Computer Graphics
Graphic Systems
Input-Output Devices
Scan Conversion a line
Scan Conversion Circle
Scan Converting Ellipse
Filled Area Primitives
2D Transformations
2D-Viewing
Clipping Techniques
Pointing & Positioning
3D Computer Graphics
Hidden Surfaces
Projection
Programs
Computer Graphics Tutorial
It is difficult to display an image of any size on the computer screen. This method is simplified by using Computer graphics. Graphics on the computer are produced by using various algorithms and techniques. This tutorial describes how a rich visual experience is provided to the user by explaining how all these processed by the computer.
Introduction of Computer Graphics
Computer Graphics involves technology to access. The Process transforms and presents information in a visual form. The role of computer graphics insensible. In today life, computer graphics has now become a common element in user interfaces, T.V. commercial motion pictures.
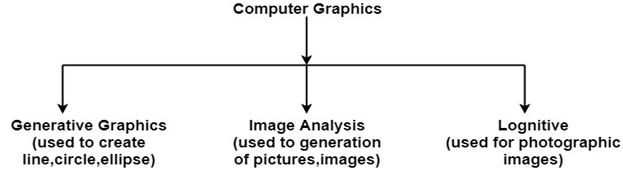
Computer Graphics is the creation of pictures with the help of a computer. The end product of the computer graphics is a picture it may be a business graph, drawing, and engineering.
5.6M
911
Polymorphism in Java | Dynamic Method Dispatch
In computer graphics, two or three-dimensional pictures can be created that are used for research. Many hardware devices algorithm has been developing for improving the speed of picture generation with the passes of time. It includes the creation storage of models and image of objects. These models for various fields like engineering, mathematical and so on.
Today computer graphics is entirely different from the earlier one. It is not possible. It is an interactive user can control the structure of an object of various input devices.
Definition of Computer Graphics:
It is the use of computers to create and manipulate pictures on a display device. It comprises of software techniques to create, store, modify, represents pictures.
Why computer graphics used?
Suppose a shoe manufacturing company want to show the sale of shoes for five years. For this vast amount of information is to store. So a lot of time and memory will be needed. This method will be tough to understand by a common man. In this situation graphics is a better alternative. Graphics tools are charts and graphs. Using graphs, data can be represented in pictorial form. A picture can be understood easily just with a single look.
Interactive computer graphics work using the concept of two-way communication between computer users. The computer will receive signals from the input device, and the picture is modified accordingly. Picture will be changed quickly when we apply command.
Computer Graphics Tutorial Index
Computer Graphics Tutorial
- Computer Graphics Tutorial
- Application of Computer Graphics
- Interactive and Passive Graphics
Graphic Systems
- Display Processor
- Cathode Ray Tube (CRT)
- Random Scan vs Raster Scan
- Color CRT Monitors
- Direct View Storage Tubes
- Flat Panel Display
Input-Output Devices
- Input Devices
- Trackball
- Light Pen
- Image Scanner
- Output Devices
- Plotters
Scan Conversion a line
- Scan Conversion Definition
- Scan Converting a Point
- Scan Converting a Straight Line
- DDA Algorithm
- Bresenham's Line Algorithm
Scan Conversion Circle
- Defining a Circle
- Defining a Circle using Polynomial Method
- Defining a Circle using Polar Coordinates Method
- Bresenham's Circle Algorithm
- Midpoint Circle Algorithm
Scan Converting Ellipse
- Scan converting a Ellipse
- Polynomial Method
- Trignometric Method
- Midpoint Ellipse Algorithm
Filled Area Primitives
- Boundary Fill Algorithm
- Flood Fill Algorithm
- Scan Line Polygon Fill Algorithm
2D Transformations
- Introduction of Transformation
- Translation
- Scaling
- Rotation
- Reflection
- Shearing
- Matrix Representation
- Homogeneous Coordinates
- Composite Transformation
- Pivot Point Rotation
2D-Viewing
- Window
- Window to Viewport Co-ordinate Transformation
- Zooming
- Panning
Clipping Techniques
- Clipping
- Point Clipping
- Line Clipping
- Midpoint Subdivision Algorithm
- Text Clipping
- Polygon
- Sutherland-Hodgeman Polygon Clipping
- Weiler-Atherton Polygon Clipping
Pointing & Positioning
- Pointing & Positioning Techniques
- Elastic or Rubber Band Techniques
- Dragging
Shading
- Introduction of Shading
- Constant Intensity Shading
- Gouraud shading
- Phong Shading
Animation
- Animation
- Application Areas of Animation
- Animation Functions
3D Computer Graphics
- Three Dimensional Graphics
- Three Dimensional Transformations
- Scaling
- Rotation
- Rotation about Arbitrary Axis
- Inverse Transformations
- Reflection
- Shearing
Hidden Surfaces
- Hidden Surface Removal
- Back Face Removal Algorithm
- Z-Buffer Algorithm
- Painter's Algorithm
- Scan Line Algorithm
- Subdivision Algorithm
- 3D Modelling System
Projection
- Projection
- Perspective Projection
- Parallel Projection
Programs
- Computer Graphics Programs
Prerequisite
Good knowledge and understanding of the concepts of C programming language are necessary for learning the concepts of Computer graphics. Good understanding about basic mathematics allows us to better understand the concept of computer graphics.
Audience
This tutorial is helpful for the students who are interested in learning the use of graphics on the computer. The tutorial covers the basics of graphics and development of various visuals by the implementation of graphics in the computer.
Problems
We assure that you will not find any problem with this Computer Graphics Tutorial. But if there is any mistake, please post the problem in the contact form.


