Android Tutorial
Android Widgets
- UI Widgets
- Android Button
- Android Toast
- Android Custom Toast
- Android ToggleButton
- Android CheckBox
- Android Custom CheckBox
- Android RadioButton
- Android Dynamic RadioButton
- Custom RadioButton
- AlertDialog
- Spinner
- Auto Complete Text View
- ListView
- Custom ListView
- RatingBar
- WebView
- SeekBar
- DatePicker
- TimePicker
- Analog clock and Digital clock
- ProgressBar
- ScrollView Vertical
- HorizontalScrollView
- Image Switcher
- Image Slider
- ViewStub
- TabLayout
- TabLayout with FrameLayout
- SearchView
- SearchView on ToolBar
- EditText with TextWatcher
Activity and Intents
Android Fragments
Android Menu
Android Service
Android AlarmManager
Android Storage
Android SQLite
XML and JSON
Android Multimedia
Android Speech
Android Telephony
Android Device
Camera Tutorial
Sensor Tutorial
Android Graphics
Android Animation
Android Web Service
Android Examples
- QR Code / Bar Code Scanner
- RSS Feed Reader
- Volley Library Fetching JSON Data from URL
- Linkify Example
- Introduction Slider (Launch very first time when app start)
- RecyclerView List
- Swipe to Delete RecyclerView items with UNDU
- Swipe to refresh Android Activity
- Volley Library - Registration, Log-in, and Log-out
- Network Connectivity Services
- Firebase Authentication - Google Login
- Android Notification
- Using Google reCAPTCHA in Android Application
Android Social
Android Versions
Android Misc
- Android Device Manager
- Android Studio
- Android Auto
- Android to Mac
- Android Messages
- Android TV
- Android Screenshot
- Android Pay
- Android Watch
- Android Phones
- Android Tablet
- Android Find My Phone
- Android One
- Android Wear OS
- Android Data Recovery
- Android Antivirus
- Android x86
- Android Emulator for PC
- Android File Manager
- Android ad blocker
- Android Podcast App
- Fortnite Android an Epic Game
- FaceTime on Android
- ShowBox for Android
- Android App Store
- Virus Removal for Android
- cache in Android
- Root Android Device
- Android Screen Recorder
- block a number
- Canon printer app
- Wireless HP printer app
- How to Update Android
- iMessage for Android
- iCloud for Android
- Best Call Recorder
- Videoder Android
- YouTube Video Downloader
- Airdrop for Android
- RoboKiller for Android
- Clean my Android Phone
- How to hide apps, files, and photos on Android
- Best weather apps with widgets for Android
- Android File Transfer for Mac
- Mobdro for Android
- Screen Mirroring in Android
- Stock market apps for Android
- How to turn On or Off safe mode on Android
- Best browsers for Android
- Best clocks for Android
- Best email apps for Android
- Music player for Android
- Android smartwatch for women
- Best keyboard for Android
- Best messaging app for Android
Android MCQ
Android Interview
Android Quiz
Internal Details
Here, we are going to learn the internal details or working of hello android example.
Android application contains different components such as java source code, string resources, images, manifest file, apk file etc. Let's understand the project structure of android application.
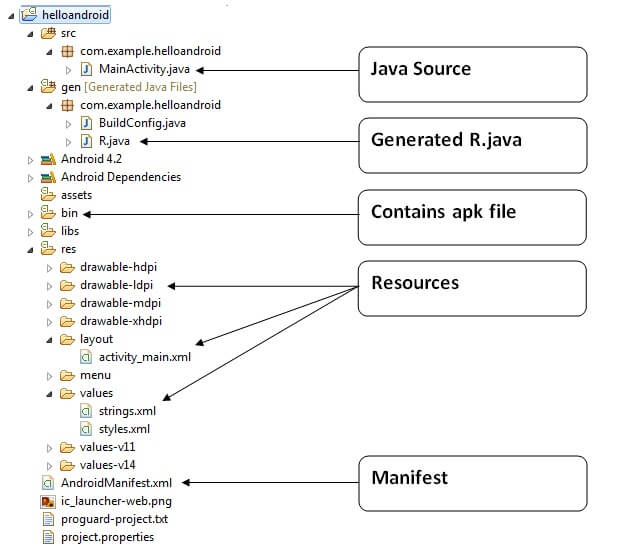
Java Source Code
Let's see the java source file created by the Eclipse IDE:
File: MainActivity.java
import android.app.Activity;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {//(1)
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {//(2)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);//(3)
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {//(4)
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_main, menu);
return true;
}
}
(1) Activity is a java class that creates and default window on the screen where we can place different components such as Button, EditText, TextView, Spinner etc. It is like the Frame of Java AWT.
It provides life cycle methods for activity such as onCreate, onStop, OnResume etc.
(2) The onCreate method is called when Activity class is first created.
(3) The setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) gives information about our layout resource. Here, our layout resources are defined in activity_main.xml file.
File: activity_main.xml
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
As you can see, a textview is created by the framework automatically. But the message for this string is defined in the strings.xml file. The @string/hello_world provides information about the textview message. The value of the attribute hello_world is defined in the strings.xml file.
File: strings.xml
helloandroid
Hello world!
Settings
You can change the value of the hello_world attribute from this file.
Generated R.java file
It is the auto-generated file that contains IDs for all the resources of res directory. It is generated by aapt(Android Asset Packaging Tool). Whenever you create any component on activity_main, a corresponding ID is created in the R.java file which can be used in the Java Source file later.
File: R.java
*
* This class was automatically generated by the
* aapt tool from the resource data it found. It
* should not be modified by hand.
*/
package com.example.helloandroid;
public final class R {
public static final class attr {
}
public static final class drawable {
public static final int ic_launcher=0x7f020000;
}
public static final class id {
public static final int menu_settings=0x7f070000;
}
public static final class layout {
public static final int activity_main=0x7f030000;
}
public static final class menu {
public static final int activity_main=0x7f060000;
}
public static final class string {
public static final int app_name=0x7f040000;
public static final int hello_world=0x7f040001;
public static final int menu_settings=0x7f040002;
}
public static final class style {
/**
Base application theme, dependent on API level. This theme is replaced
by AppBaseTheme from res/values-vXX/styles.xml on newer devices.
Theme customizations available in newer API levels can go in
res/values-vXX/styles.xml, while customizations related to
backward-compatibility can go here.
Base application theme for API 11+. This theme completely replaces
AppBaseTheme from res/values/styles.xml on API 11+ devices.
API 11 theme customizations can go here.
Base application theme for API 14+. This theme completely replaces
AppBaseTheme from BOTH res/values/styles.xml and
res/values-v11/styles.xml on API 14+ devices.
API 14 theme customizations can go here.
*/
public static final int AppBaseTheme=0x7f050000;
/** Application theme.
All customizations that are NOT specific to a particular API-level can go here.
*/
public static final int AppTheme=0x7f050001;
}
}
APK File
An apk file is created by the framework aut
omatically. If you want to run the android application on the mobile, transfer and install it.
Resources
It contains resource files including activity_main, strings, styles etc.
Manifest file
It contains information about package including components such as activities, services, content providers etc.
For more information about manifest file visit here: AndroidManifest.xml file.


