Tutorial
Physical Layer
Data Link layer
Network Layer
Routing Algorithm
Transport Layer
Application Layer
Network Security
Misc
- Router
- OSI vs TCP/IP
- TCP vs UDP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP port
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- ARP Packet Format
- ARP Table
- Working of ARP
- FTP Client
- FTP Commands
- FTP Server
- I2C Protocol
- Sliding Window Protocol
- SPI Protocol
- IP
- ARP Commands
- ARP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- ARP and its types
- TCP Retransmission
- CAN protocol
- HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- RIP Protocol
- UDP Protocol
- ICMP Protocol
- MQTT protocol
- OSPF Protocol
- Stop and Wait Protocol
- IMAP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- CIFS
- DAS
- DIMM
- iSCSI
- NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- NFS
- NVMe
- SAN
- Border Gateway Protocol
- Go-Back-N ARQ
- RJ Cable
- Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Service
- CDMA vs. GSM
- What is MAC Address
- Modem vs. Router
- Switch Vs. Router
- USB 2.0 vs 3.0
- Difference between CSMA CA and CSMA CD
- Multiple access protocol- ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
- URI vs URL
- IMAP vs. POP3
- SSH Meaning| SSH Protocol
- UTP vs STP
- Status Code 400
- MIME Protocol
- IP address
- proxy server
- How to set up and use a proxy server
- network security
- WWW is based on which model
- Proxy Server List
- Fundamentals of Computer Networking
- IP Address Format and Table
- Bus topology and Ring topology
- Bus topology and Star topology
- Circuit Switching and Packet switching?
- Difference between star and ring topology
- Difference between Router and Bridge
- TCP Connection Termination
- Image Steganography
- Network Neutrality
- Onion Routing
- Adaptive security appliance (ASA) features
- Relabel-to-front Algorithm
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Access Lists (ACL)
- What is a proxy server and how does it work
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Operating system based Virtualization
- Context based Access Control (CBAC)
- Cristian's Algorithm
- Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)
- Extended Access List
- Li-fi vs. Wi-fi
- Reflexive Access List
- Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
- Wifi protected access (WPA)
- Wifi Protected Setup (WPS)
- Standard Access List
- Time Access List
- What is 3D Internet
- 4G Mobile Communication Technology
- Types of Wireless Transmission Media
- Best Computer Networking Courses
- Data Representation
- Network Criteria
- Classful vs Classless addressing
- Difference between BOOTP and RARP in Computer Networking
- What is AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- External IP Address
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- Types of Authentication Protocols
- What is a CISCO Packet Tracer
- BOOTP work
- Subnetting in Computer Networks
- Mesh Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ring Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Star Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Tree Topology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Zigbee Technology-The smart home protocol
- Network Layer in OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer in OSI Model
- Internet explorer shortcut keys
- Network Layer Security | SSL Protocols
- Presentation Layer in OSI Model
- Session Layer in OSI Model
- SUBNET MASK
- Transport Layer Security | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and SSL Architecture
- Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Layer
- Protocols in Noiseless and Noisy Channel
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Cloud Networking - Managing and Optimizing Cloud-Based Networks
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
- Count to Infinity Problem in Distance Vector Routing
- Difference Between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat Protocol
- Difference between Stop and Wait, GoBackN, and Selective Repeat
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): transforming Network Architecture with Virtualized Functions
- Network-Layer Security | IPSec Modes
- Next - Prev Network-Layer Security | IPSec Protocols and Services
- Ping vs Traceroute
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): Benefits and Challenges of Network Virtualization
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) vs. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- Virtual Circuits vs Datagram Networks
- BlueSmack Attack in Wireless Networks
- Bluesnarfing Attack in Wireless Networks
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
- Warchalking in Wireless Networks
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- Wireless security encryption
- Wireless Security in an Enterprise
- Quantum Networking
- Network Automation
- Difference between MSS and MTU
- What is MTU
- Mesh Networks: A decentralized and Self-Organizing Approach to Networking
- What is Autonomous System
- What is MSS
- Cyber security & Software security
- Information security & Network security.
- Security Engineer & Security Architect
- Protection Methods for Network Security
- Trusted Systems in Network Security
- What are Authentication Tokens in Network security
- Cookies in Network Security
- Intruders in Network Security
- Network Security Toolkit (NST) in virtual box
- Pivoting-Moving Inside a Network
- Security Environment in Computer Networks
- Voice Biometric technique in Network Security
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Testing
- Difference between Kerberos and LDAP
- Cyber security and Information Security
- GraphQL Attacks and Security
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Applications of Remote Sensing
- Seven Layers of IT Security
- What is Ad Hoc TCP
- What is Server Name Indication(SNI)
Router
The router is a physical or virtual internetworking device that is designed to receive, analyze, and forward data packets between computer networks. A router examines a destination IP address of a given data packet, and it uses the headers and forwarding tables to decide the best way to transfer the packets. There are some popular companies that develop routers; such are Cisco, 3Com, HP, Juniper, D-Link, Nortel, etc. Some important points of routers are given below:
- A router is used in LAN (Local Area Network) and WAN (Wide Area Network) environments. For example, it is used in offices for connectivity, and you can also establish the connection between distant networks such as from Bhopal to
- It shares information with other routers in networking.
- It uses the routing protocol to transfer the data across a network.
- Furthermore, it is more expensive than other networking devices like switches and hubs.

A router works on the third layer of the OSI model, and it is based on the IP address of a computer. It uses protocols such as ICMP to communicate between two or more networks. It is also known as an intelligent device as it can calculate the best route to pass the network packets from source to the destination automatically.
A virtual router is a software function or software-based framework that performs the same functions as a physical router. It may be used to increase the reliability of the network by virtual router redundancy protocol, which is done by configuring a virtual router as a default gateway. A virtual router runs on commodity servers, and it is packaged with alone or other network functions, like load balancing, firewall packet filtering, and wide area network optimization capabilities.
Why Routers?
A router is more capable as compared to other network devices, such as a hub, switch, etc., as these devices are only able to execute the basic functions of the network. For example, a hub is a basic networking device that is mainly used to forward the data between connected devices, but it cannot analyze or change anything with the transferring data. On the other hand, the router has the capability to analyze and modify the data while transferring it over a network, and it can send it to another network. For example, generally, routers allow sharing a single network connection between multiple devices.
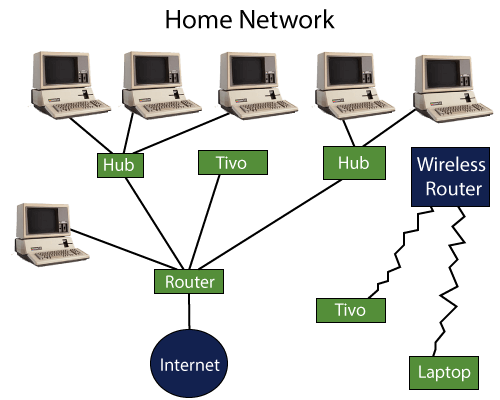
How does Router work?
A router analyzes a destination IP address of a given packet header and compares it with the routing table to decide the packet's next path. The list of routing tables provides directions to transfer the data to a particular network destination. They have a set of rules that compute the best path to forward the data to the given IP address.
Routers use a modem such as a cable, fiber, or DSL modem to allow communication between other devices and the internet. Most of the routers have several ports to connect different devices to the internet at the same time. It uses the routing tables to determine where to send data and from where the traffic is coming.
A routing table mainly defines the default path used by the router. So, it may fail to find the best way to forward the data for a given packet. For example, the office router along a single default path instructs all networks to its internet services provider.
There are two types of tables in the router that are static and dynamic. The static routing tables are configured manually, and the dynamic routing tables are updated automatically by dynamic routers based on network activity.
Features of Router
- A router works on the 3rd layer (Network Layer) of the OSI model, and it is able to communicate with its adjacent devices with the help of IP addresses and subnet.
- A router provides high-speed internet connectivity with the different types of ports like gigabit, fast-Ethernet, and STM link port.
- It allows the users to configure the port as per their requirements in the network.
- Routers' main components are central processing unit (CPU), flash memory, RAM, Non-Volatile RAM, console, network, and interface card.
- Routers are capable of routing the traffic in a large networking system by considering the sub-network as an intact network.
- Routers filter out the unwanted interference, as well as carry out the data encapsulation and decapsulation process.
- Routers provide the redundancy as it always works in master and slave mode.
- It allows the users to connect several LAN and WAN.
- Furthermore, a router creates various paths to forward the data.
Applications of Routers
There are various areas where a router is used:
- Routers are used to connect hardware equipment with remote location networks like BSC, MGW, IN, SGSN, and other servers.
- It provides support for a fast rate of data transmission because it uses high STM links for connectivity; that's why it is used in both wired or wireless communication.
- Internet service providers widely use routers to send the data from source to destination in the form of e-mail, a web page, image, voice, or a video file. Furthermore, it can send data all over the world with the help of an IP address of the destination.
- Routers offer access restrictions. It can be configured in a way that allows for few users to access the overall data and allows others to access the few data only, which is defined for them.
- Routers are also used by software testers for WAN communications. For example, the software manager of an organization is located in Agra, and its executive is located at a different place like Pune or Bangalore. Then the router provides the executive the method to share his software tools and other applications with the manager with the help of routers by connecting their PCs to the router using WAN architecture.
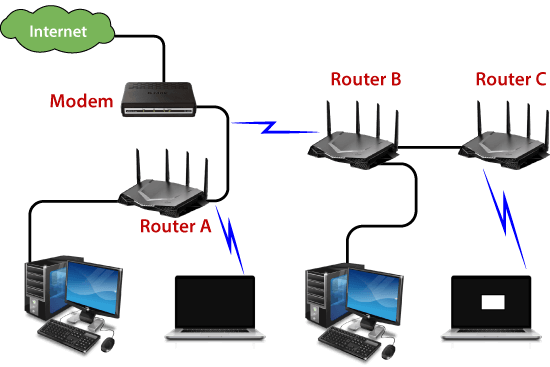
- In wireless networks, by configuring VPN in routers, it can be used in the client-server model, which allows sharing the internet, video, data, voice, and hardware resources. As shown in the below picture:
- In modern times, routers have the facility of inbuilt USB ports within the hardware. They have enough internal storage capacity. External storage devices can be used with routers to store and share data.
- Routers are used to set up the operation and maintenance center of an organization, which is known as the NOC center. All equipment at a distant location are connected by routers on optical cable at a central location, which also offer redundancy through the main link and protection link topology.
Types of Routers
There are various types of routers in networking; such are given below:
1. Wireless Router: Wireless routers are used to offer Wi-Fi connectivity to laptops, smartphones, and other devices with Wi-Fi network capabilities, and it can also provide standard ethernet routing for a small number of wired network systems.
Wireless routers are capable of generating a wireless signal in your home or office, and it allows the computers to connect with routers within a range, and use the internet. If the connection is indoors, the range of the wireless router is about 150 feet, and when the connection is outdoors, then its range is up to 300 feet.
Furthermore, you can make more secure wireless routers with a password or get your IP address. Thereafter, you can log in to your router by using a user ID and password that will come with your router.
2. Brouter: A brouter is a combination of the bridge and a router. It allows transferring the data between networks like a bridge. And like a router, it can also route the data within a network to the individual systems. Thus, it combines these two functions of bridge and router by routing some incoming data to the correct systems while transferring the other data to another network.
3. Core router: A core router is a type of router that can route the data within a network, but it is not able to route the data between the networks. It is a computer communication system device and the backbone of networks, as it helps to link all network devices. It is used by internet service providers (ISPs), and it also provides various types of fast and powerful data communication interfaces.
4. Edge router: An edge router is a lower-capacity device that is placed at the boundary of a network. It allows an internal network to connect with the external networks. It is also called as an access router. It uses an External BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) to provides connectivity with remote networks over the internet.
There are two types of edge routers in networking:
- Subscriber edge router
- Label edge router
The subscriber edge router belongs to an end-user organization, and it works in a situation where it acts on a border device.
The label edge router is used in the boundary of Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) networks. It acts as a gateway between the LAN, WAN, or the internet.
5. Broadband routers: Broadband routers are mainly used to provide high-speed internet access to computers. It is needed when you connect to the internet through phone and use voice over IP technology (VOIP).
All broadband routers have the option of three or four Ethernet ports for connecting the laptop and desktop systems. A broadband router is configured and provided by the internet service provider (ISP). It is also known as a broadband modem, asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL), or digital subscriber line (DSL) modem.
Benefits of Router
There are so many benefits of a router, which are given below:
- Security: Router provides the security, as LANs work in broadcast mode. The information is transmitted over the network and traverses the entire cable system. Although the data is available to each station, but the station which is specifically addressed reads the data.
- Performance enhancement: It enhances the performance within the individual network. For example, if a network has 14 workstations, and all generate approximately the same volume of traffic. The traffic of 14 workstations runs through the same cable in a single network. But if the network is divided into two sub-networks each with 7 workstations, then a load of traffic is reduced to half. As each of the networks has its own servers and hard disk, so fewer PCs will need the network cabling system.
- Reliability: Routers provide reliability. If one network gets down when the server has stopped, or there is a defect in the cable, then the router services, and other networks will not be affected. The routers separate the affected network, whereas the unaffected networks remain connected, without interrupting the work and any data loss.
- Networking Range: In networking, a cable is used to connect the devices, but its length cannot exceed 1000 meters. A router can overcome this limitation by performing the function of a repeater (Regenerating the signals). The physical range can be as per the requirement of a particular installation, as long as a router is installed before the maximum cable range exceeds.
Routing Protocols
Routing protocols specify a way for the router to identify other routers on the network and make dynamic decisions to send all network messages. There are several protocols, which are given below:
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF): It is used to calculate the best route for the given packets to reach the destination, as they move via a set of connected networks. It is identified by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as Interior Gateway Protocol.
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP): It helps manage how packets are routed on the internet via exchange of information between edge routers. It provides network stability for routers if one internet connection goes down while forwarding the packets, it can adapt another network connection quickly to send the packets.
Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP): It specifies how routing information will be exchanged between gateways within an independent network. Then, the other network protocols can use the routing information to determine how transmissions should be routed.
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP): In this protocol, if a router is unable to find a path to a destination from the tables, it asks route to its neighbors, and they pass the query to their neighbors until a router has found the path. When the entry of routing table changes in one of the routers, it informs its neighbors only about the changes, but do not send the entire table.
Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP): It decides how routing information can be exchanged between two neighbor gateway hosts, each of which has its own router. Additionally, it is commonly used to exchange routing table information between hosts on the internet.
Routing Information Protocol (RIP): It determines how routers can share information while transferring traffic among connected group of local area networks. The maximum number of hops that can be allowed for RIP is 15, which restricts the size of networks that RIP can support.
Difference between Bridge and Router
| Bridge | Router |
|---|---|
| A bridge is a networking device that is used to connect two local area networks (LANs) by using media access control addresses and transmit the data between them. | A router is also a networking device that sends the data from one network to another network with the help of their IP addresses. |
| A bridge is able to connect only two different LAN segments. | A router is capable of connecting the LAN and WAN. |
| A bridge transfers the data in the form of frames. | A router transfers the data in the form of packets. |
| It sends data based on the MAC address of a device. | It sends data based on the IP address of a device. |
| The bridge has only one port to connect the device. | The router has several ports to connect the devices. |
| The bridge does not use any table to forward the data. | The router uses a routing table to send the data. |
Difference between Hub, Switch, and Router
There are three primarily networking devices that connect the computers from one to another. These devices are hub, switch, and router. These all have the ability to connect one computer to another, but there is some difference between them. The difference between a hub, switch, and router are given below:
Hub: A hub is a basic networking device that is used to connect computers or other networking devices together. A hub does not use any routing table to send the data to the destination. Although it can identify basic errors of networks like collisions, it can be a security risk to broadcast all information to the multiple ports. As the hub is a dumb device, it does not need an IP address. Furthermore, Hubs are cheaper than a switch or router.
Switch: A switch is a hardware device that also connects computers to each other. A switch is different as compared to a hub in that way; it handles packets of data. Whenever a switch receives a packet, it decides the device to which the packet can be sent, and sends it to that device only. A hub broadcasts the packet to all computers, but the switch does not circulate the packet to all devices, which means bandwidth is not shared with the network, and thus it increases the efficiency of the network. That's why switches are more preferred as compared to a hub.
Router: A router is more different from a switch or hub. It is mainly used to route the data packets to another network instead of transmitting the data to the local networks only. A router is commonly found in homes and offices as it allows your network to communicate with other networks through the internet. Basically, a router provides more features to your networks like firewall, VPN, QoS, traffic monitoring, etc.
What is Routing Table in Router?
A routing table determines the path for a given packet with the help of an IP address of a device and necessary information from the table and sends the packet to the destination network. The routers have the internal memory that is known as Random Access Memory (RAM). All the information of the routing table is stored in RAM of routers.
For example:
| Destination (Network ID) | Subnet mask | Interface |
|---|---|---|
| 200.1.2.0 | 255.255.255.0 | Eth0 |
| 200.1.2.64 | 255.255.255.128 | Eth1 |
| 200.1.2.128 | 255.255.255.255 | Eth2 |
| Default | Eth3 |
A routing table contains the following entities:
- It contains an IP address of all routers which are required to decide the way to reach the destination network.
- It includes extrovert interface information.
- Furthermore, it is also contained IP addresses and subnet mask of the destination host.
Network Element in Router
There are two types of a network element in the router which are as follows:
Control plane: A router supports a routing table that determines which path and physical interface connection should be used to send the packet. It is done by using internal pre-configured directives, which are called static routes, or by learning routes with the help of routing protocol. A routing table stores the static and dynamic routes. Then the control-plane logic eliminates the unnecessary directives from the table and constructs a forwarding information base that is used by the forwarding plane.
Forwarding plane: A router sends data packets between incoming and outgoing interface connections. It uses information stored in the packet header and matches it to entries in the FIB, which is supplied by the control plane; accordingly, it forwards the data packet to the correct network type. It is also called the user plane or data plane.
How to buy a Router?
There are many points to keep in mind while buying a router:
- Type of Connection: Which kind of router should you buy depends on the type of connection you have. For example, if you want to use the internet connection from your telephone services providers like BSNL or MTNL, you will need an ADSL router. In this router, you have to use the hardware that is provided to you with your connection. Although this router may have limited functionalities on some fronts.
Alternatively, you can purchase an advanced router that allows you sharing storage, including printer over a wireless connection. If you use the connection provided by the local cable operator, you will need a non-ADSL router. - Standard: The routers support standards like 802.11ac, 802.11n, etc. The routers that support 802.11ac standard, enhances the speed to transfer the data more than three times the speed of 802.11n standard routers. It uses the 5GHz frequency band, which is less crowded as compared to the regular 2.4GHz band. Furthermore, it also provides better network performance for file transfers and streaming media content.
The routers that support 802.11ac standard are beneficial as they are compatible with 'n' standard, by which your older devices can also work without any problem.Alternatively; you can save some money and full fill your requirements by purchasing 'n' standard routers. - Dual-band: Most of 'n' standard routers operate in the 2.4GHz frequency, but a dual-band router is better as it supports the 5GHz band. Furthermore, it can also connect with smartphones and laptops on 5GHz, while other routers can operate over 2.4GHz only.
- USB port: Routers with USB ports allow you to plug flash drives, including printers, to share these resources over the network. These functions are suitable for a small area as they can be used within the wireless network without using the internet.
Some routers provide backup internet by 3G data dongles when your main connection goes down. But these routers work with specific brands only. So, before purchasing a router, check if it supports the dongle you are using. - Multiple antennas: External antennas are strong enough to increase the overall range of your router as well as are suitable for environments where you need signals across multiple walls or doors.


