Computer Components
Computer Memory
Computer Network
Computer Virus
Number Systems
Shortcut Keys
Terms
- What is a Browser
- Google Chrome
- Mozilla Firefox
- Internet Explorer
- Windows
- Computer Ports
- program
- Printers
- Microphone
- Monitor
- Motherboard
- Incognito Mode
- Mouse
- Memory Card
- CD
- ID
- ISO
- character
- server
- Keyboard
- Remote
- webcam
- Data
- URL
- keypad
- hub
- File
- Bytes
- Exabyte
- Gb
- Kilobyte
- Megabyte
- Petabyte
- Terabyte
- What is HDD
- What is SSD
- Memory vs Storage
- Non-volatile memory
- What is M.2 SSD
- How To Reboot A Computer
- Multi-Level Cell
- NAND Flash Memory
- What is the lock screen
- Block Storage
- Universal Serial Bus
- VRAM
- Cloud Hosting
- CompactFlash card
- What is WAP
- Classification of Memory
- Hardware vs Software
- Uses of Computer
- Uses of Internet
- Abacus
- Best Proxy Servers
- SSL VS. TLS
- Web Console
- GPU
- Difference Between LAN and WAN
- SSD and HDD
- Computer
- Data Migration
- JEDEC
- MLC vs. TLC vs. SLC NAND Flash
- VirtualBox Installation
- Num Lock
- PC
- MAC
- Continuous Data Protection
- Persistent Storage
- What is Bit
- Software Definition
- What is a File System
- When was the first computer invented
- How many generations of the computer
- Minicomputer
- Fourth Generation of Computer
- What is a Username
- What is ALU
Questions
Computer Ports
A port is a connection or a jack provided on a computer to connect external or peripheral devices to the computer, for example, you will need a port on your device to connect a keyboard, mouse, pen-drives, etc. So, it acts as an interface or a point of attachment between computer and external devices. It is also called a communication port, as it is the point where you plug in a peripheral device to allow data transfer or communication between the device and computer. Generally, they are four to six in number and present on the back or sides of the computer.
Based on the type of protocol used for communication, computer ports can be of two types: Serial Ports and Parallel Ports.
Serial Port:

This type of ports provides an interface to connect to peripheral devices using a serial protocol. In this port, the rate of transmission of data is one bit at a time through a single communication line. For example, D-Subminiature or D-sub connector is a commonly used serial port, which carries RS-232 signals.
Parallel Port:

As the name suggests, a parallel port is an interface that allows communication or data transfer between a computer and a device in a parallel manner through more than one communication line. For example, a printer port is a parallel port.
Examples of Computer Ports:
1) PS/2:
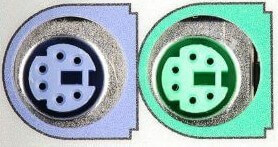
As the name suggests, it was introduced with IBM's Personal Systems/2 series of computers. These connectors are colour coded, e.g., green was for mouse, and purple was for the keyboard. Besides this, it is a DIN connector with six pins. At present, it is superseded by USB ports.
2) VGA Port:

This port is commonly found in computers, projectors, and high definition TVs. It is a D-sub connector called DR-15 as it has 15 pins, which are arranged in 3 rows with five pins in each row. It was most often used to connect CPU with CRT monitors. Still, most of the LCD and LED monitors come with VGA ports. However, these ports don't assure high picture quality as VGA can carry only analogue video signals up to a resolution of 648X480.
As the demand and emphasis on video quality kept growing, the VGA ports were gradually replaced by more advanced ports that can assure high video quality such as HDMI and Display Ports.
3) Digital Video Interface (DVI):

It is another interface between a CPU and a monitor. It is a high-speed interface that is developed to transmit the lossless digital video signals and to replace analogue digital video signal transmission through VGA technology.
The DVI interface can be of three types based on the signals transmitted by it: DVI-I, DVI-D, and DVI-A. The DVI-I supports combined digital and analogue signals, whereas DVI-A supports only analogue signals, and DVI-D supports only digital signals.
Mini-DVI: As the name suggests, it is smaller than a commonly used DVI port. It is a 32 pin port developed by Apple as a substitute to Mini-VGA port. It can transmit various types of signals such as S-Video, VGA, and composite signals using respective adapters.
4) Display Port:
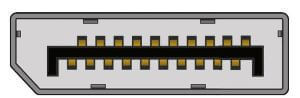
This interface allows transmitting a video and audio from a device to a display screen. It is an advanced display technology that is developed as a substitute for older interfaces such as DVI and VGA. A display port can be seen on laptops, desktops computers, tablets, monitors, etc. It has a 20-pin connector and offers a better resolution than DVI port.
5) RCA Connector:

It is designed to accept composite video and stereo signals transmitted by three cables called RCA cable. A RAC cable has three color-coded plugs that are connected to the three corresponding coloured jacks of an RCA connector. Each of the coloured jack is ringed with metal. The red jack supports the right stereo channel, and the white one supports the left stereo channel, while the yellow is used for composite video.
6) Component Video:

This interface allows splitting video signals into three channels. The component video generally has three color-coded slots; Red, Blue, and Green. Each slot receives and then transmits a particular component of the video signal. It offers high-quality videos than composite video and can carry both analogue and digital video signals.
7) HDMI port:

HDMI (High Definition Media Interface) is a digital interface developed to connect high definition devices such as digital cameras, gaming consoles, etc., to computers and TVs with HDMI ports. Besides this, it can carry uncompressed video and uncompressed or compressed audio signals. The advanced version of HDMI, such as 2.0, can transfer video signals of up to a resolution of 4096x2160.
8) USB:
USB (Universal Serial Bus) port is very versatile in use; It can be used for various purposes, such as to transfer data, to connect peripheral devices, and even as an interface for charging devices such as smartphones, digital cameras, etc. Today, it has replaced PS/2 connectors, game ports, serial and parallel ports, etc.
Types of USB ports:
USB Type A:

It is a four-pin connector and has many versions that include USB 1.1, USB 2.0 and USB 3.0, and USB 3.1. Version 3.0 is a common standard that supports a data transfer rate of upto 400 MBps. Version 3.1 allows a data rate of upto 10 Gbps.
USB Type C:

It is the latest design of the USB that comes with 24 pins and can handle a current of 3A. As it can handle high current, it is also used in devices for fast charging. This port was developed by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF). One of the distinguishing features of this port is that it has no up or down orientation, which means you don't need to flip the male connecter over to plug it in the USB port. For example, a USB-C plug is symmetrical, so that it can be inserted or plugged in either way.
9) RJ-45:

It is an Ethernet style network port found on the computer and other devices such as routers, switches, etc. This port allows your computer to interact or communicate with other computers and networking devices where Ethernet networking is required.
Its full form is Registered Jack 45. It is also known as Ethernet port, network jack, or RJ45 jack. It has eight pins; accordingly, the RJ45 cable comprises eight separate wires of different colours. Besides this, it looks like a telephone jack; however, it is slightly wider than that.
10) RJ11:

It is also a registered jack, which is often used as an interface for modem, ADSL, and telephone and for terminating the telephone wires. Although it looks like RJ45, it is different from that as it is smaller and has only six pins; it is a 6P4C connector that shows it has six pins with four contacts. This port is mainly used to connect to dial-up modems and is also known as a phone connector, modem port, phone jack, etc.
11) 3.5 mm Audio Jack:

It is a small round connector, port, or an audio jack commonly found on laptops, computers, phones, etc. It is designed to connect to wired headphones and speakers. In other words, it accepts a pin-shaped plug from a headphone, earphone, etc. The measurement "3.5 mm" denotes the diameter of the connector.
However, in older devices, there were two audio jacks, one for mic and another one for headphone. Besides this, they have a 2.5 mm jack or port for phone headphones.


