Tutorial
Physical Layer
Data Link layer
Network Layer
Routing Algorithm
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Network Security
Misc
- Router
- OSI vs TCP/IP
- TCP vs UDP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP port
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- ARP Packet Format
- ARP Table
- Working of ARP
- FTP Client
- FTP Commands
- FTP Server
- I2C Protocol
- Sliding Window Protocol
- SPI Protocol
- IP
- ARP Commands
- ARP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP and its types
- TCP Retransmission
- CAN protocol
- HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- RIP Protocol
- UDP Protocol
- ICMP Protocol
- MQTT protocol
- OSPF Protocol
- Stop and Wait Protocol
- IMAP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- CIFS
- DAS
- DIMM
- iSCSI
- NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- NFS
- NVMe
- SAN
- Border Gateway Protocol
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- RJ Cable
- Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Service
- CDMA vs. GSM
- What is MAC Address
- Modem vs. Router
- Switch Vs. Router
- USB 2.0 vs 3.0
- Difference between CSMA CA and CSMA CD
- Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
- URI vs URL
- IMAP vs. POP3
- SSH Meaning| SSH Protocol
- UTP vs STP
- Status Code 400
- MIME Protocol
- IP address
- proxy server
- How to set up and use a proxy server
- network security
- WWW is based on which model
- Proxy Server List
- Fundamentals of Computer Networking
- IP Address Format and Table
- Bus topology and Ring topology
- Bus topology and Star topology
- Circuit Switching and Packet switching?
- Difference between star and ring topology
- Difference between Router and Bridge
- TCP Connection Termination
- Image Steganography
- Network Neutrality
- Onion Routing
- Adaptive security appliance (ASA) features
- Relabel-to-front Algorithm
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Access Lists (ACL)
- What is a proxy server and how does it work
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Operating system based Virtualization
- Context based Access Control (CBAC)
- Cristian's Algorithm
- Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)
- Extended Access List
- Li-fi vs. Wi-fi
- Reflexive Access List
- Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
- Wifi protected access (WPA)
- Wifi Protected Setup (WPS)
- Standard Access List
- Time Access List
- What is 3D Internet
- 4G Mobile Communication Technology
- Types of Wireless Transmission Media
- Best Computer Networking Courses
- Data Representation
- Network Criteria
- Classful vs Classless addressing
- Difference between BOOTP and RARP in Computer Networking
- What is AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- External IP Address
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Types of Authentication Protocols
- What is a CISCO Packet Tracer
- BOOTP work
- Subnetting in Computer Networks
- Mesh Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ring Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Star Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Zigbee Technology-The smart home protocol
- Network Layer in OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer in OSI Model
- Internet explorer shortcut keys
- Network Layer Security | SSL Protocols
- Presentation Layer in OSI Model
- Session Layer in OSI Model
- SUBNET MASK
- Transport Layer Security | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and SSL Architecture
- Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Layer
- Protocols in Noiseless and Noisy Channel
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
- Count to Infinity Problem in Distance Vector Routing
- Difference Between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat Protocol
- Difference between Stop and Wait, GoBackN, and Selective Repeat
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): transforming Network Architecture with Virtualized Functions
- Network-Layer Security | IPSec Modes
- Next - Prev Network-Layer Security | IPSec Protocols and Services
- Ping vs Traceroute
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): Benefits and Challenges of Network Virtualization
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) vs. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- Virtual Circuits vs Datagram Networks
- BlueSmack Attack in Wireless Networks
- Bluesnarfing Attack in Wireless Networks
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Warchalking in Wireless Networks
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- Wireless security encryption
- Wireless Security in an Enterprise
- Quantum Networking
- Network Automation
- Difference between MSS and MTU
- What is MTU
- Mesh Networks: A decentralized and Self-Organizing Approach to Networking
- What is Autonomous System
- What is MSS
- Cyber security & Software security
- Information security & Network security.
- Security Engineer & Security Architect
- Protection Methods for Network Security
- Trusted Systems in Network Security
- What are Authentication Tokens in Network security
- Cookies in Network Security
- Intruders in Network Security
- Network Security Toolkit (NST) in virtual box
- Pivoting-Moving Inside a Network
- Security Environment in Computer Networks
- Voice Biometric technique in Network Security
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Testing
- Difference between Kerberos and LDAP
- Cyber security and Information Security
- GraphQL Attacks and Security
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Applications of Remote Sensing
- Seven Layers of IT Security
- What is Ad Hoc TCP
- What is Server Name Indication(SNI)
OSI Model
- OSI stands for Open System Interconnection is a reference model that describes how information from a software application in one computer moves through a physical medium to the software application in another computer.
- OSI consists of seven layers, and each layer performs a particular network function.
- OSI model was developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 1984, and it is now considered as an architectural model for the inter-computer communications.
- OSI model divides the whole task into seven smaller and manageable tasks. Each layer is assigned a particular task.
- Each layer is self-contained, so that task assigned to each layer can be performed independently.
Characteristics of OSI Model:
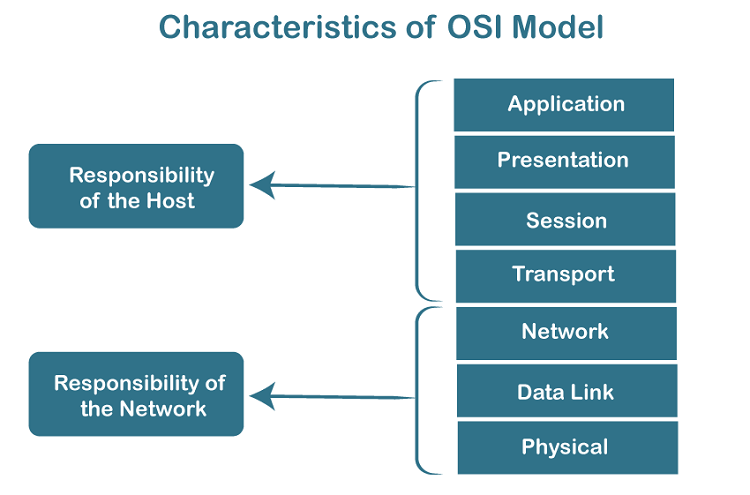
- The OSI model is divided into two layers: upper layers and lower layers.
- The upper layer of the OSI model mainly deals with the application related issues, and they are implemented only in the software. The application layer is closest to the end user. Both the end user and the application layer interact with the software applications. An upper layer refers to the layer just above another layer.
- The lower layer of the OSI model deals with the data transport issues. The data link layer and the physical layer are implemented in hardware and software. The physical layer is the lowest layer of the OSI model and is closest to the physical medium. The physical layer is mainly responsible for placing the information on the physical medium.
7 Layers of OSI Model
There are the seven OSI layers. Each layer has different functions. A list of seven layers are given below:
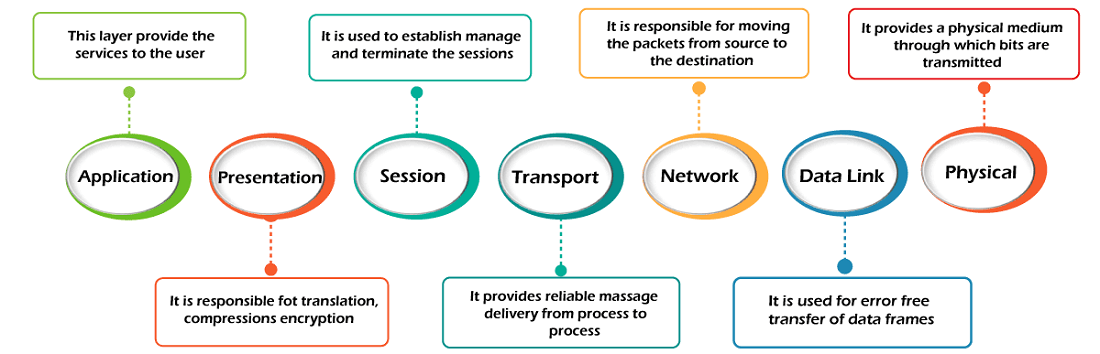
- Physical Layer
- Data-Link Layer
- Network Layer
- Transport Layer
- Session Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Application Layer
1) Physical layer
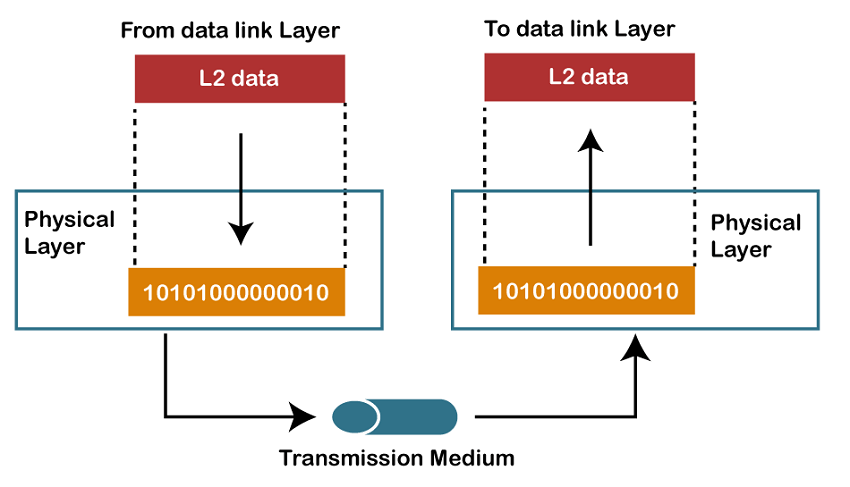
- The main functionality of the physical layer is to transmit the individual bits from one node to another node.
- It is the lowest layer of the OSI model.
- It establishes, maintains and deactivates the physical connection.
- It specifies the mechanical, electrical and procedural network interface specifications.
Functions of a Physical layer:
- Line Configuration: It defines the way how two or more devices can be connected physically.
- Data Transmission: It defines the transmission mode whether it is simplex, half-duplex or full-duplex mode between the two devices on the network.
- Topology: It defines the way how network devices are arranged.
- Signals: It determines the type of the signal used for transmitting the information.
2) Data-Link Layer
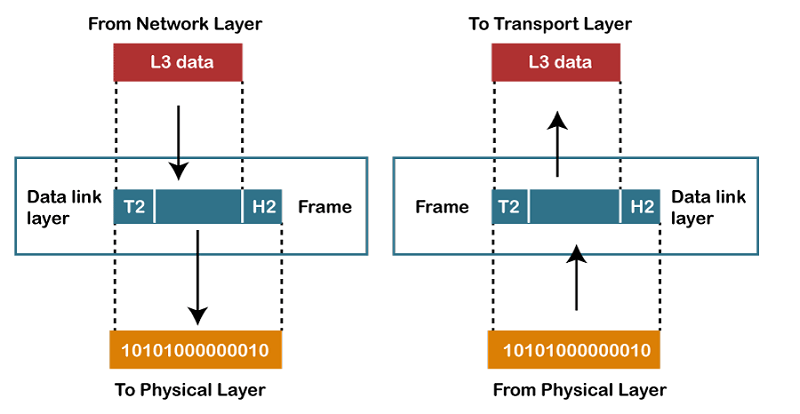
- This layer is responsible for the error-free transfer of data frames.
- It defines the format of the data on the network.
- It provides a reliable and efficient communication between two or more devices.
- It is mainly responsible for the unique identification of each device that resides on a local network.
- It contains two sub-layers:
- Logical Link Control Layer
- It is responsible for transferring the packets to the Network layer of the receiver that is receiving.
- It identifies the address of the network layer protocol from the header.
- It also provides flow control.
- Media Access Control Layer
- A Media access control layer is a link between the Logical Link Control layer and the network's physical layer.
- It is used for transferring the packets over the network.
- Logical Link Control Layer
Functions of the Data-link layer
- Framing: The data link layer translates the physical's raw bit stream into packets known as Frames. The Data link layer adds the header and trailer to the frame. The header which is added to the frame contains the hardware destination and source address.

- Physical Addressing: The Data link layer adds a header to the frame that contains a destination address. The frame is transmitted to the destination address mentioned in the header.
- Flow Control: Flow control is the main functionality of the Data-link layer. It is the technique through which the constant data rate is maintained on both the sides so that no data get corrupted. It ensures that the transmitting station such as a server with higher processing speed does not exceed the receiving station, with lower processing speed.
- Error Control: Error control is achieved by adding a calculated value CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) that is placed to the Data link layer's trailer which is added to the message frame before it is sent to the physical layer. If any error seems to occurr, then the receiver sends the acknowledgment for the retransmission of the corrupted frames.
- Access Control: When two or more devices are connected to the same communication channel, then the data link layer protocols are used to determine which device has control over the link at a given time.
3) Network Layer
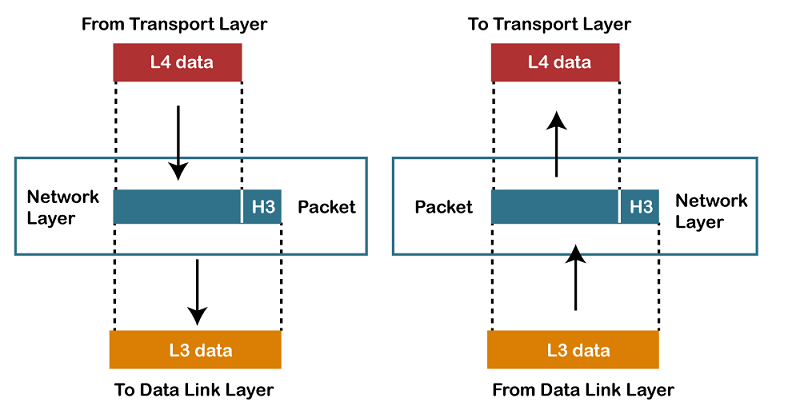
- It is a layer 3 that manages device addressing, tracks the location of devices on the network.
- It determines the best path to move data from source to the destination based on the network conditions, the priority of service, and other factors.
- The Data link layer is responsible for routing and forwarding the packets.
- Routers are the layer 3 devices, they are specified in this layer and used to provide the routing services within an internetwork.
- The protocols used to route the network traffic are known as Network layer protocols. Examples of protocols are IP and Ipv6.
Functions of Network Layer:
- Internetworking: An internetworking is the main responsibility of the network layer. It provides a logical connection between different devices.
- Addressing: A Network layer adds the source and destination address to the header of the frame. Addressing is used to identify the device on the internet.
- Routing: Routing is the major component of the network layer, and it determines the best optimal path out of the multiple paths from source to the destination.
- Packetizing: A Network Layer receives the packets from the upper layer and converts them into packets. This process is known as Packetizing. It is achieved by internet protocol (IP).
4) Transport Layer
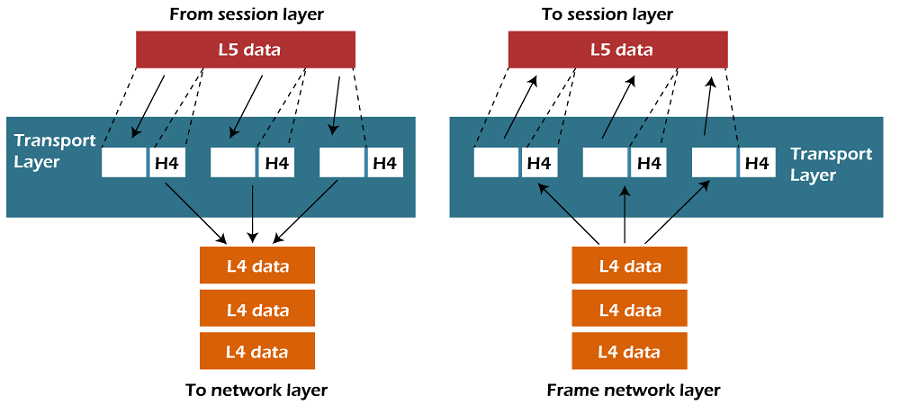
- The Transport layer is a Layer 4 ensures that messages are transmitted in the order in which they are sent and there is no duplication of data.
- The main responsibility of the transport layer is to transfer the data completely.
- It receives the data from the upper layer and converts them into smaller units known as segments.
- This layer can be termed as an end-to-end layer as it provides a point-to-point connection between source and destination to deliver the data reliably.
The two protocols used in this layer are:
- Transmission Control Protocol
- It is a standard protocol that allows the systems to communicate over the internet.
- It establishes and maintains a connection between hosts.
- When data is sent over the TCP connection, then the TCP protocol divides the data into smaller units known as segments. Each segment travels over the internet using multiple routes, and they arrive in different orders at the destination. The transmission control protocol reorders the packets in the correct order at the receiving end.
- User Datagram Protocol
- User Datagram Protocol is a transport layer protocol.
- It is an unreliable transport protocol as in this case receiver does not send any acknowledgment when the packet is received, the sender does not wait for any acknowledgment. Therefore, this makes a protocol unreliable.
Functions of Transport Layer:
- Service-point addressing: Computers run several programs simultaneously due to this reason, the transmission of data from source to the destination not only from one computer to another computer but also from one process to another process. The transport layer adds the header that contains the address known as a service-point address or port address. The responsibility of the network layer is to transmit the data from one computer to another computer and the responsibility of the transport layer is to transmit the message to the correct process.
- Segmentation and reassembly: When the transport layer receives the message from the upper layer, it divides the message into multiple segments, and each segment is assigned with a sequence number that uniquely identifies each segment. When the message has arrived at the destination, then the transport layer reassembles the message based on their sequence numbers.
- Connection control: Transport layer provides two services Connection-oriented service and connectionless service. A connectionless service treats each segment as an individual packet, and they all travel in different routes to reach the destination. A connection-oriented service makes a connection with the transport layer at the destination machine before delivering the packets. In connection-oriented service, all the packets travel in the single route.
- Flow control: The transport layer also responsible for flow control but it is performed end-to-end rather than across a single link.
- Error control: The transport layer is also responsible for Error control. Error control is performed end-to-end rather than across the single link. The sender transport layer ensures that message reach at the destination without any error.
5) Session Layer
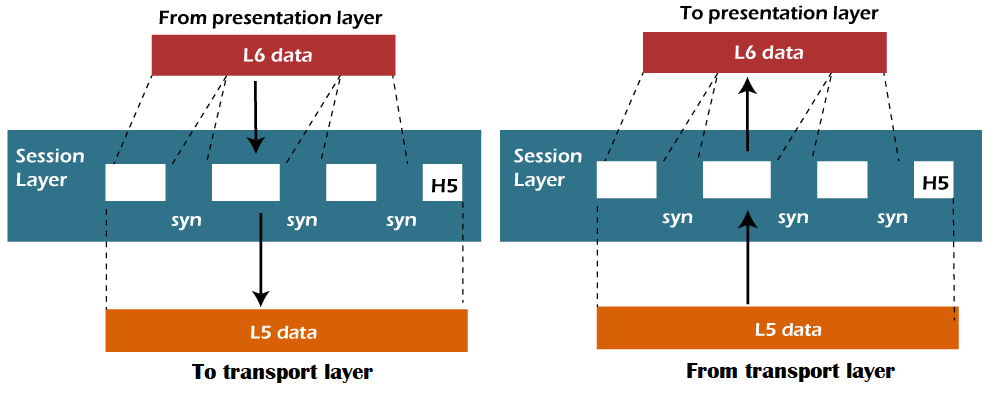
- It is a layer 3 in the OSI model.
- The Session layer is used to establish, maintain and synchronizes the interaction between communicating devices.
Functions of Session layer:
- Dialog control: Session layer acts as a dialog controller that creates a dialog between two processes or we can say that it allows the communication between two processes which can be either half-duplex or full-duplex.
- Synchronization: Session layer adds some checkpoints when transmitting the data in a sequence. If some error occurs in the middle of the transmission of data, then the transmission will take place again from the checkpoint. This process is known as Synchronization and recovery.
6) Presentation Layer
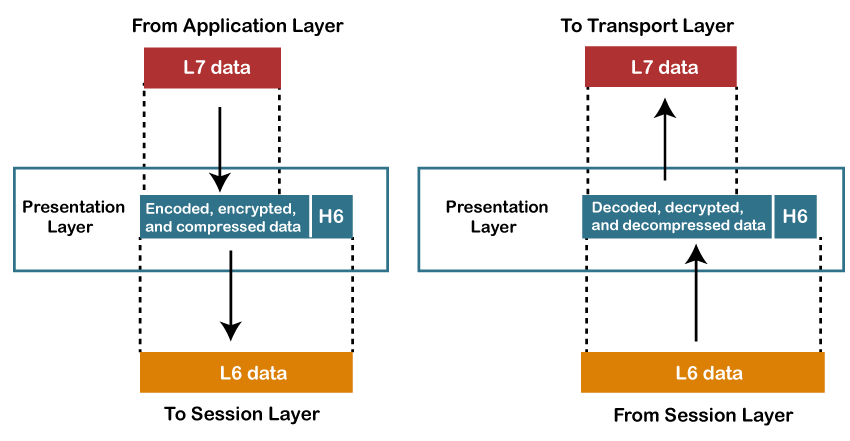
- A Presentation layer is mainly concerned with the syntax and semantics of the information exchanged between the two systems.
- It acts as a data translator for a network.
- This layer is a part of the operating system that converts the data from one presentation format to another format.
- The Presentation layer is also known as the syntax layer.
Functions of Presentation layer:
- Translation: The processes in two systems exchange the information in the form of character strings, numbers and so on. Different computers use different encoding methods, the presentation layer handles the interoperability between the different encoding methods. It converts the data from sender-dependent format into a common format and changes the common format into receiver-dependent format at the receiving end.
- Encryption: Encryption is needed to maintain privacy. Encryption is a process of converting the sender-transmitted information into another form and sends the resulting message over the network.
- Compression: Data compression is a process of compressing the data, i.e., it reduces the number of bits to be transmitted. Data compression is very important in multimedia such as text, audio, video.
7) Application Layer
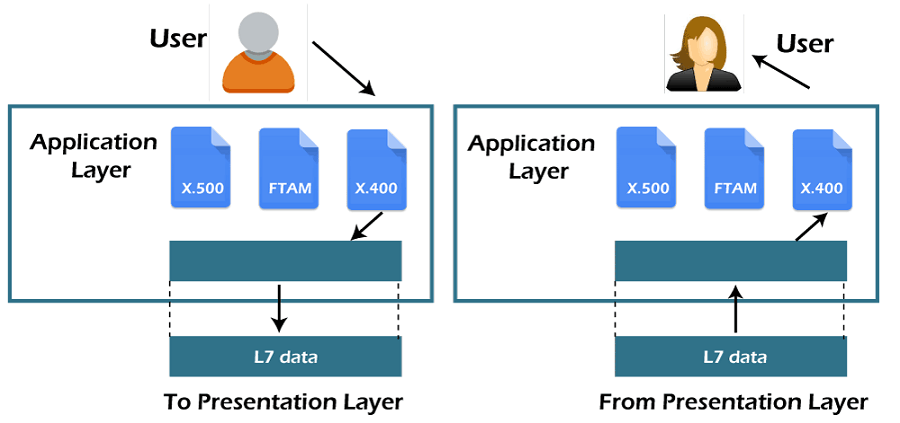
- An application layer serves as a window for users and application processes to access network service.
- It handles issues such as network transparency, resource allocation, etc.
- An application layer is not an application, but it performs the application layer functions.
- This layer provides the network services to the end-users.
Functions of Application layer:
- File transfer, access, and management (FTAM): An application layer allows a user to access the files in a remote computer, to retrieve the files from a computer and to manage the files in a remote computer.
- Mail services: An application layer provides the facility for email forwarding and storage.
- Directory services: An application provides the distributed database sources and is used to provide that global information about various objects.


