React Native Tutorial
- React Native Tutorial
- React Native Environment Setups
- React Native First Application Hello World
- React Native View
- React Native State
- React Native Props
- React Native Style
- React Native Height and Width
- React Native Button
- React Native Layout and Flexbox
- React Native Positioning Element with Flex
- React Native ScrollView
- React Native ListView
- React Native FlatList
- React Native SectionList
- React Native Touchables
- React Native Text Input
- React Native ActivityIndicator
- React Native Picker
- React Native StatusBar
- React Native Switch
- React Native WebView
- React Native ProgressBarAndroid
- React Native ProgressBar With Animated
Navigation
- React Native Navigation
- React Native Configuring Header Bar
- React Native Moving Between Screens
- React Native Passing Value between Screen
- React Native Tab Navigation
- React Native Adding Icons at the Bottom of Tab Navigation
- React Native Create Material Bottom Tab Navigator
- React Native Top Tab Navigator
- React Native Drawer Navigation
Storage
React Misc
- React Native Google Map
- React Native Modal
- React Native Vector Icons
- React Native Splash Screen
- React Native vs. Ionic
- React Native vs. Xamarin
- React Native vs Flutter
- React Native vs React
- React Native vs Swift
- Box shadow in React Native
- React Native IAP
- React-Native Localization
- React Native Toast
- React Native Sound
React Native Props
The properties of React Native components are simply pronounced as props. In React Native, most of the components can be customized at the time of their creation with different parameters. These parameters are known as props. They are immutable, and they cannot be changed.
One of the examples of props is a source property if Image component which controls the image is displayed over the device screen.
React Native Default custom Props
import {
Platform,
StyleSheet,
Image,
Text,
View
} from 'react-native';
export default class App extends Component<{}> {
render() {
let imagePath = { uri: 'https://facebook.github.io/react-native/img/header_logo.png'};
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text style={styles.welcome}>Welcome to React Native!</Text>
<Image source={imagePath} style={{width: 250, height: 250}} />
</View>
);
}
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
backgroundColor: '#a7a6a9',
},
welcome: {
fontSize: 30,
textAlign: 'center',
margin: 20,
}
});
Output:

Using props in our own Component
We can also use props in our components. A single component can be used in many different places in the app by making slightly different properties in each place. To implement the props in our component, this.props is applied followed by the property.
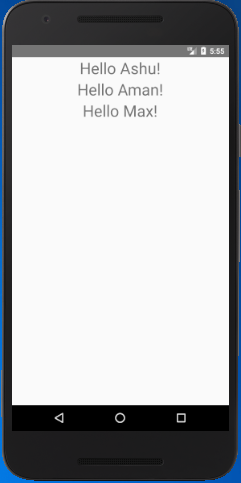
For example, one of the basic React Native components is Text. When we create a Text component, we can use a prop "name" as props to control its appearance. We also apply the StyleSheet to the component which is used as our component.
App.js
import { StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native';
class ChildClass extends Component {
render() {
return (
<View style={{alignItems: 'center'}}>
<Text style={styles.welcome}>Hello {this.props.name}!</Text>
</View>
);
}
}
export default class ParentsClass extends Component {
render() {
return (
<View style={{alignItems: 'center'}}>
<ChildClass name='Ashu' />
<ChildClass name='Aman' />
<ChildClass name='Max' />
</View>
);
}
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
welcome: {
fontSize: 30,
}
});
// skip this line if using Create React Native App
//AppRegistry.registerComponent('MyReactNativeApp', () => ParentsClass);
Output: