Computer Components
Computer Memory
Computer Network
Computer Virus
Number Systems
Shortcut Keys
Terms
- What is a Browser
- Google Chrome
- Mozilla Firefox
- Internet Explorer
- Windows
- Computer Ports
- program
- Printers
- Microphone
- Monitor
- Motherboard
- Incognito Mode
- Mouse
- Memory Card
- CD
- ID
- ISO
- character
- server
- Keyboard
- Remote
- webcam
- Data
- URL
- keypad
- hub
- File
- Bytes
- Exabyte
- Gb
- Kilobyte
- Megabyte
- Petabyte
- Terabyte
- What is HDD
- What is SSD
- Memory vs Storage
- Non-volatile memory
- What is M.2 SSD
- How To Reboot A Computer
- Multi-Level Cell
- NAND Flash Memory
- What is the lock screen
- Block Storage
- Universal Serial Bus
- VRAM
- Cloud Hosting
- CompactFlash card
- What is WAP
- Classification of Memory
- Hardware vs Software
- Uses of Computer
- Uses of Internet
- Abacus
- Best Proxy Servers
- SSL VS. TLS
- Web Console
- GPU
- Difference Between LAN and WAN
- SSD and HDD
- Computer
- Data Migration
- JEDEC
- MLC vs. TLC vs. SLC NAND Flash
- VirtualBox Installation
- Num Lock
- PC
- MAC
- Continuous Data Protection
- Persistent Storage
- What is Bit
- Software Definition
- What is a File System
- When was the first computer invented
- How many generations of the computer
- Minicomputer
- Fourth Generation of Computer
- What is a Username
- What is ALU
Questions
How many generations of the computer
A computer is an electronic machine that operates information; it accepts raw data as an input and provides a meaningful result after processing. It can be used to edit or create spreadsheets, presentations, type documents, browse the Web, play games, send an email, and more.
The generation of computers is based on when major technological changes occur within the computer, like the employment of the microprocessor, vacuum tubes, and transistors. The primary generation of this complex system began about 1940, and there are five generations of the computer till 2020.
First-generation (1940 - 1956)
The first electronic computer used vacuum tubes as a serious piece of technology that was ENIAC, which stands for Electronic Numeric Integrated And Calculator, invented by J.W.Mauchy and J.P.Eckert. From 1940 through 1956, vacuum tubes were widely employed in computers. The first-generation computers were very large in size and took up much space in the room because vacuum tubes were larger components used in the computers. Even some of the first-generation computers were such large in size; they took up an entire room. It weighed more than 30 tons and included 70,000 resistors, 10,000 capacitors, additionally as approximately 20,000 vacuum tubes. The below picture is of the vacuum tubes. Some samples of the primary generation of computers are given below:
- UNIVAC
- IBM-701
- ENIAC
- EDVAC
- IBM-650

Advantages of the first-generation computer
- These computers were in no time in terms of calculating. They might calculate in milliseconds.
- Vacuum tubes are the electronic components available at that time, which were used by these computers.
Disadvantages of the first-generation computer
- These computers' weight was about 30 tones and took up a lot of space as they were very big in size.
- These computers were very costly and based on vacuum tubes.
- Due to the presence of magnetic drums, they were only able to store a small amount of information.
- As the first generation of computers were used vacuum tubes, which need a large cooling system.
- They consumed a large amount of energy and had less work efficiency.
- They needed punch cards to give input and had limited programming capabilities.
Second generation (1956 - 1963)
Instead of vacuum tubes, the second generation of computers was supported transistors. From 1956 through 1963, transistors were widely utilized within the second generation of computers. As compared to the primary generation of computers, these computers were small in size because they used transistors in these generations of computers that were smaller than vacuum tubes. Also, in terms of speed, the second generation of computers was faster. And they were cheaper to create. In 1956, computer TX-0 was introduced, which was the primary computer that used transistors. Some samples of the second generation of computers are given below:
- CDC 3600
- Honeywell 400
- UNIVAC 1108
- IBM 7094
- CDC 1604, and many more
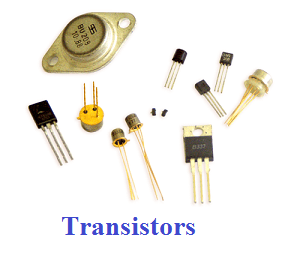
Advantages of the second generation of computers
- The dimensions of the electron component decreased thanks to the existence of transistors rather than vacuum tubes. Hence, the scale of those computers was small in size as compared to the previous generation of computers.
- These computers consumed less energy and did not produce the maximum amount of heat because of the first generation of computers.
- In these computers, punch cards and Assembly language were used to give input.
- As compared to the first generation, it had better portability and low cost.
- Furthermore, these computers were faster in speed as could calculate data in microseconds.
Disadvantages of the second generation of computers
- It required a cooling system and constant maintenance.
- Also, these computers were used only for a particular objective.
Third generation (1964 - 1971)
The third generation of computers was supported Integrated circuits. In 1958-1959, Jack Kilby and Robert Noyce invented the IC (Integrated circuit), which was a signal component that could have a number of transistors. The utilization of Integrated circuits within the computers made them faster and helped reduce the scale of computers as compared to second-generation computers.
In the mid to late 1960s, almost all computers have used Integrated circuits. Although many people considered the time period of the third-generation computer is from 1964 to 1971. Today's computers are still using Integrated circuits. Below, some examples of the third generation of computers are given:
- IBM 370
- PDP-8
- ICL 2900
- IBM 360
- PDP-11, and many more

Advantages of the third generation of computers
- As compared to the second-generation computer, these computers were cheaper in cost.
- This generation's computers used Integrated circuits that made them small in size. Also, they were reliable and faster in speed.
- The use of an Integrated circuit was not only beneficial for reducing the size of the computer; it also enhances the performance of the computer comparing the second-generation computer.
- The third generation of computers introduced a big storage capacity.
- In these computers, keyboard and mouse were used to give the input rather than punch cards.
- These generation computers were much fast in terms of calculation; they decrease the computational time from microseconds to nanoseconds.
- Furthermore, for better performance, these computers used operating systems and used multiple programming and the concept of time-sharing.
Disadvantages of the third generation of computers
- Air conditioning was required by these computers.
- The manufacturing of IC chips required a highly sophisticated technology; also, IC chips are not easy to maintain.
Fourth generation (1972 - 2010)
The Microprocessor, commonly called a CPU (Central Processing Unit), was used by the fourth generation of computers. A microprocessor is used in a computer that led to makes a computer more powerful and small in size as well as fits easily on a desk. Also, microprocessors, along with integrated circuits, helped to introduce the laptop. For providing users more comfort, GUI (Graphics User Interface) technology was exploited. The IBM 5100, Altair 8800, Micral, and some others are older computers that used a microprocessor. Although the fourth generation is considered to have ended in 2010, in modern times, the microprocessor is still in use in computers. The below is of the microprocessor. Some examples of the fourth-generation computers are given below:
- STAR 1000
- PUP 11
- IBM 4341
- DEC 10
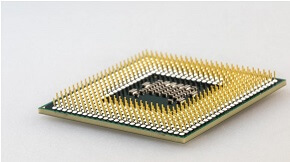
Advantages of the fourth generation of computers
- The first advantage of this generation computer is that the size gets reduced and fastest in computation, comparing to the previous generation of computer.
- Its heat generated is negligible and required less maintenance.
- In these types of computers, all kinds of high-level language can be used.
Disadvantages of the fourth generation of computers
- The fabrication and design of the microprocessor are not simple.
- In many cases, air conditioning is needed due to the occurrence of Integrated circuits.
- For making the Integrated circuit, advanced technology is required.
Fifth-generation (2010 to present)
The fifth generation of computers is predicated on artificial intelligence. AI is an advanced technology that contains various possible applications all over the world. The primary purpose of this generation of computers is to make a device more capable of self-organization and learning, including could respond to natural language input. The ten million electronic components have consisted of the production of a microprocessor as this generation is based on Ultra Large-Scale Integration (ULSI). Although AI made computers more powerful, there is still a need for some improvement in the computer.
IBM's Watson is a common example of computers used AI, which was featured as a contestant on the TV show Jeopardy.Microsoft's Cortana on Windows 8 and Windows 10 computers and. Apple's Siri on the iPhone are some other examples of computers that used AI. Furthermore, AI is also used in a search engine like Google to process user searches. Some more examples are:
- UltraBook
- Chromebook
- Desktop
- Laptop
- NoteBook

Advantages of the fifth generation of computers
- It has unique features and is available in several sizes.
- It is more reliable and has the ability to work much faster.
- It offers computers that have a more friendly UI (User Interface), including multimedia features.
Disadvantages of the fifth generation of computers
- In these computers, very low-level languages are required.
- They may be harmful in terms of making human brains doomed and dull.
How can be defined as the term generation?

The term "generation" means that the new components and computers are released with the latest technology. For instance, the two different generations of computer processors are the Intel Pentium and Intel Pentium II, are both IBM compatible processor. The Apple II and ENIAC are another example of generations of computers. The updated generation may include the latest feature and capabilities that make devices more appropriate as compared to previous generations or make previous generations incompatible or obsolete.


