SQL Tutorial
SQL Database
SQL Table
SQL Select
SQL Order By
SQL Insert
SQL Update
SQL Delete
Difference
SQL Injection
SQL String Functions
Miscl
- SQL Formatter
- SQL group by
- SQL add/drop/update column operation
- SQL CAST Function
- SQL Comments
- SQL CONCAT Function
- CTE (Common Table Expression)SQL
- How to use distinct in SQL?
- Joining Three or More Tables in SQL
- What is Web SQL?
- How to create functions in SQL?
- How to run SQL Script?
- How to Delete Duplicate Rows in SQL?
- Nth Highest salary
- 12 Codd's Rules
- SQL EXCEPT
- Types of SQL JOIN
- Change datatype of column in SQL
- SQL Auto Increment
- SQL Like
- Commit and Rollback in SQL
- SQL Concatenate
- SQL get month from the date
- Savepoint in SQL
- SQL ORDER BY DATE
- TIME Datatype in SQL
- SQL BETWEEN
- CRUD Operations in SQL
- SQL INDEX
- Scalar Functions in SQL
- SET Operators in SQL
- Types of SQL Commands
- TCL Commands in SQL
- SQL Subquery
- SQL View
- Constraints in SQL
- Pattern Matching in SQL
- SQL Date Functions
- DDL Commands in SQL
- DML Commands in SQL
- SQL CASE
- SQL Inner Join
- SQL IN Operator
- Check Constraint in SQL
- SQL CLAUSES
- SQL LOGICAL OPERATORS
- Delete Column from Table
- Add Column in the Table
- Delete one row in SQL
- Change the Column Value
- How to Add Foreign Key in SQL
- Add a Primary Key
- Insert One or More rows
- How to Use LIKE in SQL
- Cursor in SQL
- Difference Between DROP and Truncate
- SQL Comparison Operators
- SQL COUNT WHERE
- SQL SELECT MIN
- SQL Stored Procedure
- SQL SELECT AVG
- SQL SELECT MAX
- SQL ADD COLUMN
- How to use Auto-Increment in SQL
- SQL Languages
- SQL Arithmetic Operators
- How to Use GROUP BY in SQL
- How to Use ORDER BY in SQL
- Trigger in SQL
- What is Race Condition
- SQL COUNT DISTINCT
PL/SQL Tutorial
Sql Interview Question
SQl Quiz
SQL OR
The SQL OR condition is used in SQL query to create a SQL statement where records are returned when any one condition met. It can be used in a SELECT statement, INSERT statement, UPDATE statement or DELETE statement.
Let's see the syntax for the OR condition:
| ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harshad | Kuwar | Marketing | Pune |
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
| 3 | Chaitali | Tarle | IT | Chennai |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
| 5 | Suraj | Tripathi | Marketing | Pune |
| 6 | Roshni | Jadhav | Finance | Bangalore |
| 7 | Sandhya | Jain | Finance | Bangalore |
- SQL "OR" example with SQL SELECT
This is how an SQL "OR" condition can be used in the SQL SELECT statement.
Example 1:
Write a query to get the records from emp tables in which department of the employee is IT or location is Chennai.
Query:
| ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
| 3 | Chaitali | Tarle | IT | Chennai |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
In the emp table, there are three employees whose department is IT. But there are only two records whose location is Chennai. Still, all three records are displayed. This happened because we have specified OR operator in the query, according to which the record will be considered in the result set even any one condition is met.
Example 2:
Write a query to get the records from emp tables in which department of the employee is Marketing or location is Noida.
Query:
| ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harshad | Kuwar | Marketing | Pune |
| 5 | Suraj | Tripathi | Marketing | Pune |
| 7 | Sandhya | Jain | Finance | Bangalore |
There are two employees whose department is Marketing in the emp table, but still, three records are displayed. This happened because of the use of the OR operator in the query. Among the three records displayed above, the first two records satisfy condition 1; the second record satisfies both the conditions and the third record satisfies only condition 1. Due to the OR operator, even if anyone condition is satisfied, the record is considered in the result-set.
- SQL "OR" example with SQL UPDATE
This is how the "OR" condition can be used in the SQL UPDATE statement.
Example 1:
Write a query to update the records in emp tables in which department of the employee is Marketing, or the last name is Tarle. For that particular employee, set the updated value of the location as Delhi.
Query:

We will use the SELECT query to verify the updated record.
| ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harshad | Kuwar | Marketing | Pune |
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
| 3 | Chaitali | Tarle | IT | Chennai |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
| 5 | Suraj | Tripathi | Marketing | Pune |
| 6 | Roshni | Jadhav | Finance | Bangalore |
| 7 | Sandhya | Jain | Finance | Bangalore |
There are two employees whose department is 'Marketing' and one record whose last name is 'Tarle' in the emp table. Though only one condition is still met, that record is considered and updated in the table due to the OR operator.
Example 2:
Write a query to update the records in the emp table in which department of the employee is Finance, or the first name is Sandhya. For that particular employee, set the updated value of the department as HR.
Query:

We will use the SELECT query to verify the updated record.
| ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harshad | Kuwar | Marketing | Delhi |
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
| 3 | Chaitali | Tarle | IT | Delhi |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
| 5 | Suraj | Tripathi | Marketing | Delhi |
| 6 | Roshni | Jadhav | HR | Bangalore |
| 7 | Sandhya | Jain | HR | Noida |
There are two employees whose department is 'Finance,' and among these two records, one record satisfies both the conditions in the emp table. However, both the records are considered and updated in the table due to the OR operator.
- SQL "OR" example with SQL DELETE
This is how an SQL "OR" condition can be used in the SQL DELETE statement.
Example 1:
Write a query to delete the records from the emp table in which the last name of the employee is Jain or Location is Bangalore.
Query:
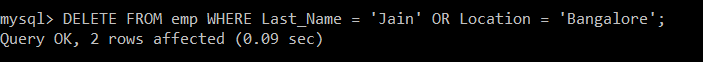
We will use the SELECT query to verify the deleted record.
| ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harshad | Kuwar | Marketing | Pune |
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
| 3 | Chaitali | Tarle | IT | Chennai |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
| 5 | Suraj | Tripathi | Marketing | Pune |
There is only one record in the emp table whose last name is Jain and one record whose location is Bangalore. But still, due to the presence of an OR operator, even if anyone condition is satisfied, that particular record is deleted.
Example 2:
Write a query to delete the records from the emp table in which department of the employee is marketing and Location is Delhi.
Query:
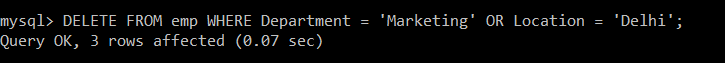
We will use the SELECT query to verify the deleted record.
| ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
There is only one record in the emp table whose department is Marketing and one record whose location is Delhi. But still, due to the presence of an OR operator, even if anyone condition is satisfied, that particular record is deleted.


