Computer Graphics
Graphic Systems
Input-Output Devices
Scan Conversion a line
Scan Conversion Circle
Scan Converting Ellipse
Filled Area Primitives
2D Transformations
2D-Viewing
Clipping Techniques
Pointing & Positioning
3D Computer Graphics
Hidden Surfaces
Projection
Programs
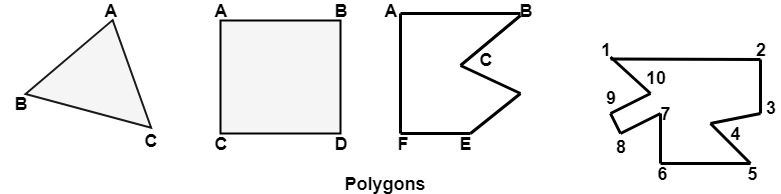
Polygon
Polygon is a representation of the surface. It is primitive which is closed in nature. It is formed using a collection of lines. It is also called as many-sided figure. The lines combined to form polygon are called sides or edges. The lines are obtained by combining two vertices.
Example of Polygon:
- Triangle
- Rectangle
- Hexagon
- Pentagon
Following figures shows some polygons.
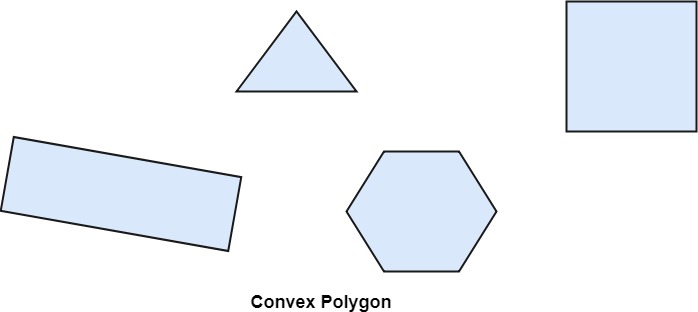
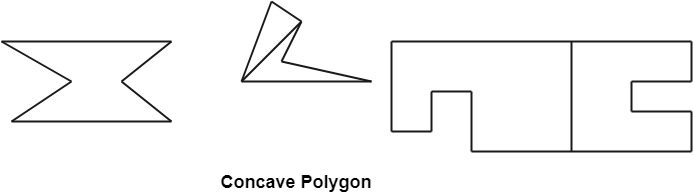
Types of Polygons
- Concave
- Convex
A polygon is called convex of line joining any two interior points of the polygon lies inside the polygon. A non-convex polygon is said to be concave. A concave polygon has one interior angle greater than 180°. So that it can be clipped into similar polygons.
Difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM
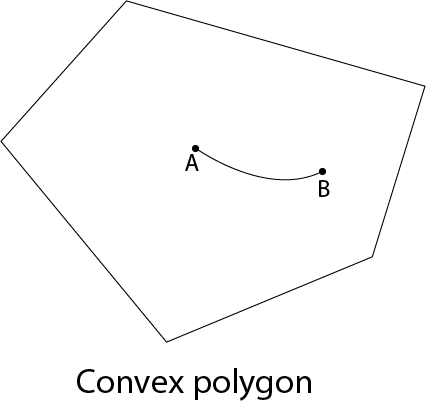
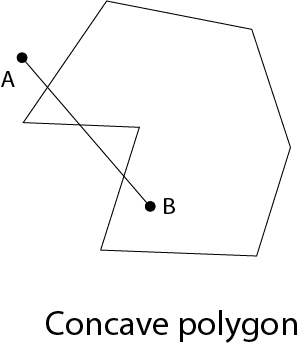
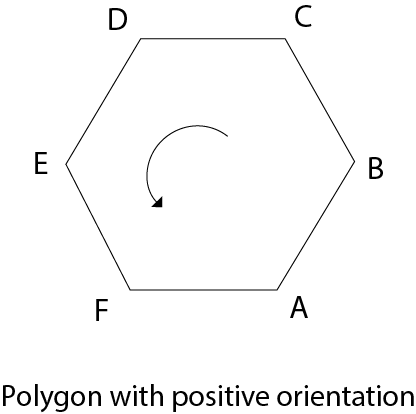
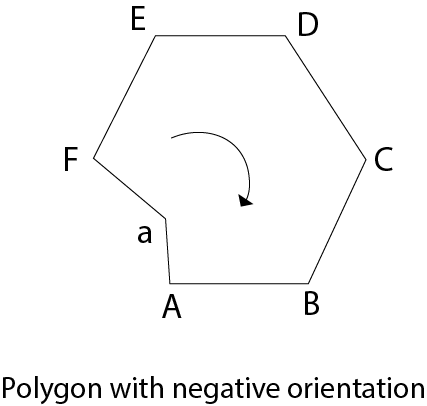
A polygon can be positive or negative oriented. If we visit vertices and vertices visit produces counterclockwise circuit, then orientation is said to be positive.