Tutorial
Physical Layer
Data Link layer
Network Layer
Routing Algorithm
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Network Security
Misc
- Router
- OSI vs TCP/IP
- TCP vs UDP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP port
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- ARP Packet Format
- ARP Table
- Working of ARP
- FTP Client
- FTP Commands
- FTP Server
- I2C Protocol
- Sliding Window Protocol
- SPI Protocol
- IP
- ARP Commands
- ARP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP and its types
- TCP Retransmission
- CAN protocol
- HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- RIP Protocol
- UDP Protocol
- ICMP Protocol
- MQTT protocol
- OSPF Protocol
- Stop and Wait Protocol
- IMAP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- CIFS
- DAS
- DIMM
- iSCSI
- NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- NFS
- NVMe
- SAN
- Border Gateway Protocol
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- RJ Cable
- Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Service
- CDMA vs. GSM
- What is MAC Address
- Modem vs. Router
- Switch Vs. Router
- USB 2.0 vs 3.0
- Difference between CSMA CA and CSMA CD
- Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
- URI vs URL
- IMAP vs. POP3
- SSH Meaning| SSH Protocol
- UTP vs STP
- Status Code 400
- MIME Protocol
- IP address
- proxy server
- How to set up and use a proxy server
- network security
- WWW is based on which model
- Proxy Server List
- Fundamentals of Computer Networking
- IP Address Format and Table
- Bus topology and Ring topology
- Bus topology and Star topology
- Circuit Switching and Packet switching?
- Difference between star and ring topology
- Difference between Router and Bridge
- TCP Connection Termination
- Image Steganography
- Network Neutrality
- Onion Routing
- Adaptive security appliance (ASA) features
- Relabel-to-front Algorithm
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Access Lists (ACL)
- What is a proxy server and how does it work
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Operating system based Virtualization
- Context based Access Control (CBAC)
- Cristian's Algorithm
- Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)
- Extended Access List
- Li-fi vs. Wi-fi
- Reflexive Access List
- Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
- Wifi protected access (WPA)
- Wifi Protected Setup (WPS)
- Standard Access List
- Time Access List
- What is 3D Internet
- 4G Mobile Communication Technology
- Types of Wireless Transmission Media
- Best Computer Networking Courses
- Data Representation
- Network Criteria
- Classful vs Classless addressing
- Difference between BOOTP and RARP in Computer Networking
- What is AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- External IP Address
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Types of Authentication Protocols
- What is a CISCO Packet Tracer
- BOOTP work
- Subnetting in Computer Networks
- Mesh Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ring Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Star Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Zigbee Technology-The smart home protocol
- Network Layer in OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer in OSI Model
- Internet explorer shortcut keys
- Network Layer Security | SSL Protocols
- Presentation Layer in OSI Model
- Session Layer in OSI Model
- SUBNET MASK
- Transport Layer Security | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and SSL Architecture
- Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Layer
- Protocols in Noiseless and Noisy Channel
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
- Count to Infinity Problem in Distance Vector Routing
- Difference Between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat Protocol
- Difference between Stop and Wait, GoBackN, and Selective Repeat
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): transforming Network Architecture with Virtualized Functions
- Network-Layer Security | IPSec Modes
- Next - Prev Network-Layer Security | IPSec Protocols and Services
- Ping vs Traceroute
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): Benefits and Challenges of Network Virtualization
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) vs. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- Virtual Circuits vs Datagram Networks
- BlueSmack Attack in Wireless Networks
- Bluesnarfing Attack in Wireless Networks
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Warchalking in Wireless Networks
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- Wireless security encryption
- Wireless Security in an Enterprise
- Quantum Networking
- Network Automation
- Difference between MSS and MTU
- What is MTU
- Mesh Networks: A decentralized and Self-Organizing Approach to Networking
- What is Autonomous System
- What is MSS
- Cyber security & Software security
- Information security & Network security.
- Security Engineer & Security Architect
- Protection Methods for Network Security
- Trusted Systems in Network Security
- What are Authentication Tokens in Network security
- Cookies in Network Security
- Intruders in Network Security
- Network Security Toolkit (NST) in virtual box
- Pivoting-Moving Inside a Network
- Security Environment in Computer Networks
- Voice Biometric technique in Network Security
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Testing
- Difference between Kerberos and LDAP
- Cyber security and Information Security
- GraphQL Attacks and Security
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Applications of Remote Sensing
- Seven Layers of IT Security
- What is Ad Hoc TCP
- What is Server Name Indication(SNI)
Session Layer in OSI Model
The session layer is Layer 5 layer from the bottom in the OSI model. The job of the session layer is to control and maintain connections between systems to share data. It establishes, maintains, and ends sessions across all channels. In case of a network error, it checks the authenticity and provides recovery options for active sessions. It manages sessions and synchronizes data flow.
Basically, this layer regulates when computers can send data and how much data they can send. Essentially it coordinates communication between devices.
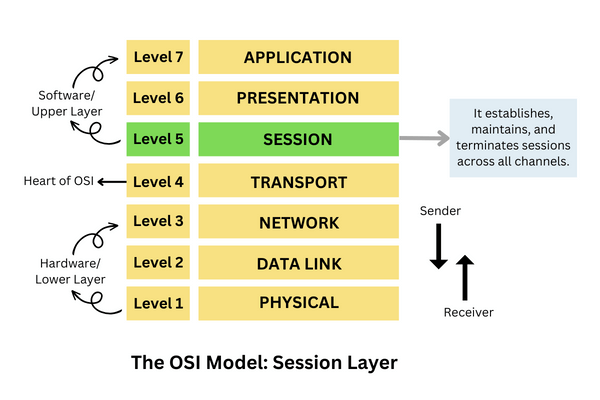
Functions of the Session Layer:
- Session Establishment: The session layer establishes connections between devices which is known as sessions. The session which is created allows users to share data, remote access, and file management. When the session is released, the transport connection is mapped. The ways in which transport connection maps are one-to-many, one-to-one, and many-to-one.
- Data Transfer: It is the very basic function of the session layer, which handles the exchange of data between systems in a full-duplex or half-duplex mode of transmission. The session layer allows only one user to transmit data in half-duplex as well as exchange data in full-duplex mode.
- Dialog Management: The session layer keeps log data on which connections are established to transmit and receive data, which is called dialog management. It is accountable for establishing, synchronizing, preserving, and ending the conversation between the sender and the receiver. It uses a token mechanism in which the user sharing the data is given a token in case of half duplex mode and, after the exchange, transfers it to another device. The token method maintains the efficiency of the connection.
- Synchronization: The session maintains proper connectivity between systems, and if any error occurs, then it provides a recovery option which is called a known state. The session layer adds synchronization bits to the message to use the known state in the event of an error. These bits can be used as checkpoints. It adds synchronization points or checkpoints to the data stream for longer communication. It ensures that the data streams are successfully received and acknowledged up to the checkpoints. In case of any failure, only the stream needs to be retransmitted after the checkpoints.
- Authentication: The process of identification is known as authentication. It takes a guarantee from the user to permit them access to the data. Authentication is very important because it provides security.
- Authorization: It grants privileges after authentication of the user. Authorization means providing access to the data that is authorized to the specific user.
Protocols of the Session Layer:
The session layer offers many network protocols for the safety, security, and efficiency of communication between devices.
Some of these protocols are discussed below:
- RTCP: It is an abbreviation for Real-time Transport Control Protocol. It is used to provide audio and video over the Internet. Basically, it periodically transmits control packets to all participants in the session. It provides feedback on QoS (Quality of Service) to all participants in the session. It is used in video conferencing, television services, etc.
- PPTP: It is the full form of Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol. This is the technology used to implement VPN. With the help of PPTP, data can be transmitted securely from one node to another through a tunnel.
- PAP: It is an abbreviation for Password Authentication Protocol. The point-to-point protocol uses it to authenticate the user. It takes care of whether the user is authentic or not and then grants access. It works in such a way that the user will enter the id and password, then after the authentication, the server will reply with a confirmation. It is a weak type of authentication system as it is highly vulnerable to attackers.
- ADSP: It is an abbreviation for AppleTalk Data Stream Protocol. It is a networking protocol that was introduced 38 years ago, in 1985, and was created for Apple Macintosh networks. It allows users to share printers and folders for access by other network users.
- RPC: It is an abbreviation for Remote Procedure Call Protocol. It helps in communication between processes that are residing in different systems connected over a network. It helps one program to request a service from another program located on another computer on a network. The processes that are communicating do not need to comprehend the details of the network.
- iSNS: It is an abbreviation for Internet Storage Name Service. It manages and configures Fibre Channel and iSCSI devices. This protocol is used by many platforms.
- SDP: It is an abbreviation for Sockets Direct Protocol. It is a standard wire protocol that supports stream sockets on RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access) fabrics.
Conclusion:
- In this article, you have gained knowledge of the session layer in the OSI model. It is the fifth layer of the OSI model. The work of this layer is to open, maintain and end the session for safe and secure communication.
- You have studied the various functions of the session layer in OSI model, such as session establishment, dialog management, data transfer, synchronization, authentication, and authorization.
- You have read some of the protocols used in the session layer like Real-time Transport Control Protocol (RTCP), Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP), AppleTalk Data Stream Protocol (ADSP), Remote Procedure Call Protocol (RPC), Password Authentication Protocol (PAP), Sockets Direct Protocol (SDP), and Internet Storage Name Service (iSNS).


