Tutorial
Physical Layer
Data Link layer
Network Layer
Routing Algorithm
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Network Security
Misc
- Router
- OSI vs TCP/IP
- TCP vs UDP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP port
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- ARP Packet Format
- ARP Table
- Working of ARP
- FTP Client
- FTP Commands
- FTP Server
- I2C Protocol
- Sliding Window Protocol
- SPI Protocol
- IP
- ARP Commands
- ARP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP and its types
- TCP Retransmission
- CAN protocol
- HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- RIP Protocol
- UDP Protocol
- ICMP Protocol
- MQTT protocol
- OSPF Protocol
- Stop and Wait Protocol
- IMAP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- CIFS
- DAS
- DIMM
- iSCSI
- NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- NFS
- NVMe
- SAN
- Border Gateway Protocol
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- RJ Cable
- Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Service
- CDMA vs. GSM
- What is MAC Address
- Modem vs. Router
- Switch Vs. Router
- USB 2.0 vs 3.0
- Difference between CSMA CA and CSMA CD
- Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
- URI vs URL
- IMAP vs. POP3
- SSH Meaning| SSH Protocol
- UTP vs STP
- Status Code 400
- MIME Protocol
- IP address
- proxy server
- How to set up and use a proxy server
- network security
- WWW is based on which model
- Proxy Server List
- Fundamentals of Computer Networking
- IP Address Format and Table
- Bus topology and Ring topology
- Bus topology and Star topology
- Circuit Switching and Packet switching?
- Difference between star and ring topology
- Difference between Router and Bridge
- TCP Connection Termination
- Image Steganography
- Network Neutrality
- Onion Routing
- Adaptive security appliance (ASA) features
- Relabel-to-front Algorithm
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Access Lists (ACL)
- What is a proxy server and how does it work
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Operating system based Virtualization
- Context based Access Control (CBAC)
- Cristian's Algorithm
- Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)
- Extended Access List
- Li-fi vs. Wi-fi
- Reflexive Access List
- Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
- Wifi protected access (WPA)
- Wifi Protected Setup (WPS)
- Standard Access List
- Time Access List
- What is 3D Internet
- 4G Mobile Communication Technology
- Types of Wireless Transmission Media
- Best Computer Networking Courses
- Data Representation
- Network Criteria
- Classful vs Classless addressing
- Difference between BOOTP and RARP in Computer Networking
- What is AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- External IP Address
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Types of Authentication Protocols
- What is a CISCO Packet Tracer
- BOOTP work
- Subnetting in Computer Networks
- Mesh Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ring Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Star Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Zigbee Technology-The smart home protocol
- Network Layer in OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer in OSI Model
- Internet explorer shortcut keys
- Network Layer Security | SSL Protocols
- Presentation Layer in OSI Model
- Session Layer in OSI Model
- SUBNET MASK
- Transport Layer Security | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and SSL Architecture
- Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Layer
- Protocols in Noiseless and Noisy Channel
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
- Count to Infinity Problem in Distance Vector Routing
- Difference Between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat Protocol
- Difference between Stop and Wait, GoBackN, and Selective Repeat
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): transforming Network Architecture with Virtualized Functions
- Network-Layer Security | IPSec Modes
- Next - Prev Network-Layer Security | IPSec Protocols and Services
- Ping vs Traceroute
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): Benefits and Challenges of Network Virtualization
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) vs. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- Virtual Circuits vs Datagram Networks
- BlueSmack Attack in Wireless Networks
- Bluesnarfing Attack in Wireless Networks
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Warchalking in Wireless Networks
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- Wireless security encryption
- Wireless Security in an Enterprise
- Quantum Networking
- Network Automation
- Difference between MSS and MTU
- What is MTU
- Mesh Networks: A decentralized and Self-Organizing Approach to Networking
- What is Autonomous System
- What is MSS
- Cyber security & Software security
- Information security & Network security.
- Security Engineer & Security Architect
- Protection Methods for Network Security
- Trusted Systems in Network Security
- What are Authentication Tokens in Network security
- Cookies in Network Security
- Intruders in Network Security
- Network Security Toolkit (NST) in virtual box
- Pivoting-Moving Inside a Network
- Security Environment in Computer Networks
- Voice Biometric technique in Network Security
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Testing
- Difference between Kerberos and LDAP
- Cyber security and Information Security
- GraphQL Attacks and Security
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Applications of Remote Sensing
- Seven Layers of IT Security
- What is Ad Hoc TCP
- What is Server Name Indication(SNI)
Modem vs. Router
A modem is a box-type device that connects your home/office network directly to the internet. The router is also a box-type device that enables multiple computer systems (either wired or wireless) to simultaneously use the internet. Nowadays, both the devices are integrated and usually provided by the ISP(Internet Service Provider) when we take the new internet plan. But to get the internet connection for our home/office network, we need both modem and router either integrated or individual. Although most of the time people get confused to identify both the devices, both devices have two different roles on a network that we will know on this topic. In this topic, we will understand the difference between the modem and router, but before understanding the main differences, we will first understand what Modem and Router are, their features, how they work, and what feature makes them different.
What is a Modem?
- A modem is a device that modulates or demodulates the signal. It maintains a dedicated connection with the ISP to get the internet connection for home or business.

- It acts as a bridge between the internet/telephone line and the computer.
- The reason to use the modem for an internet connection is that both the internet and the computer take two different signals. It means that the internet sends the analog signal, but the computer system can only understand the digital signal. So, we need a device that can convert an analog signal to a digital signal and vice versa. To do this, we need a modem.
- It modulates the incoming analog signal from the internet to digital signal and directs it to the computer, and vice versa.
- Usually, we get the modem from the ISP only when we take a new internet plan.
- It also performs data compression, error correction and controls the flow of information. It speed-up the process of transmission of data by grouping the data and send it in one go.
How does modem work?
As you must have understood till now that modem is responsible for modulating and demodulating the signal. The working principle of the modem is based on the same process.
The modem is placed between the telephone line and the computer system or router. It connects the devices with the ethernet port given in it. It connects the ISP(internet service provider) to the home network directly for the single PC. Or it is connected with the router to connect with multiple devices.
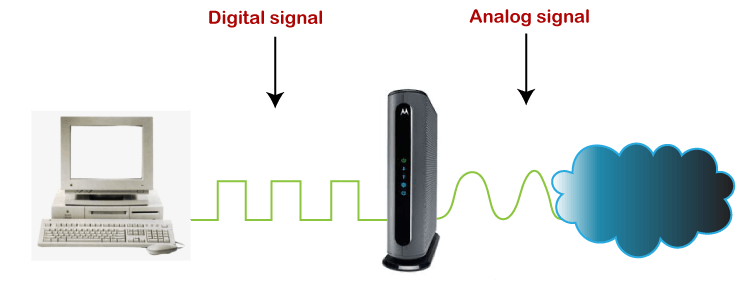
The below diagram is converting the incoming analog signal coming from telephone-lines/optical fiber to a digital signal and sending it to the PC. Without a modem, we cannot connect to the internet.
Types of Modem
The modem can be of various types based on data transmission and how it is installed. These types are given below:
1. External Modem:
- The external modem is connected outside the computer system using a serial cable.
- The installation is very easy, and it also provides a high data transmission rate.
- It is expensive but still used due to its high-speed data transmission in offices, mostly to avoid interruption in network connectivity.
2. Internal Modem:
- As its name suggests, the internal modem is installed over a PC's motherboard, termed as the internal modem.
- It looks similar to an electronic circuit and mounted into an expansion slot of the motherboard.
- The installation is complex, and its data transmission speed is also slow; hence it is used for the dedicated computer in homes/ or small spaces.
3. Wireless Modem
- Wireless modems are connected to the computer systems without any cable, and most people use these modems for their personal use.
- These modems use radio frequencies to transmit the data through the air and also provides good transmission speed.
4. Dial-up Modem
- Dial-up modem establishes the internet connection by connecting the ISP to the computer using the conventional telephone line.
- It uses a PSTN facility (Public Switched telephone network) and provides a transmission speed of 56kb/sec.
5. Cable Modem
- The cable modem is known as the broadband device as it allows the computer to communicate with ISP over a landline connection.
- It is connected with the landline connection using the coaxial cable and with the computer using the ethernet.
6. DSL Modem
- DSL stands for Digital Subscriber line that allows the transmission of data over the normal telephone line.
- It provides a high data transmission speed, hence widely used in offices/homes.
- It can be used to connect to a computer or router to provide the internet connection through the ethernet port or USB port.
- The DSL modems are of two types:
- ADSL Modem
- SDSL Modem
7. Satellite Modem
- Satellite modems are expensive modems and do not require any telephone connection for the internet.
- It uses satellite technology to send or receive the data.
- The speed of the modem is comparatively slower than DSL or cable Modem.
8. Half-duplex Modem
- As the name suggests, it allows transmitting the data in one direction only at a time.
- It means if it is receiving the signal from one end, at that time, it will stop receiving the signal at another end. Once the transmission of one end is completed, then only the other end can transmit the data.
9. Full Duplex Modem
- The full-duplex modems can transmit the data from both ends at the same time.
- It means it can receive the data from one end and the other end simultaneously without any interruption.
10. Four-wire Modem
- It splits the pair of wires for incoming and outgoing data carriers.
- With this split, it can transmit the same frequency on both ends.
11. Two-wire Modem
- It uses a pair of wires hence called two-wire modems. Only these two wires are used for incoming and outgoing carriers.
Functions of Modem
There are mainly two functions that a modem performs, which are given below:
- Modulate and demodulate the electrical signal from analog to digital and digital to analog.
- Provide a secure connection to protect against line overload and other connection problems.
Advantages of Modems
- The modem enables us to use the internet connection to connect with the entire world.
- Speed is dependent on the cost of the modem.
What is a Router?
As its name suggests, the router is a networking device responsible for routing the data packets from source to destination over a network. It distributes or routes the internet connection from the modem to all the networking devices, either wired or wireless, such as PC, Laptop, Mobile phone, tablet, etc. It also enables multiple devices to communicate with each other over the same network.
In the early days, there were only single computer systems in homes. Nowadays, multiple devices need the internet to work on, so to provide internet connectivity to all the available devices within the home/office, we need routers.

The routers are mainly two types; Wired and Wireless.
In a wired router, we need an ethernet cable to connect with it for the internet connection. Whereas, in a wireless router, we don't need any cable, and with the help of Wi-fi technology, we can connect our networking devices with it.
It also provides us the security features and makes our devices secure over the given network form any threat.
How does a router work?
- A router first connects the modem to other devices to allow communication between these devices and the internet.
- Router routes/transmit the data packets with the defined IP address from one network to another or within a network. It does it by providing a local IP address to each device over the internet; it ensures the right destination so that data reach the right place rather than lost within the network.
- It finds out the best and fastest path and then sends data packets from that path to the network's devices.
- It works similar to the delivery package that has a defined address so that it can reach the right recipient only.

The function of a Router
- The main function of a router is to keep the network up & to run smoothly.
- To do this, they connect computers and other networking devices such as Mobile, tablets, printers, etc., to communicate with each other.
Types of Router
There are different types of the router; some popular types are given below:
1. Wireless Router
- Wireless routers are the most commonly used routers in offices and homes as they don't need any wire or cable to connect with networking devices.
- It provides a secure connection, and only authenticated users can access the network using the id & password.
- It can be accessed by the n number of users within the specified range.
2. Wired Router/Broadband Router
- As its name suggests, it requires a wire or cable to connect to the network devices.
- Such routers are used mostly in schools or small offices to connect the PCs with the Ethernet cable.
- It also has a Wi-fi access point, and a mobile phone can be connected to it using the VOIP (Voice-over-Internet Protocol) technology.
- It is connected to the ADSL modems to take the transmission data from the modem and distribute it to a further network.
3. Edge Router
- Edge router can be either Wired/Wireless types that transmit the data packet between two or more networks, not within a network.
- These routers are placed at the edge of networks, hence called Edge router, and connect with ISP or another network in an organization.
- The main task of the edge router is to maintain smooth communication between the networks.
4. Core Router
- The core routers are also wired/wireless routers, which distribute the data packets within a network, not between two networks.
- These are designed to become the backbone of a network and allow the heavy transfer of data.
5. Virtual Router
- This software allows the computers and servers to operate like routers and share data packets similar to the physical ones.
- These are more flexible than the physical, as they can be scaled up as per the business requirement.
Advantages of Router
- The wireless routers are mostly used that enable most of the networking devices to connect easily at any time, without the worry of a bunch of wires.
- It can connect with the different architecture of networks such as Ethernet cable, Wi-fi, or WLAN.
- It provides highly secures network access with password protection.
- It reduces the network traffic with the help of the collision feature.
- It provides data packets to the correct destination with the best route using the routing table and intelligence.
Difference chart between Modem and Router
| Parameters | Modem | Router |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A modem is a device that modulates and demodulates the electrical signal and maintains a dedicated connection between the internet and home/office network. | The router is a networking device that enables multiple devices to connect to wired or wireless networks. |
| Operating Layer of OSI model. | It works on the data link layer of the OSI model. | It works on the physical, data-link, and network layers of the OSI model. |
| How does it work? | It acts like a signal modulate and demodulator, which means it modulates the electrical signal to a digital signal and sends it to a PC or computer, demodulates the signal from digital to analog, and sends it to the internet. | It routes the data packets from one source to a defined destination by following the routing table. It enables multiple network devices to connect over the given network. |
| Security | The modem transmits the data without any authentication; hence it is not secure. | The router provides complete security with passwords and checks each data packet before transmitting it over a given network. |
| Cable Used | RJ45 to connect with router, and RJ11 to connect with a telephone line. | RJ45 cable is used. |
| Placed | A modem is placed between the telephone line and computer or router. | A router is placed between the modem and other networking devices. |
| Internet Access | It is essential to have a modem to access the internet as it connects the ISP to our PC. | We can access the internet without using a router. |
| Main Purpose | It takes the requested information from the internet to the computer. | It distributes the information from the modem to the given network. |
| Number of connected devices | It can directly be connected to only one device that can be either a PC or a router. | Routers can connect to multiple network devices using ethernet cable or Wi-Fi. |
| Ports | Two ports are used to connect the telephone line/ISP and one for the router. | The number of Ports varies, and at minimum, it can have 2 to 4 ports. |
Conclusion
After discussing a lot about the modems and routers, we can conclude that to have an internet connection in the office/home, we need a modem, but it will be just for a single networking device. So, to distribute this data to other networking devices, we need routers. Nowadays, both devices come together in integrated form, it means modem and router in a single device, so we don't need two different devices.


