Tutorial
Physical Layer
Data Link layer
Network Layer
Routing Algorithm
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Network Security
Misc
- Router
- OSI vs TCP/IP
- TCP vs UDP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP port
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- ARP Packet Format
- ARP Table
- Working of ARP
- FTP Client
- FTP Commands
- FTP Server
- I2C Protocol
- Sliding Window Protocol
- SPI Protocol
- IP
- ARP Commands
- ARP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP and its types
- TCP Retransmission
- CAN protocol
- HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- RIP Protocol
- UDP Protocol
- ICMP Protocol
- MQTT protocol
- OSPF Protocol
- Stop and Wait Protocol
- IMAP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- CIFS
- DAS
- DIMM
- iSCSI
- NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- NFS
- NVMe
- SAN
- Border Gateway Protocol
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- RJ Cable
- Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Service
- CDMA vs. GSM
- What is MAC Address
- Modem vs. Router
- Switch Vs. Router
- USB 2.0 vs 3.0
- Difference between CSMA CA and CSMA CD
- Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
- URI vs URL
- IMAP vs. POP3
- SSH Meaning| SSH Protocol
- UTP vs STP
- Status Code 400
- MIME Protocol
- IP address
- proxy server
- How to set up and use a proxy server
- network security
- WWW is based on which model
- Proxy Server List
- Fundamentals of Computer Networking
- IP Address Format and Table
- Bus topology and Ring topology
- Bus topology and Star topology
- Circuit Switching and Packet switching?
- Difference between star and ring topology
- Difference between Router and Bridge
- TCP Connection Termination
- Image Steganography
- Network Neutrality
- Onion Routing
- Adaptive security appliance (ASA) features
- Relabel-to-front Algorithm
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Access Lists (ACL)
- What is a proxy server and how does it work
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Operating system based Virtualization
- Context based Access Control (CBAC)
- Cristian's Algorithm
- Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)
- Extended Access List
- Li-fi vs. Wi-fi
- Reflexive Access List
- Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
- Wifi protected access (WPA)
- Wifi Protected Setup (WPS)
- Standard Access List
- Time Access List
- What is 3D Internet
- 4G Mobile Communication Technology
- Types of Wireless Transmission Media
- Best Computer Networking Courses
- Data Representation
- Network Criteria
- Classful vs Classless addressing
- Difference between BOOTP and RARP in Computer Networking
- What is AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- External IP Address
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Types of Authentication Protocols
- What is a CISCO Packet Tracer
- BOOTP work
- Subnetting in Computer Networks
- Mesh Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ring Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Star Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Zigbee Technology-The smart home protocol
- Network Layer in OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer in OSI Model
- Internet explorer shortcut keys
- Network Layer Security | SSL Protocols
- Presentation Layer in OSI Model
- Session Layer in OSI Model
- SUBNET MASK
- Transport Layer Security | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and SSL Architecture
- Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Layer
- Protocols in Noiseless and Noisy Channel
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
- Count to Infinity Problem in Distance Vector Routing
- Difference Between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat Protocol
- Difference between Stop and Wait, GoBackN, and Selective Repeat
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): transforming Network Architecture with Virtualized Functions
- Network-Layer Security | IPSec Modes
- Next - Prev Network-Layer Security | IPSec Protocols and Services
- Ping vs Traceroute
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): Benefits and Challenges of Network Virtualization
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) vs. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- Virtual Circuits vs Datagram Networks
- BlueSmack Attack in Wireless Networks
- Bluesnarfing Attack in Wireless Networks
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Warchalking in Wireless Networks
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- Wireless security encryption
- Wireless Security in an Enterprise
- Quantum Networking
- Network Automation
- Difference between MSS and MTU
- What is MTU
- Mesh Networks: A decentralized and Self-Organizing Approach to Networking
- What is Autonomous System
- What is MSS
- Cyber security & Software security
- Information security & Network security.
- Security Engineer & Security Architect
- Protection Methods for Network Security
- Trusted Systems in Network Security
- What are Authentication Tokens in Network security
- Cookies in Network Security
- Intruders in Network Security
- Network Security Toolkit (NST) in virtual box
- Pivoting-Moving Inside a Network
- Security Environment in Computer Networks
- Voice Biometric technique in Network Security
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Testing
- Difference between Kerberos and LDAP
- Cyber security and Information Security
- GraphQL Attacks and Security
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Applications of Remote Sensing
- Seven Layers of IT Security
- What is Ad Hoc TCP
- What is Server Name Indication(SNI)
IMAP vs. POP3
POP3 and IMAP are the popular email protocols that are used to access emails from a third-party email client or software. These two are the commonly used Email Protocols on the internet. Both these protocols help to connect to the mail server with the email client through which you have set up your email address. We can select any one of them to set up our email address. Similar to Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), POP3 and IMAP also have specific functions and working principles. Let's discuss the POP3 and IMAP in detail, along with their differences.
What is IMAP?
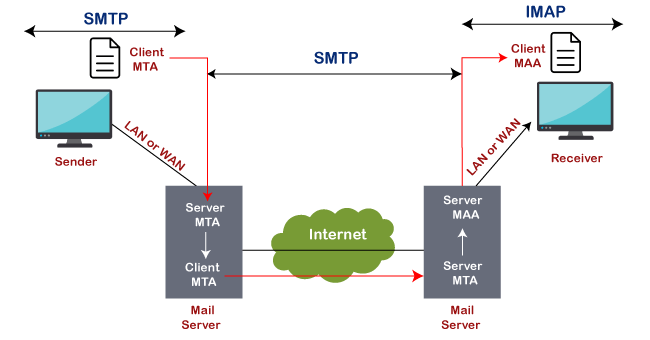
IMAP is abbreviated as Internet Message Access Protocol. IMAP is an internet protocol that works on managing and retrieving emails on the remote server from a local client. It also works as MAA or Message Accessing Agent. Since IMAP deals with the retrieval of messages so we can't send emails using IMAP protocol on the internet. The IMAP protocol is supported by all email clients and web servers.
The working of IMAP is shown in below image:
When to use IMAP?
If you are accessing your email from different devices like mobile, laptop and workstation desktop, etc., then it always better to use the IMAP protocol.
Features of IMAP
There are some features of IMAP, which are as follows:
- Emails are stored on the server instead of an email client.
- Sent messages are also stored on the server-side in the sent folder, which allows us to check the sent email from anywhere.
- You can synchronize the messages and access youremail from multiple devices.
- It is more complex and flexible.
- It helps to download email data from AOL to your device or software.
- We will not lose our emails even if our device is destroyed or stolen.
- The server also saves the status of the emails, such as read, unread, or replied. It helps to check the status of an email from any computer or device.
- When we start downloading emails using IMAP, it firstly shows the header (Sender, date, email subject); at that instant, we can decide whether to download the email or not.
What is POP3?
POP3 is abbreviated as Post Office Protocol, and the number three stands for "version 3," which is the latest version and the most widely used email protocol on the internet. Similar to IMAP protocol, it is another protocol for receiving emails from remote servers. It also acts as a message accessing agent to retrieve the message from the mail server to the receiver's system. It helps to protect emails from spam and viruses on the internet.
POP3 works on two modes: Delete mode and Keep mode.
It works on Delete mode when a user is accessing an email service from a permanent device. In this, once the mails are downloaded or retrieved from the mailbox, mails are deleted from the mailbox permanently.
It operates on Keep mode when the user is not accessing mails from the primary device. In this, it keeps the mails after retrieval also for later retrieval.
When to Use POP3?
Use POP3 for the following cases:
- We should use POP3 if we want to access mails using a single device
- If the number of emails is high.
- If we want to access the mails offline.
Features of POP3
- In POP3, all the emails are downloaded to the local computer, and once all the emails are downloaded, they are deleted from the server.
- Downloaded emails can be accessed offline also.
- Emails are not synchronized between different devices, which means if we set up our email using our mobile phone with POP3, those emails will be downloaded completely on your mobile phone, and cant be accessed from other devices.
Difference table between IMAP and POP3
| Feature | IMAP | POP3 |
|---|---|---|
| Stands for | IMAP stands for Internet Message Access Protocol. | It stands for Post Office Protocol3. |
| Used for | IMAP is an advanced protocol that allows a user to check all the folders on the mail server and is used to retrieve the mails. | POP is a simple protocol compared to IMAP and used only for downloading the messages from our inbox to the local computer. |
| Port number | It listens on port number 143, and IMAPDS(IMAP with SSL) Listens on port 993. | It listens on port number 110, and POP3DS(POP3 with SSL) listens on port 995. |
| Accessibility | Using IMAP, the messages can be accessed using different devices. | Using POP3, mail can only be accessed using a single device at a time. |
| Readability | We can partially read the message before finishing the download. | We can only read the message once it is downloaded. |
| Change | In IMAP, a mail can be updated using email software or a web interface. | In POP3, mail can be updated using the local email software. |
| Update | IMAP allows the user to create, delete, or update the mailboxes on the mail server and also allows to create a hierarchy of mailboxes in the folder. | POP3 does not allow the user to create, delete, or update the mailboxes on the mail server. |
| Mail organization | It allows the user to organize the mails on the server. | It does not allow to organize the mails on the server. |
| Download | In IMAP, the message header is previewed before downloading a message. | Using POP3, all the messages can be downloaded at once. |
| Email storage | Emails are stored on a single device once they are downloaded and removed from the server. | Emails are stored on the server and synced & can be accessed using multiple devices. |
Conclusion
As per the above discussion, we can conclude that IMAP is more powerful, and it is best to use it if we want to access our emails using multiple devices, for example, using smartphones and computers. On the other hand, POP3 is suitable if we access mails using one device only, with a large number of emails, and want to access those emails offline.


