SQL Tutorial
SQL Database
SQL Table
SQL Select
SQL Order By
SQL Insert
SQL Update
SQL Delete
Difference
SQL Injection
SQL String Functions
Miscl
- SQL Formatter
- SQL group by
- SQL add/drop/update column operation
- SQL CAST Function
- SQL Comments
- SQL CONCAT Function
- CTE (Common Table Expression)SQL
- How to use distinct in SQL?
- Joining Three or More Tables in SQL
- What is Web SQL?
- How to create functions in SQL?
- How to run SQL Script?
- How to Delete Duplicate Rows in SQL?
- Nth Highest salary
- 12 Codd's Rules
- SQL EXCEPT
- Types of SQL JOIN
- Change datatype of column in SQL
- SQL Auto Increment
- SQL Like
- Commit and Rollback in SQL
- SQL Concatenate
- SQL get month from the date
- Savepoint in SQL
- SQL ORDER BY DATE
- TIME Datatype in SQL
- SQL BETWEEN
- CRUD Operations in SQL
- SQL INDEX
- Scalar Functions in SQL
- SET Operators in SQL
- Types of SQL Commands
- TCL Commands in SQL
- SQL Subquery
- SQL View
- Constraints in SQL
- Pattern Matching in SQL
- SQL Date Functions
- DDL Commands in SQL
- DML Commands in SQL
- SQL CASE
- SQL Inner Join
- SQL IN Operator
- Check Constraint in SQL
- SQL CLAUSES
- SQL LOGICAL OPERATORS
- Delete Column from Table
- Add Column in the Table
- Delete one row in SQL
- Change the Column Value
- How to Add Foreign Key in SQL
- Add a Primary Key
- Insert One or More rows
- How to Use LIKE in SQL
- Cursor in SQL
- Difference Between DROP and Truncate
- SQL Comparison Operators
- SQL COUNT WHERE
- SQL SELECT MIN
- SQL Stored Procedure
- SQL SELECT AVG
- SQL SELECT MAX
- SQL ADD COLUMN
- How to use Auto-Increment in SQL
- SQL Languages
- SQL Arithmetic Operators
- How to Use GROUP BY in SQL
- How to Use ORDER BY in SQL
- Trigger in SQL
- What is Race Condition
- SQL COUNT DISTINCT
PL/SQL Tutorial
Sql Interview Question
SQl Quiz
Nth Highest salary
Finding the Nth highest salary( 2nd, 3rd, or nth highest) in a table is the most important and common question asked in various interviews.
Here we will show you the best and easiest way to write SQL queries to find nth highest salary in a table.
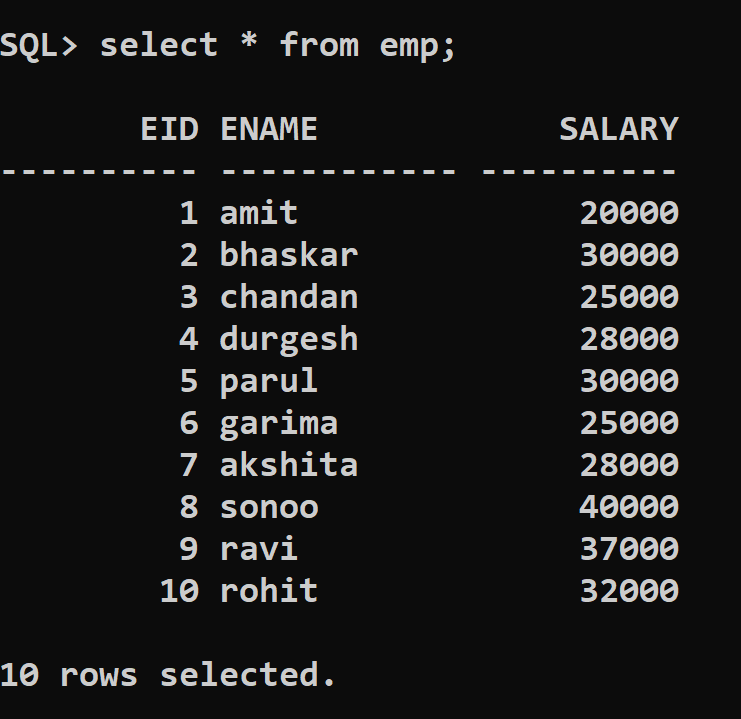
To show this, we are using Table Emp having employee details like EID, ENAME, and SALARY. Data present in the Emp Table is shown below:
Table Name: Emp
| EID | ENAME | SALARY |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Amit | 20000 |
| 2 | Bhaskar | 30000 |
| 3 | Chandan | 25000 |
| 4 | Durgesh | 28000 |
| 5 | Parul | 30000 |
| 6 | Garima | 25000 |
| 7 | Akshita | 28000 |
| 8 | Sonu | 40000 |
| 9 | Ravi | 37000 |
| 10 | Rajesh | 320000 |
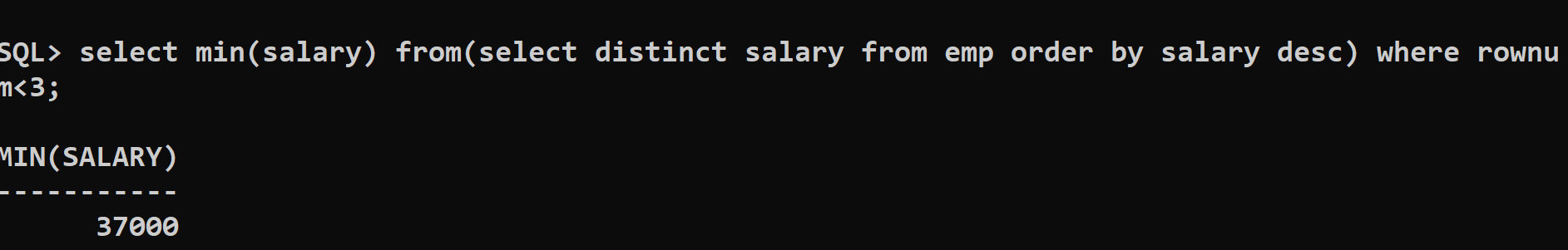
The SQL query to calculate second highest salary in database table name as Emp
Query: 1
(select distinct salary from emp order by salary desc)
where rownum < 3;
In order to calculate the second highest salary use rownum < 3
In order to calculate the third highest salary use rownum < 4
Output:
MIN(SALARY)
-----------
37000
The Structure and data in Emp Table
The Output Screen
Let us understand how this query is working:
Step 1: First this part of the query will get executed then the outer part of the query will act on the result produced by this query: select distinct salary from emp order by salary desc
As you can see that few employees are getting the same salary (for example Bhaskar, Parul, and Chandan, Garima are getting the same salary, therefore we have used distinct keyword, order by salary desc will arrange salary in descending order.
The output of select distinct salary from emp order by salary desc
SALARY
----------
40000
37000
32000
30000
28000
25000
20000
Step 2: SQL> select min(salary) from
(select distinct salary from emp order by salary desc)
where rownum < 3;
In step two we are applying the outer part of the nested query into the results we obtained from the internal query.
Select min(salary) from: will select min salary as 20000 which is not the second-highest salary, because of which we have used rownum < 3, the rownum < 3 will only give the number of rows from the top which is less than 3 i.e. 2.
The output of rownum< 3 will be:
SALARY
----------
40000
37000
Step 3: Now select min(salary).
The output will be:
SALARY
----------
37000
37000 is the second-highest salary.
Simillarly to find:
To find 3rd highest salary set rownum < 4
To find 4th highest salary set rownum < 5
And so on...
The SQL query to calculate second highest salary in database table name as Emp
Query: 2
select ename, salary, dense_rank()
over(order by salary desc)rank from Emp)
where rank = & num;
In order to calculate the second highest salary use num = 2
In order to calculate the third highest salary use num = 3
and so on...
Output:
ENAME SALARY Rank ------------ ---------- ---------- ravi 37000 2
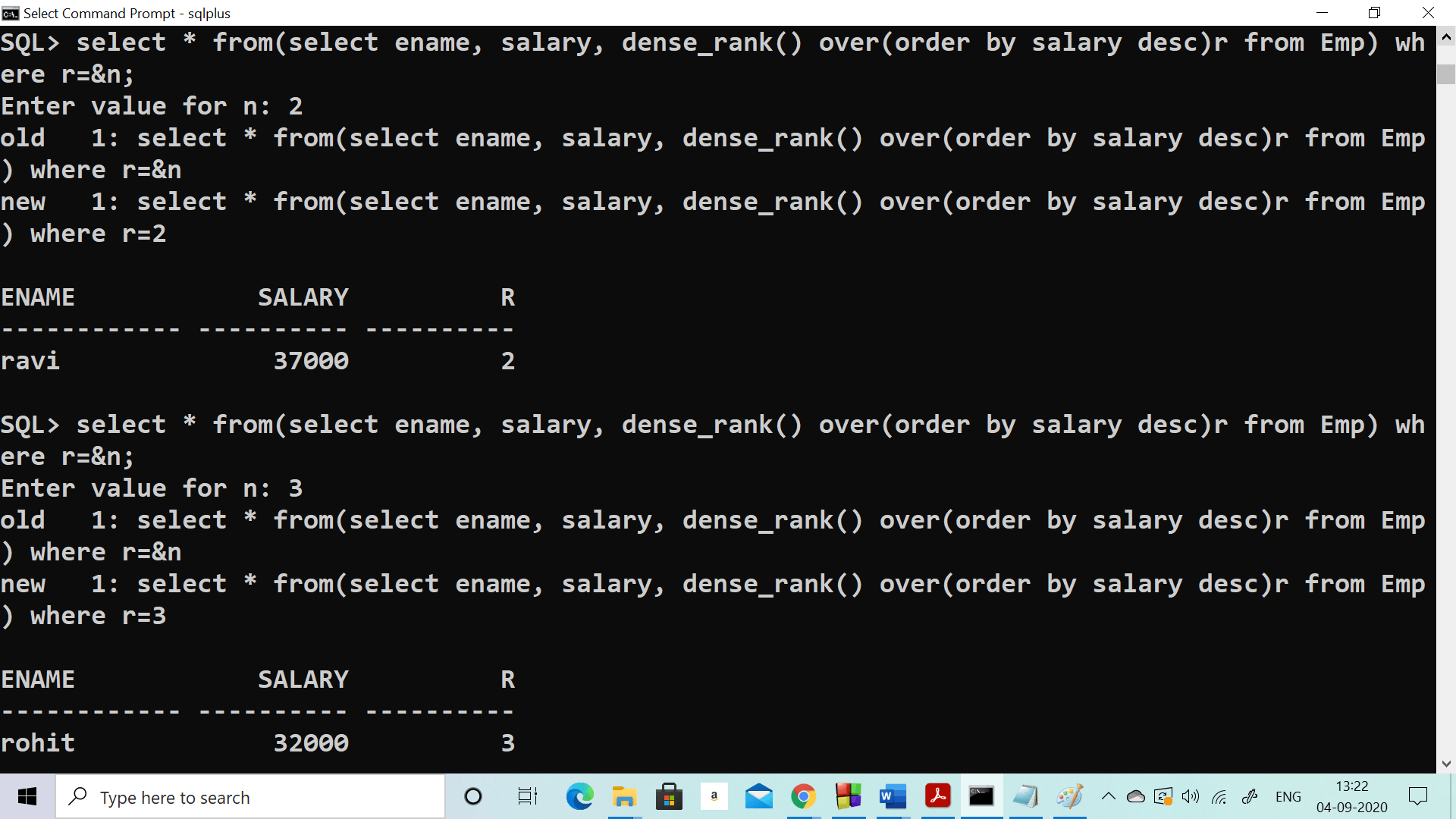
Let us understand how this query is working:
Step 1: First this part of the query will get executed then the outer part of the query will act on the result produced by this query :
select ename, salary, dense_rank() over(order by salary desc)rank from Emp
dense_rank() calculates the rank of each row in an ordered group of rows and returns the rank as a number. The ranks start from integer 1 and so on in a consecutive manner.
If we talk about the above SQL query, based on the salary of the emp table the rank is returned. In case two or more than two rows have an equal salary, it assigns an equal rank to all the rows.
As you can see that few employees are getting the same salary(for example Bhaskar, Parul, and Chandan, Garima are getting the same salary, therefore we have used dense_rank(), order by salary desc will arrange salary in descending order.
Output of : select ename, salary, dense_rank() over(order by salary desc)rank from Emp
ENAME SALARY RANK
------------ ---------- ----------
sonoo 40000 1
ravi 37000 2
rohit 32000 3
bhaskar 30000 4
parul 30000 4
akshita 28000 5
durgesh 28000 5
garima 25000 6
chandan 25000 6
amit 20000 7
you can see from the output that Bhaskar, Parul are getting rank 4 as they both are getting equal salary) and Akshita, Durgesh are getting rank 4(as they both are getting equal salary) similarly Garima and Chandan.
Step 2: SQL> select * from(
select ename, salary, dense_rank()
over(order by salary desc)rank from Emp)
where r = &n;
In step 2 we are applying the outer part of the nested query into the result we obtained from the internal query.
Select * from: will select all the rows which are not the second-highest salary, because of which we have used r = &n, the r = &n will only give the matching rows according to the values entered by the user for n. if n = 2 resultant will be
Output for n = 2 will be:
Enter the value for n: 2
old 1: select * from(select ename, salary, dense_rank() over(order by salary desc)r from Emp) where r=&n
new 1: select * from(select ename, salary, dense_rank() over(order by salary desc)r from Emp) where r=2
ENAME SALARY R
------------ ---------- ----------
ravi 37000 2
To Find fourth highest salary:
Enter value for n: 4
old 1: select * from(select ename, salary, dense_rank() over(order by salary desc)r from Emp) where r=&n
new 1: select * from(select ename, salary, dense_rank() over(order by salary desc)r from Emp) where r=4
ENAME SALARY R
------------ ---------- ----------
bhaskar 30000 4
parul 30000 4
Similarly, to find:
To find 5th highest salary set n = 5
To find 6th highest salary set n = 6
And so on...
The SQL query to calculate second highest salary in database table name as Emp
Let's say the job is to calculate the Nth highest salary of employee from the above table. The procedure is as follows:
- First task is to Identify the employee having TOP n non similar(distinct) salary.
- Calculate the minimum salary among all the salaries resulted from above query, by doing this we get nth highest salary.
- From the result of above query, identify the details of the employee whose salary is the minimum salary.
Query No: 3
where salary IN (select distinct TOP N
salary from emp order by salary desc )
)
The above SQL query will find out the details of the emp with the nth highest salary.
Let's see the working of the above SQL query in detail:
- Consider n = 5.
The processing done by server is that, it starts with most inner query, the query: "select distinct TOP 5 salary from emp order by salary desc" will generate following result:
• 37000
• 32000
• 30000
• 28000
- The next outer query is: "select min(salary) from emp where salary IN (the result of a previous SQL query )". This will produce the following result:
From above result it is verified that the required Fifth highest salary is 28000.
- Lastly, the query which is outer most, is: "select * from emp where salary = result of previous SQL query ". The result of this query will be the details of employees having Fifth highest salary.
• ename salary
• ________________________
• akshita | 28000
• |
Working of query
As these queries are nested queries so this query involves the use of an inner query. There are two versions of Inner queries. Correlated and Uncorrelated queries. Uncorrelated queries are those where the inner query can run independently of the outer query, and the correlated query is those where the inner query runs in conjunction with the outer query. The query we took to calculate nth highest salary is an example of a correlated query.
Performance analysis of SQL query
From the above, we have learned that the inner query executes every time, single row of the outer query is processed, this ultimately brings a lot of performance overhead, especially when the number of rows is very large.
To avoid this, it is recommended to use Data Base specific keywords to get the result faster.


