COA Tutorial
Basic CO and Design
Computer Instructions
Digital Logic Circuits
Map Simplification
Combinational Circuits
Flip - Flops
Digital Components
Register Transfer
Micro-Operations
Memory Organization
COA_Misc
- Booth's Multiplication Algorithm
- Branch Instruction in Computer Organization
- Data Representation in Computer Organization
- ALU and Data Path in Computer Organization
- External memory in Computer Organization
- Structured Computer Organization
- Types of Register in Computer Organization
- Secondary Storage Devices in Computer Organization
- Types of Operands in Computer Organization
- Serial Communication in Computer organization
- Addressing Sequencing in Computer Organization
- Simplified Instructional Computer (SIC)
- Arithmetic Instructions in AVR microcontroller
- Conventional Computing VS Quantum Computing
- Instruction set used in Simplified Instructional Computer
- Branch Instruction in AVR microcontroller
- Conditional Branch instruction in AVR Microcontroller
- Data transfer instruction in AVR microcontroller
- Difference between Memory-based and Register-based addressing modes
- Difference between 1's complement Representation and 2's complement Representation
- CALL Instructions and Stack in AVR Microcontroller
- Difference between Call and Jump Instructions
- Overflow in Arithmetic Addition in Binary number System
- Horizontal Micro-programmed Vs. Vertical Micro-programmed Control Unit
- Hardwired Vs. Micro-programmed Control Unit
- Non-Restoring Division Algorithm for Unsigned Integer
- Restoring Division Algorithm for Unsigned Integer
- Debugging a Machine-level Program
- Dependencies and Data Hazard in pipeline in Computer Organization
- Execution, Stages and Throughput in Pipeline
- Types of Pipeline Delay and Stalling
- Timing Diagram of MOV Instruction
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Flash Memory
- Importance/Need of negative feedback in amplifiers
- Anti-Aliasing - Computer Graphics
- Bus Arbitration in Computer Organization
- Convert a number from Base 2 (Binary) to Base 6
- Cache Coherence
- EHCI
- Cache Memory and Virtual Memory
- Electrical Potential and Potential Difference
- RAM and Cache
- SIM and RIM instructions in 8085 processor
- Clusters in Computer Organization
- Data Types and Addressing Modes of 80386/80386DX Microprocessor
Memory Hierarchy
A memory unit is an essential component in any digital computer since it is needed for storing programs and data.
Typically, a memory unit can be classified into two categories:
- The memory unit that establishes direct communication with the CPU is called Main Memory. The main memory is often referred to as RAM (Random Access Memory).
- The memory units that provide backup storage are called Auxiliary Memory. For instance, magnetic disks and magnetic tapes are the most commonly used auxiliary memories.
Apart from the basic classifications of a memory unit, the memory hierarchy consists all of the storage devices available in a computer system ranging from the slow but high-capacity auxiliary memory to relatively faster main memory.
The following image illustrates the components in a typical memory hierarchy.
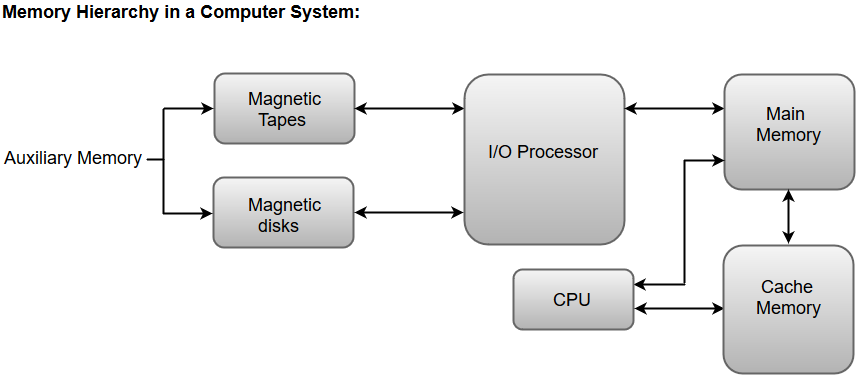
Auxiliary Memory
Auxiliary memory is known as the lowest-cost, highest-capacity and slowest-access storage in a computer system. Auxiliary memory provides storage for programs and data that are kept for long-term storage or when not in immediate use. The most common examples of auxiliary memories are magnetic tapes and magnetic disks.
A magnetic disk is a digital computer memory that uses a magnetization process to write, rewrite and access data. For example, hard drives, zip disks, and floppy disks.
Magnetic tape is a storage medium that allows for data archiving, collection, and backup for different kinds of data.
Main Memory
The main memory in a computer system is often referred to as Random Access Memory (RAM). This memory unit communicates directly with the CPU and with auxiliary memory devices through an I/O processor.
The programs that are not currently required in the main memory are transferred into auxiliary memory to provide space for currently used programs and data.
I/O Processor
The primary function of an I/O Processor is to manage the data transfers between auxiliary memories and the main memory.
Cache Memory
The data or contents of the main memory that are used frequently by CPU are stored in the cache memory so that the processor can easily access that data in a shorter time. Whenever the CPU requires accessing memory, it first checks the required data into the cache memory. If the data is found in the cache memory, it is read from the fast memory. Otherwise, the CPU moves onto the main memory for the required data.
We will discuss each component of the memory hierarchy in more detail later in this chapter.


