Computer Components
Computer Memory
Computer Network
Computer Virus
Number Systems
Shortcut Keys
Terms
- What is a Browser
- Google Chrome
- Mozilla Firefox
- Internet Explorer
- Windows
- Computer Ports
- program
- Printers
- Microphone
- Monitor
- Motherboard
- Incognito Mode
- Mouse
- Memory Card
- CD
- ID
- ISO
- character
- server
- Keyboard
- Remote
- webcam
- Data
- URL
- keypad
- hub
- File
- Bytes
- Exabyte
- Gb
- Kilobyte
- Megabyte
- Petabyte
- Terabyte
- What is HDD
- What is SSD
- Memory vs Storage
- Non-volatile memory
- What is M.2 SSD
- How To Reboot A Computer
- Multi-Level Cell
- NAND Flash Memory
- What is the lock screen
- Block Storage
- Universal Serial Bus
- VRAM
- Cloud Hosting
- CompactFlash card
- What is WAP
- Classification of Memory
- Hardware vs Software
- Uses of Computer
- Uses of Internet
- Abacus
- Best Proxy Servers
- SSL VS. TLS
- Web Console
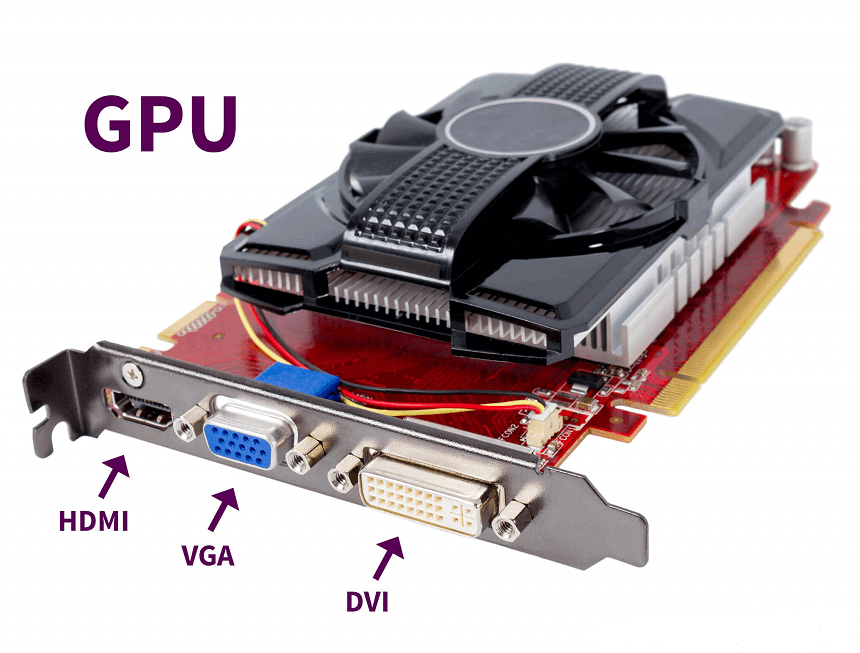
- GPU
- Difference Between LAN and WAN
- SSD and HDD
- Computer
- Data Migration
- JEDEC
- MLC vs. TLC vs. SLC NAND Flash
- VirtualBox Installation
- Num Lock
- PC
- MAC
- Continuous Data Protection
- Persistent Storage
- What is Bit
- Software Definition
- What is a File System
- When was the first computer invented
- How many generations of the computer
- Minicomputer
- Fourth Generation of Computer
- What is a Username
- What is ALU
Questions
VRAM
Video RAM is just like a normal RAM, but video RAM's job is to process the picture so that the monitor can show you the picture. All types of VRAMs are special arrangements for dynamic RAM. The video RAM is a buffer between the computer and the monitor. It is also called a frame buffer. When images are sent to display on the screen by the system, they are read by the processor onto the dedicated video RAM or integrated video RAM. Then the video is processed into the RAM and appears on the monitor.
Previous high-performance Video RAM types were a double-ported, which means that while the CPU is making a new picture to VRAM, the screen reads from VRAM to modify its current display data. The double-port design was the main difference between computer RAM and video RAM in the 1980s and 1990s.
Synchronous Graphics RAM is a relatively low-cost, clock-synchronized DRAM video memory. SGRAM is singular-port memory, but this can function like dual-port memory by constructing new memory pages simultaneously, rather than just one.
Windows RAM has no association with Microsoft Windows. It is a high-performance dual-ported VRAM with around 25 percent more capacity than VRAM, but it costs less money. It has characteristics that read the data for use in block fills and text drawings more effectively. Using the right color, WRAM can be used for very high resolution.
VRAM usage
Modern graphics cards use an SGRAM variant called GDDR5. As the title suggests, GDDR5 is the RAM double data rate. The DDR4 is used in today's electronics as machine RAM.
The only key difference between VRAM and device RAM is the speed and the potential to imitate dual-port functionality. VRAM is ideal for applications that view complex textures of images or render three-dimensional structures based on polygons. Video games or 3D graphic design software are the most popular example of these applications.
The number of VRAM on a system's video card is not nearly significant for services that run on complex data processing functions.
Importance of Video RAM for gaming
VRAM plays an important role in efficiency with gaming, such as loading times and image quality. Certain VRAM levels are required to run games at various resolutions. Rendering a massive AAA game at 1920*1080 resolution is different from rendering a game at 4K UHD quality, which requires extra graphics memory (like 6GB, 8GB, 12GB). Extra Video RAM is needed to render an image of high quality properly, otherwise, the textures and images that a user attempts to render would overwhelm the Video RAM and cause the GPU to spill data into the RAM. This can cause performance issues.
Multibank Dynamic RAM is a high-performance RAM built by MoSys, which separates memory into multiple 32-kilobyte sections or banks that can be independently accessed. Traditional VRAM is monolithic with access to the entire frame buffer at one time. Having contiguous memory banks enables the simultaneous execution of accesses, boosting overall performance. Multibank Dynamic RAM is also cheaper since cards can be produced with only the correct amount of space for a given resolution bandwidth, rather than multiple megabytes, unlike many other Video RAM types.


