Computer Graphics
Graphic Systems
Input-Output Devices
Scan Conversion a line
Scan Conversion Circle
Scan Converting Ellipse
Filled Area Primitives
2D Transformations
2D-Viewing
Clipping Techniques
Pointing & Positioning
3D Computer Graphics
Hidden Surfaces
Projection
Programs
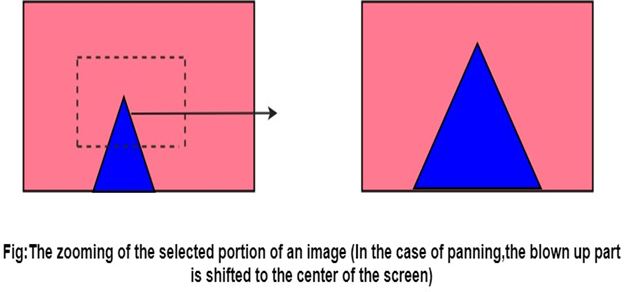
Computer Graphics Zooming
Zooming is a transformation often provided with an imaginary software. The transformation effectively scales down or blows up a pixel map or a portion of it with the instructions from the user. Such scaling is commonly implemented at the pixel level rather than at the coordinates level. A video display or an image is necessarily a pixel map, i.e., a collection of pixels which are the smallest addressable elements of a picture. The process of zooming replicates pixels along successive scan lines.
Example: for a zoom factor of two
Each pixel value is used four times twice on each of the two successive scan lines.
Polymorphism in Java | Dynamic Method Dispatch
Figure shows the effect of zooming by a factor of 2.

Such integration of pixels sometimes involves replication using a set of ordered patterns, commonly known as Dithering.
The two most common dither types are:
- Ordered dither.
- Random dither.
There are widely used, especially when the grey levels (share of brightness) are synthetically generated.