Computer Components
Computer Memory
Computer Network
Computer Virus
Number Systems
Shortcut Keys
Terms
- What is a Browser
- Google Chrome
- Mozilla Firefox
- Internet Explorer
- Windows
- Computer Ports
- program
- Printers
- Microphone
- Monitor
- Motherboard
- Incognito Mode
- Mouse
- Memory Card
- CD
- ID
- ISO
- character
- server
- Keyboard
- Remote
- webcam
- Data
- URL
- keypad
- hub
- File
- Bytes
- Exabyte
- Gb
- Kilobyte
- Megabyte
- Petabyte
- Terabyte
- What is HDD
- What is SSD
- Memory vs Storage
- Non-volatile memory
- What is M.2 SSD
- How To Reboot A Computer
- Multi-Level Cell
- NAND Flash Memory
- What is the lock screen
- Block Storage
- Universal Serial Bus
- VRAM
- Cloud Hosting
- CompactFlash card
- What is WAP
- Classification of Memory
- Hardware vs Software
- Uses of Computer
- Uses of Internet
- Abacus
- Best Proxy Servers
- SSL VS. TLS
- Web Console
- GPU
- Difference Between LAN and WAN
- SSD and HDD
- Computer
- Data Migration
- JEDEC
- MLC vs. TLC vs. SLC NAND Flash
- VirtualBox Installation
- Num Lock
- PC
- MAC
- Continuous Data Protection
- Persistent Storage
- What is Bit
- Software Definition
- What is a File System
- When was the first computer invented
- How many generations of the computer
- Minicomputer
- Fourth Generation of Computer
- What is a Username
- What is ALU
Questions
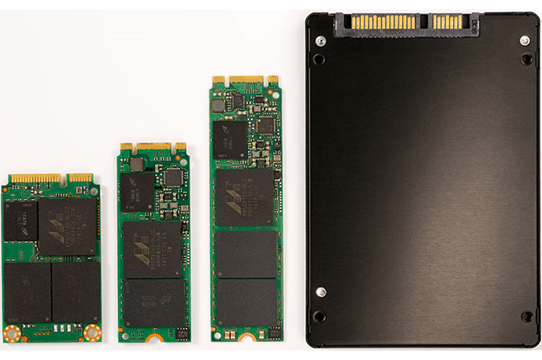
What is M.2 SSD
M.2 SSD that we often call Solid State Drive, used as storage in computers and speeding up the operating system speed. Also, it is in a very small form factor that easily fits into thin laptops. M.2 SSD is 25 times or even quicker than a regular hard disc drive. It helps us to load the installed software's on our computer very fast.
SSDs are a storage media format that stores permanent solid-state flash memory data. An SSD has no moving parts to split or turn up or down instead of a hard disc drive. The M.2 SSD design was known simply as the Next-Generation feature set, but the term "Next-Generation" has been updated in place of the M.2 written M-dot-2.
M.2 SSD form factor
The M.2 SSD is rectangular in shape. It can be 22 millimeters wide and 60 millimeters or longer. And the volume of the card can vary, too. It can have more NAND chips inside a smaller form factor, which provides more data to the computer. The M.2 SSD could be of two different forms. One can be in the form of a card, and another is in the ordinary hard disk, which we can easily put in our old laptop or computer that does not have our M.2 slot.
Notice the 22 mm width; that's the norm for windows computers. An 80 mm, or 110 mm long card can accommodate 8 NAND chips having 2 TB storage.
M.2 SSD pros and cons
The two most significant advantages in the form factor of M.2 SSD are size and capacity. For example, it uses very little space inside an ordinary laptop, making the laptop very compact and easy to carry. M.2 SSD uses a lot more power than a simple SATA or SAS interface because it has no moving parts. They also use their chips in phones, which have the capacity to store a lot of data.
The M.2 interface is a multi-function platform that configures PCIe, SATA, USB 3.0, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi. If you have a laptop that consists of an M.2 interface, then it will be available with lots of input/output devices configuration options.
M.2 SSD capacity key disadvantages are prices and lack of not being so common. Prices of 2,5-inch SATA SSDs have also decreased exponentially, as they were manufactured in greater numbers.
A 1 TB SATA SSD has been around $99 or less in recent years; relative to the price of the SATA drive, an equivalent size M.2 SSD is around two and a half times higher. Restricted storage is another disadvantage of the M.2 SSDs. Although 1 to 2 TB is likely appropriate for most mobile applications, M.2 would need higher capacities to find its way into more corporate storage systems.
M.2 vendors
In general, a 2 TB M.2 SSD cost varies from $230 to $400; low storage costs a little less. Samsung provides a variety of M.2 SSDs in various storage variants. Intel is the biggest provider of M.2 Wireless Adapter.
M.2 SSD vs. mSATA
M.2 is frequently known as a substitute for mSATA, but mSATA SSDs still present and are likely to continue in laptop platforms that support this feature set for some time. Since M.2 and mSATA cards are different design factors and have different connectors, they can't be attached to the same machines; they both have their own use purposes.