing video calls.
Real Estate
3D internet can transform and could be much beneficial for the Real Estate market. With it, customers can have a complete 3D view of the property online in which they are interested.
Components of 3D Internet
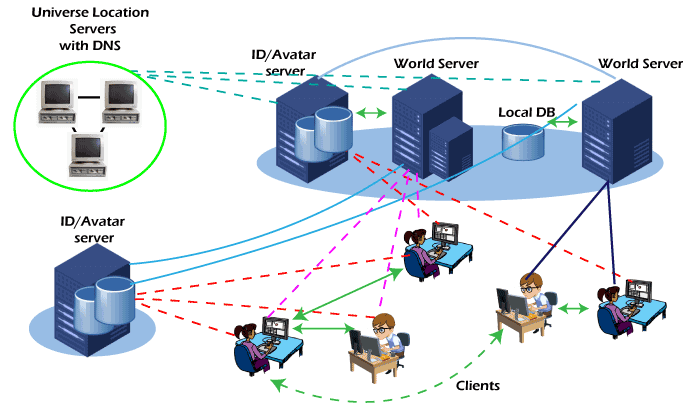
World Servers
World server provides static and dynamic content created by either user or server-side and generates a specific 3D environment or web place that includes visuals, avatar data, media, etc., to client programs. Its main task is to coordinate with the connecting users, initiate communication between them, and ensure in-world consistency in real-time. It also provides different services to users, including email, instant sagging, etc.
Avatar/ID servers
In 3D internet, there is a virtual identity management system that contains identity and avatar information along with an inventory of registered users. The system provides all this information to specific world servers and relevant client programs(owner) with complete privacy and security of contained information. It can also be a part of world servers.
Universe Location Servers:
Virtual location management systems are similar to current DNS, which provide virtual geographical information. Moreover, it also provides a connection to the internet using methods similar to SLurl. They can also work as a distributed directory of the world, avatar servers and users.
Client
Clients are browser-like viewer programs that run on the end-users device containing extensive networking, caching, and 3D rendering capabilities.
Technical Implications of 3D Internet
Speed
If we talk about the internet, then speed is one the main thing that comes out immediately to easily navigate web pages. If internet speed is not sufficient, then users may face various trouble during web surfing. To use 3D internet, speed is the most significant implication. Still, various countries across the world are not in the state of implementation of 3D internet.
Solution: Speed issues of 3D internet would be resolved by implementing high-speed cellular networks such as 3G and 4G (5G in the near future). These cellular networks have higher transmission rates to access the internet at high speed.
Hardware
The main hardware implication for 3D internet is the screen display of the device to display the data. Currently, we are using the 2D display in all devices that can display images and other documents in 2D format only. But with the 3D internet, it would be difficult to display 3D objects on 2D screens. Current computer displays have a max 50-degree field of view which require the user to move the mouse in order to see the complete image, which is completely different from the real world. In the real world, we can use peripheral vision to see things beyond the direct line of sight.
Solutions:
The hardware implication problem of 3D internet can be resolved by using 3D Goggles (for now). In the market, a variety of 3D goggles are available, which can be used to see objects in 3D 2D devices.
Apart from using 3D goggles, with the use of Vision Station, we can solve the hardware implication issue. A vision station is a computer display technology which provides 180 degrees of viewing angles for users.
Advantages of 3D Internet
- With the 3D internet, discussing and sharing ideas is easy and efficient.
- 3D films will not be pirated, which will help the movie industry with good gain.
- Film industries can make better profit with 3D movies.
- Participants have control throughout the virtual space.
- 3D internet will give a better experience while interacting and communicating.
Disadvantages of 3D Internet
- Increased hacking and malware attacks can be seen.
- It may also enhance online scams and fraud.
- Limited ways to enable people in the virtual world.


