Tutorial
Physical Layer
Data Link layer
Network Layer
Routing Algorithm
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Network Security
Misc
- Router
- OSI vs TCP/IP
- TCP vs UDP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP port
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- ARP Packet Format
- ARP Table
- Working of ARP
- FTP Client
- FTP Commands
- FTP Server
- I2C Protocol
- Sliding Window Protocol
- SPI Protocol
- IP
- ARP Commands
- ARP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP and its types
- TCP Retransmission
- CAN protocol
- HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- RIP Protocol
- UDP Protocol
- ICMP Protocol
- MQTT protocol
- OSPF Protocol
- Stop and Wait Protocol
- IMAP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- CIFS
- DAS
- DIMM
- iSCSI
- NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- NFS
- NVMe
- SAN
- Border Gateway Protocol
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- RJ Cable
- Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Service
- CDMA vs. GSM
- What is MAC Address
- Modem vs. Router
- Switch Vs. Router
- USB 2.0 vs 3.0
- Difference between CSMA CA and CSMA CD
- Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
- URI vs URL
- IMAP vs. POP3
- SSH Meaning| SSH Protocol
- UTP vs STP
- Status Code 400
- MIME Protocol
- IP address
- proxy server
- How to set up and use a proxy server
- network security
- WWW is based on which model
- Proxy Server List
- Fundamentals of Computer Networking
- IP Address Format and Table
- Bus topology and Ring topology
- Bus topology and Star topology
- Circuit Switching and Packet switching?
- Difference between star and ring topology
- Difference between Router and Bridge
- TCP Connection Termination
- Image Steganography
- Network Neutrality
- Onion Routing
- Adaptive security appliance (ASA) features
- Relabel-to-front Algorithm
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Access Lists (ACL)
- What is a proxy server and how does it work
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Operating system based Virtualization
- Context based Access Control (CBAC)
- Cristian's Algorithm
- Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)
- Extended Access List
- Li-fi vs. Wi-fi
- Reflexive Access List
- Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
- Wifi protected access (WPA)
- Wifi Protected Setup (WPS)
- Standard Access List
- Time Access List
- What is 3D Internet
- 4G Mobile Communication Technology
- Types of Wireless Transmission Media
- Best Computer Networking Courses
- Data Representation
- Network Criteria
- Classful vs Classless addressing
- Difference between BOOTP and RARP in Computer Networking
- What is AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- External IP Address
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Types of Authentication Protocols
- What is a CISCO Packet Tracer
- BOOTP work
- Subnetting in Computer Networks
- Mesh Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ring Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Star Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Zigbee Technology-The smart home protocol
- Network Layer in OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer in OSI Model
- Internet explorer shortcut keys
- Network Layer Security | SSL Protocols
- Presentation Layer in OSI Model
- Session Layer in OSI Model
- SUBNET MASK
- Transport Layer Security | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and SSL Architecture
- Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Layer
- Protocols in Noiseless and Noisy Channel
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
- Count to Infinity Problem in Distance Vector Routing
- Difference Between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat Protocol
- Difference between Stop and Wait, GoBackN, and Selective Repeat
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): transforming Network Architecture with Virtualized Functions
- Network-Layer Security | IPSec Modes
- Next - Prev Network-Layer Security | IPSec Protocols and Services
- Ping vs Traceroute
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): Benefits and Challenges of Network Virtualization
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) vs. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- Virtual Circuits vs Datagram Networks
- BlueSmack Attack in Wireless Networks
- Bluesnarfing Attack in Wireless Networks
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Warchalking in Wireless Networks
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- Wireless security encryption
- Wireless Security in an Enterprise
- Quantum Networking
- Network Automation
- Difference between MSS and MTU
- What is MTU
- Mesh Networks: A decentralized and Self-Organizing Approach to Networking
- What is Autonomous System
- What is MSS
- Cyber security & Software security
- Information security & Network security.
- Security Engineer & Security Architect
- Protection Methods for Network Security
- Trusted Systems in Network Security
- What are Authentication Tokens in Network security
- Cookies in Network Security
- Intruders in Network Security
- Network Security Toolkit (NST) in virtual box
- Pivoting-Moving Inside a Network
- Security Environment in Computer Networks
- Voice Biometric technique in Network Security
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Testing
- Difference between Kerberos and LDAP
- Cyber security and Information Security
- GraphQL Attacks and Security
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Applications of Remote Sensing
- Seven Layers of IT Security
- What is Ad Hoc TCP
- What is Server Name Indication(SNI)
TCP/IP model
- The TCP/IP model was developed prior to the OSI model.
- The TCP/IP model is not exactly similar to the OSI model.
- The TCP/IP model consists of five layers: the application layer, transport layer, network layer, data link layer and physical layer.
- The first four layers provide physical standards, network interface, internetworking, and transport functions that correspond to the first four layers of the OSI model and these four layers are represented in TCP/IP model by a single layer called the application layer.
- TCP/IP is a hierarchical protocol made up of interactive modules, and each of them provides specific functionality.
Here, hierarchical means that each upper-layer protocol is supported by two or more lower-level protocols.
Functions of TCP/IP layers:
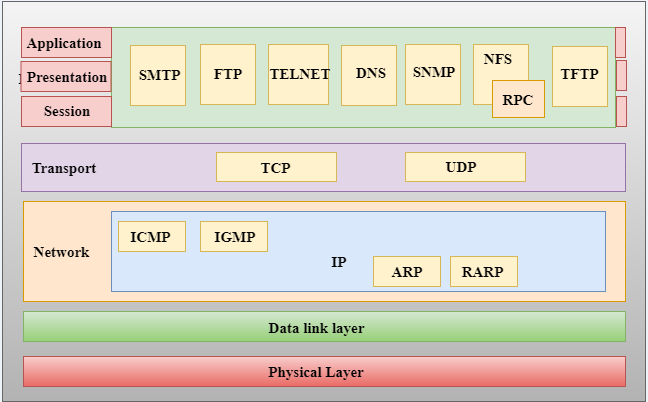
Network Access Layer
- A network layer is the lowest layer of the TCP/IP model.
- A network layer is the combination of the Physical layer and Data Link layer defined in the OSI reference model.
- It defines how the data should be sent physically through the network.
- This layer is mainly responsible for the transmission of the data between two devices on the same network.
- The functions carried out by this layer are encapsulating the IP datagram into frames transmitted by the network and mapping of IP addresses into physical addresses.
- The protocols used by this layer are ethernet, token ring, FDDI, X.25, frame relay.
Internet Layer
- An internet layer is the second layer of the TCP/IP model.
- An internet layer is also known as the network layer.
- The main responsibility of the internet layer is to send the packets from any network, and they arrive at the destination irrespective of the route they take.
Following are the protocols used in this layer are:
IP Protocol: IP protocol is used in this layer, and it is the most significant part of the entire TCP/IP suite.
Following are the responsibilities of this protocol:
- IP Addressing: This protocol implements logical host addresses known as IP addresses. The IP addresses are used by the internet and higher layers to identify the device and to provide internetwork routing.
- Host-to-host communication: It determines the path through which the data is to be transmitted.
- Data Encapsulation and Formatting: An IP protocol accepts the data from the transport layer protocol. An IP protocol ensures that the data is sent and received securely, it encapsulates the data into message known as IP datagram.
- Fragmentation and Reassembly: The limit imposed on the size of the IP datagram by data link layer protocol is known as Maximum Transmission unit (MTU). If the size of IP datagram is greater than the MTU unit, then the IP protocol splits the datagram into smaller units so that they can travel over the local network. Fragmentation can be done by the sender or intermediate router. At the receiver side, all the fragments are reassembled to form an original message.
- Routing: When IP datagram is sent over the same local network such as LAN, MAN, WAN, it is known as direct delivery. When source and destination are on the distant network, then the IP datagram is sent indirectly. This can be accomplished by routing the IP datagram through various devices such as routers.
ARP Protocol
- ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol.
- ARP is a network layer protocol which is used to find the physical address from the IP address.
- The two terms are mainly associated with the ARP Protocol:
- ARP request: When a sender wants to know the physical address of the device, it broadcasts the ARP request to the network.
- ARP reply: Every device attached to the network will accept the ARP request and process the request, but only recipient recognize the IP address and sends back its physical address in the form of ARP reply. The recipient adds the physical address both to its cache memory and to the datagram header
ICMP Protocol
- ICMP stands for Internet Control Message Protocol.
- It is a mechanism used by the hosts or routers to send notifications regarding datagram problems back to the sender.
- A datagram travels from router-to-router until it reaches its destination. If a router is unable to route the data because of some unusual conditions such as disabled links, a device is on fire or network congestion, then the ICMP protocol is used to inform the sender that the datagram is undeliverable.
- An ICMP protocol mainly uses two terms:
- ICMP Test: ICMP Test is used to test whether the destination is reachable or not.
- ICMP Reply: ICMP Reply is used to check whether the destination device is responding or not.
- The core responsibility of the ICMP protocol is to report the problems, not correct them. The responsibility of the correction lies with the sender.
- ICMP can send the messages only to the source, but not to the intermediate routers because the IP datagram carries the addresses of the source and destination but not of the router that it is passed to.
Transport Layer
The transport layer is responsible for the reliability, flow control, and correction of data which is being sent over the network.
The two protocols used in the transport layer are User Datagram protocol and Transmission control protocol.
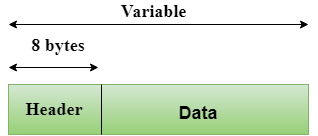
- User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
- It provides connectionless service and end-to-end delivery of transmission.
- It is an unreliable protocol as it discovers the errors but not specify the error.
- User Datagram Protocol discovers the error, and ICMP protocol reports the error to the sender that user datagram has been damaged.
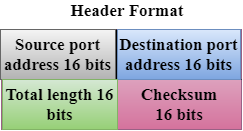
- UDP consists of the following fields:
Source port address: The source port address is the address of the application program that has created the message.
Destination port address: The destination port address is the address of the application program that receives the message.
Total length: It defines the total number of bytes of the user datagram in bytes.
Checksum: The checksum is a 16-bit field used in error detection. - UDP does not specify which packet is lost. UDP contains only checksum; it does not contain any ID of a data segment.
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
- It provides a full transport layer services to applications.
- It creates a virtual circuit between the sender and receiver, and it is active for the duration of the transmission.
- TCP is a reliable protocol as it detects the error and retransmits the damaged frames. Therefore, it ensures all the segments must be received and acknowledged before the transmission is considered to be completed and a virtual circuit is discarded.
- At the sending end, TCP divides the whole message into smaller units known as segment, and each segment contains a sequence number which is required for reordering the frames to form an original message.
- At the receiving end, TCP collects all the segments and reorders them based on sequence numbers.
Application Layer
- An application layer is the topmost layer in the TCP/IP model.
- It is responsible for handling high-level protocols, issues of representation.
- This layer allows the user to interact with the application.
- When one application layer protocol wants to communicate with another application layer, it forwards its data to the transport layer.
- There is an ambiguity occurs in the application layer. Every application cannot be placed inside the application layer except those who interact with the communication system. For example: text editor cannot be considered in application layer while web browser using HTTP protocol to interact with the network where HTTP protocol is an application layer protocol.
Following are the main protocols used in the application layer:
- HTTP: HTTP stands for Hypertext transfer protocol. This protocol allows us to access the data over the world wide web. It transfers the data in the form of plain text, audio, video. It is known as a Hypertext transfer protocol as it has the efficiency to use in a hypertext environment where there are rapid jumps from one document to another.
- SNMP: SNMP stands for Simple Network Management Protocol. It is a framework used for managing the devices on the internet by using the TCP/IP protocol suite.
- SMTP: SMTP stands for Simple mail transfer protocol. The TCP/IP protocol that supports the e-mail is known as a Simple mail transfer protocol. This protocol is used to send the data to another e-mail address.
- DNS: DNS stands for Domain Name System. An IP address is used to identify the connection of a host to the internet uniquely. But, people prefer to use the names instead of addresses. Therefore, the system that maps the name to the address is known as Domain Name System.
- TELNET: It is an abbreviation for Terminal Network. It establishes the connection between the local computer and remote computer in such a way that the local terminal appears to be a terminal at the remote system.
- FTP: FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol. FTP is a standard internet protocol used for transmitting the files from one computer to another computer.


