SQL Tutorial
SQL Database
SQL Table
SQL Select
SQL Order By
SQL Insert
SQL Update
SQL Delete
Difference
SQL Injection
SQL String Functions
Miscl
- SQL Formatter
- SQL group by
- SQL add/drop/update column operation
- SQL CAST Function
- SQL Comments
- SQL CONCAT Function
- CTE (Common Table Expression)SQL
- How to use distinct in SQL?
- Joining Three or More Tables in SQL
- What is Web SQL?
- How to create functions in SQL?
- How to run SQL Script?
- How to Delete Duplicate Rows in SQL?
- Nth Highest salary
- 12 Codd's Rules
- SQL EXCEPT
- Types of SQL JOIN
- Change datatype of column in SQL
- SQL Auto Increment
- SQL Like
- Commit and Rollback in SQL
- SQL Concatenate
- SQL get month from the date
- Savepoint in SQL
- SQL ORDER BY DATE
- TIME Datatype in SQL
- SQL BETWEEN
- CRUD Operations in SQL
- SQL INDEX
- Scalar Functions in SQL
- SET Operators in SQL
- Types of SQL Commands
- TCL Commands in SQL
- SQL Subquery
- SQL View
- Constraints in SQL
- Pattern Matching in SQL
- SQL Date Functions
- DDL Commands in SQL
- DML Commands in SQL
- SQL CASE
- SQL Inner Join
- SQL IN Operator
- Check Constraint in SQL
- SQL CLAUSES
- SQL LOGICAL OPERATORS
- Delete Column from Table
- Add Column in the Table
- Delete one row in SQL
- Change the Column Value
- How to Add Foreign Key in SQL
- Add a Primary Key
- Insert One or More rows
- How to Use LIKE in SQL
- Cursor in SQL
- Difference Between DROP and Truncate
- SQL Comparison Operators
- SQL COUNT WHERE
- SQL SELECT MIN
- SQL Stored Procedure
- SQL SELECT AVG
- SQL SELECT MAX
- SQL ADD COLUMN
- How to use Auto-Increment in SQL
- SQL Languages
- SQL Arithmetic Operators
- How to Use GROUP BY in SQL
- How to Use ORDER BY in SQL
- Trigger in SQL
- What is Race Condition
- SQL COUNT DISTINCT
PL/SQL Tutorial
Sql Interview Question
SQl Quiz
Types of SQL JOIN
SQL JOIN
A SQL Join is used to fetch or combine data (rows or columns) from two or more tables based on the defined conditions.
Table 1: Order
| OrderID | CustomerID | OrderName | ProductName |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12025 | 101 | Peter | ABC |
| 12030 | 105 | Robert | XYX |
| 12032 | 110 | James | XYZ |
| 12034 | 115 | Andrew | PQR |
| 12035 | 120 | Mathew | AAA |
Table 2: Customer
| CustomerID | CustomerName | Country |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | Messy | Maxico |
| 101 | Prince | Taiwan |
| 103 | Maria Fernandez | Turkey |
| 105 | Jasmine | Paris |
| 110 | Faf Weasel | Indonesia |
| 120 | Romen Rocket | Russia |
Now, we have two tables Order and the Customer. There is a CustomerID column common in both tables. So, write the SQL query to define the general relationship to select the matches' records from both tables.
After executing the above SQL queries, it produces the following output:
| OrderID | CustomerName | Country | ProductName |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12025 | Prince | Taiwan | ABC |
| 12030 | Jasmine | Paris | XYX |
| 12032 | Faf Weasel | Indonesia | XYZ |
| 12035 | Romen Rocket | Russia | AAA |
Types of SQL Join
There are different types of joins used in SQL:
- Inner Join / Simple Join
- Left Outer Join / Left Join
- Right Outer Join / Right Join
- Full Outer Join
- Cross Join
- Self Join
Inner Join
The inner join is used to select all matching rows or columns in both tables or as long as the defined condition is valid in SQL.
Syntax:
We can represent the inner join through the Venn diagram, as follows:
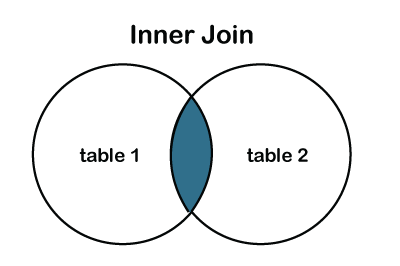
Table 1: Students
| Student_ID | StudentName | Subject | TeacherID |
|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | Alexandra | Computer Science | T201 |
| 102 | Charles | Economics | T202 |
| 103 | Tom Cruise | Computer Science | T201 |
| 104 | Aron Finch | Electronics | T203 |
| 105 | Siemen Bajoff | Web designing | T204 |
| 106 | Christopher | English Literature | T205 |
| 107 | Denim | Fashion Designer | T206 |
Table 2: Teachers
| TeacherID | TeacherName | TeacherEmail |
|---|---|---|
| T201 | Mr Davis | abc@email.com |
| T202 | Mrs Jonas | jonas@email.com |
| T201 | Mr Davis | abc@email.com |
| T204 | Mrs Lopez | lopez@email.com |
| T205 | Mrs Wiley | wiley@email.com |
| T206 | Mr Bean | bean@email.com |
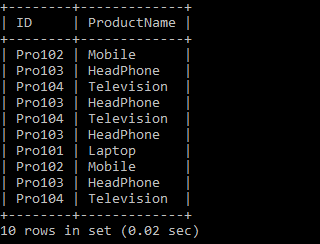
We have two tables: Students and the Teachers Tables. Let's write the SQL Queries to join the table using the INNER JOIN as follows:
After executing the query, it produces the below table.
Natural Join
It is a type of inner type that joins two or more tables based on the same column name and has the same data type present on both tables.
Syntax:
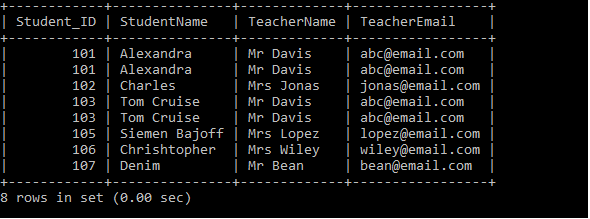
We have two tables: Students and the Teachers Tables. Let's write the SQL Queries to join the table using the Natural JOIN as follows:
After executing the above query, it produces the following table.
LEFT JOIN
The LEFT JOIN is used to retrieve all records from the left table (table1) and the matched rows or columns from the right table (table2). If both tables do not contain any matched rows or columns, it returns the NULL.
Syntax:
We can also represent the left join through the Venn diagram, as follows:
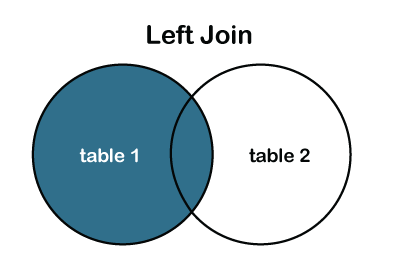
Table 1: Product_Details
| ProductID | ProductName | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Pro101 | Laptop | 56000 |
| Pro102 | Mobile | 38000 |
| Pro103 | Headphones | 5000 |
| Pro104 | Television | 25000 |
| Pro105 | iPad | 60000 |
Table 2: Customer_Details
| CustomerName | CustomerAddress | CustomerAge | ProductID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Martin Guptill | San Francisco, USA | 26 | Pro101 |
| James | Australia | 29 | Pro103 |
| Ambati Williamson | New Zealand | 27 | Pro102 |
| Jofra Archer | South Africa | 24 | Pro105 |
| Kate Wiley | Australia | 20 | Pro103 |
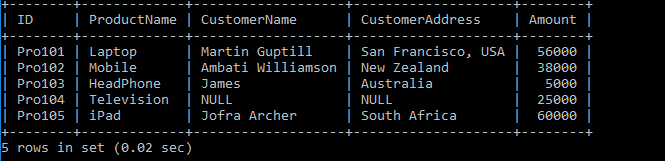
We have two tables: Product_Details and the Customer_Details Tables. Let's write the SQL Queries to join the table using the LEFT JOIN as follows:
After executing the query, it produces the following table.
RIGHT JOIN or RIGHT Outer JOIN:
The RIGHT JOIN is used to retrieve all records from the right table (table2) and the matched rows or columns from the left table (table1). If both tables do not contain any matched rows or columns, it returns the NULL.
Syntax:
We can also represent the right join through the Venn diagram, as follows:
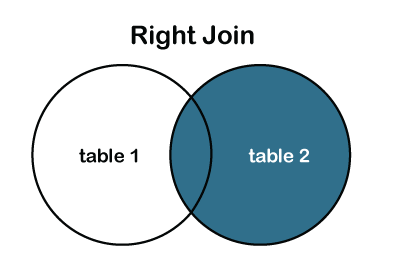
Table 1: Product_Details
| ID | ProductName | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Pro101 | Laptop | 56000 |
| Pro102 | Mobile | 38000 |
| Pro103 | Headphones | 5000 |
| Pro104 | Television | 25000 |
| Pro105 | iPad | 60000 |
Table 2: Customer_Details
| CustomerName | CustomerAddress | CustomerAge | ProductID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Martin Guptill | San Francisco, USA | 26 | Pro101 |
| James | Australia | 29 | Pro103 |
| Ambati Williamson | New Zealand | 27 | Pro102 |
| Jofra Archer | South Africa | 24 | Pro105 |
| Omen | England | 29 | Pro107 |
| Morgan | England | 20 | Pro108 |
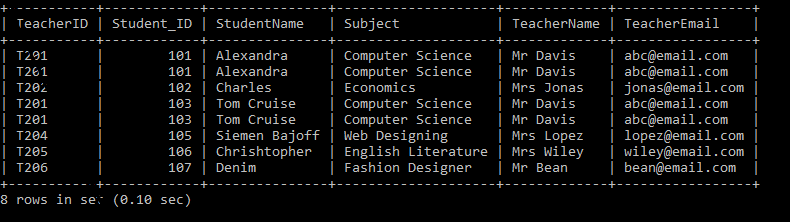
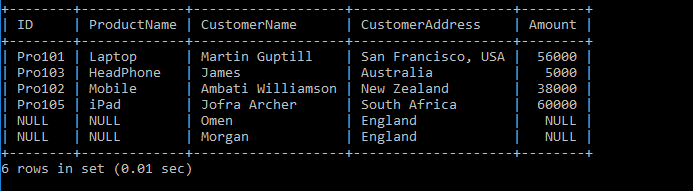
We have two tables: Product_Details and the Customer_Details Tables. Let's write the SQL Queries to join the table using the RIGHT JOIN as follows:
After executing the query, it produces the below table.
FULL JOIN or FULL Outer JOIN:
It is a combination result set of both LEFT JOIN and RIGHT JOIN. The joined tables return all records from both the tables and if no matches are found in the table, it places NULL. It is also called a FULL OUTER JOIN.
Syntax:
Or, FULL OUTER JOIN
We can also represent the full outer join through the Venn diagram, as follows:
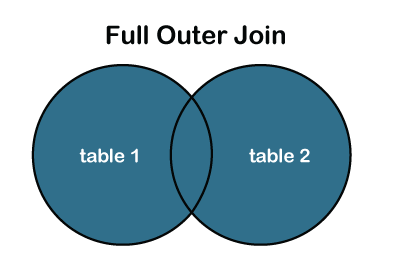
Table 1: Product_Details
| ID | ProductName | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Pro101 | Laptop | 56000 |
| Pro102 | Mobile | 38000 |
| Pro103 | Headphones | 5000 |
| Pro104 | Television | 25000 |
| Pro105 | iPad | 60000 |
Table 2: Customer_Details
| CustomerName | CustomerAddress | CustomerAge | ProductID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Martin Guptill | San Francisco, USA | 26 | Pro101 |
| James | Australia | 29 | Pro103 |
| Ambati Williamson | New Zealand | 27 | Pro102 |
| Jofra Archer | South Africa | 24 | Pro105 |
| Omen | England | 29 | Pro107 |
| Morgan | England | 20 | Pro108 |
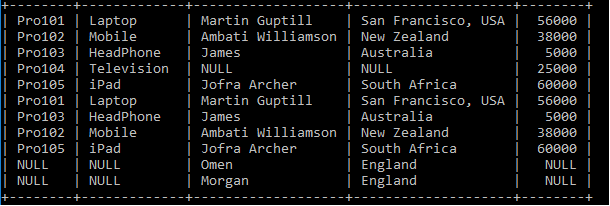
We have two tables: Product_Details and the Customer_Details Tables. Let's write the SQL Queries to join the table using the FULL JOIN as follows:
After executing the query, it produces the below table.
Here is the Syntax for UNION ALL Clause to combine the tables.
UNION ALL
Select ID, ProductName, CustomerName, CustomerAddress, Amount FROM Product_Details RIGHT JOIN Customer_Details ON Product_Details.ID = Customer_Details.ProductID
CROSS JOIN
It is also known as CARTESIAN JOIN, which returns the Cartesian product of two or more joined tables. The CROSS JOIN produces a table that merges each row from the first table with each second table row. It is not required to include any condition in CROSS JOIN.
Syntax:
Or,
Table 1: Product_Details
| ID | ProductName | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Pro101 | Laptop | 56000 |
| Pro102 | Mobile | 38000 |
| Pro103 | Headphones | 5000 |
| Pro104 | Television | 25000 |
| Pro105 | iPad | 60000 |
Table 2: Customer_Details
| CustomerName | CustomerAddress | CustomerAge | ProductID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Martin Guptill | San Francisco, USA | 26 | Pro101 |
| James | Australia | 29 | Pro103 |
| Ambati Williamson | New Zealand | 27 | Pro102 |
| Jofra Archer | South Africa | 24 | Pro105 |
| Omen | England | 29 | Pro107 |
| Morgan | England | 20 | Pro108 |
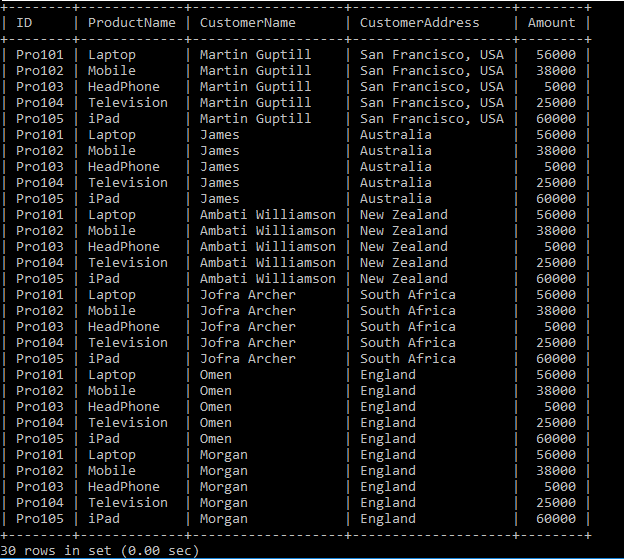
We have two tables: Product_Details and the Customer_Details Tables. Let's write the SQL Queries to join the table using the FULL JOIN as follows:
After executing the query, it produces the below table.
SELF JOIN
It is a SELF JOIN used to create a table by joining itself as there were two tables. It makes temporary naming of at least one table in an SQL statement.
Syntax:
Tbl1 and Tbl2 are two different table aliases for the same table.
Table 1: Product_Details
| ID | ProductName | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Pro101 | Laptop | 56000 |
| Pro102 | Mobile | 38000 |
| Pro103 | Headphones | 5000 |
| Pro104 | Television | 25000 |
| Pro105 | iPad | 60000 |
Let's write the SQL Queries to join the table using the SELF JOIN as follows:
WHERE TB.AMOUNT < TB2.AMOUNT;
After executing the query, it produces the below table.