Computer Graphics
Graphic Systems
Input-Output Devices
Scan Conversion a line
Scan Conversion Circle
Scan Converting Ellipse
Filled Area Primitives
2D Transformations
2D-Viewing
Clipping Techniques
Pointing & Positioning
3D Computer Graphics
Hidden Surfaces
Projection
Programs
Random Scan and Raster Scan Display
Random Scan Display:
Random Scan System uses an electron beam which operates like a pencil to create a line image on the CRT screen. The picture is constructed out of a sequence of straight-line segments. Each line segment is drawn on the screen by directing the beam to move from one point on the screen to the next, where its x & y coordinates define each point. After drawing the picture. The system cycles back to the first line and design all the lines of the image 30 to 60 time each second. The process is shown in fig:
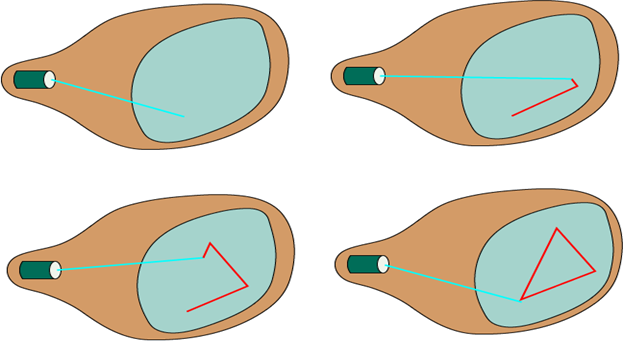
Random-scan monitors are also known as vector displays or stroke-writing displays or calligraphic displays.
Advantages:
- A CRT has the electron beam directed only to the parts of the screen where an image is to be drawn.
- Produce smooth line drawings.
- High Resolution
Disadvantages:
- Random-Scan monitors cannot display realistic shades scenes.
Raster Scan Display:
A Raster Scan Display is based on intensity control of pixels in the form of a rectangular box called Raster on the screen. Information of on and off pixels is stored in refresh buffer or Frame buffer. Televisions in our house are based on Raster Scan Method. The raster scan system can store information of each pixel position, so it is suitable for realistic display of objects. Raster Scan provides a refresh rate of 60 to 80 frames per second.
Polymorphism in Java | Dynamic Method Dispatch
Frame Buffer is also known as Raster or bit map. In Frame Buffer the positions are called picture elements or pixels. Beam refreshing is of two types. First is horizontal retracing and second is vertical retracing. When the beam starts from the top left corner and reaches the bottom right scale, it will again return to the top left side called at vertical retrace. Then it will again more horizontally from top to bottom call as horizontal retracing shown in fig:
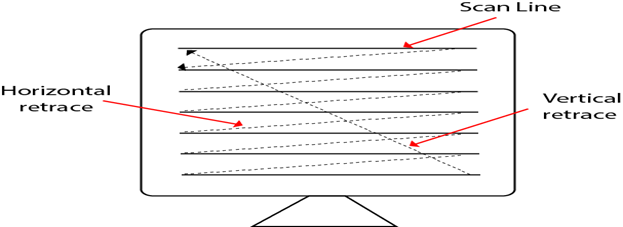
Types of Scanning or travelling of beam in Raster Scan
- Interlaced Scanning
- Non-Interlaced Scanning
In Interlaced scanning, each horizontal line of the screen is traced from top to bottom. Due to which fading of display of object may occur. This problem can be solved by Non-Interlaced scanning. In this first of all odd numbered lines are traced or visited by an electron beam, then in the next circle, even number of lines are located.
For non-interlaced display refresh rate of 30 frames per second used. But it gives flickers. For interlaced display refresh rate of 60 frames per second is used.
Advantages:
- Realistic image
- Million Different colors to be generated
- Shadow Scenes are possible.
Disadvantages:
- Low Resolution
- Expensive
Differentiate between Random and Raster Scan Display:
| Random Scan | Raster Scan |
|---|---|
| 1. It has high Resolution | 1. Its resolution is low. |
| 2. It is more expensive | 2. It is less expensive |
| 3. Any modification if needed is easy | 3.Modification is tough |
| 4. Solid pattern is tough to fill | 4.Solid pattern is easy to fill |
| 5. Refresh rate depends or resolution | 5. Refresh rate does not depend on the picture. |
| 6. Only screen with view on an area is displayed. | 6. Whole screen is scanned. |
| 7. Beam Penetration technology come under it. | 7. Shadow mark technology came under this. |
| 8. It does not use interlacing method. | 8. It uses interlacing |
| 9. It is restricted to line drawing applications | 9. It is suitable for realistic display. |


