SQL Tutorial
SQL Database
SQL Table
SQL Select
SQL Order By
SQL Insert
SQL Update
SQL Delete
Difference
SQL Injection
SQL String Functions
Miscl
- SQL Formatter
- SQL group by
- SQL add/drop/update column operation
- SQL CAST Function
- SQL Comments
- SQL CONCAT Function
- CTE (Common Table Expression)SQL
- How to use distinct in SQL?
- Joining Three or More Tables in SQL
- What is Web SQL?
- How to create functions in SQL?
- How to run SQL Script?
- How to Delete Duplicate Rows in SQL?
- Nth Highest salary
- 12 Codd's Rules
- SQL EXCEPT
- Types of SQL JOIN
- Change datatype of column in SQL
- SQL Auto Increment
- SQL Like
- Commit and Rollback in SQL
- SQL Concatenate
- SQL get month from the date
- Savepoint in SQL
- SQL ORDER BY DATE
- TIME Datatype in SQL
- SQL BETWEEN
- CRUD Operations in SQL
- SQL INDEX
- Scalar Functions in SQL
- SET Operators in SQL
- Types of SQL Commands
- TCL Commands in SQL
- SQL Subquery
- SQL View
- Constraints in SQL
- Pattern Matching in SQL
- SQL Date Functions
- DDL Commands in SQL
- DML Commands in SQL
- SQL CASE
- SQL Inner Join
- SQL IN Operator
- Check Constraint in SQL
- SQL CLAUSES
- SQL LOGICAL OPERATORS
- Delete Column from Table
- Add Column in the Table
- Delete one row in SQL
- Change the Column Value
- How to Add Foreign Key in SQL
- Add a Primary Key
- Insert One or More rows
- How to Use LIKE in SQL
- Cursor in SQL
- Difference Between DROP and Truncate
- SQL Comparison Operators
- SQL COUNT WHERE
- SQL SELECT MIN
- SQL Stored Procedure
- SQL SELECT AVG
- SQL SELECT MAX
- SQL ADD COLUMN
- How to use Auto-Increment in SQL
- SQL Languages
- SQL Arithmetic Operators
- How to Use GROUP BY in SQL
- How to Use ORDER BY in SQL
- Trigger in SQL
- What is Race Condition
- SQL COUNT DISTINCT
PL/SQL Tutorial
Sql Interview Question
SQl Quiz
Joining Three or More Tables in SQL
Joining multiple tables in SQL is some tricky task. It can be more difficult if you need to join more than two tables in single SQL query, we will analyze how to retrieve data from multiple tables using INNER JOINs. In this section, we have used two approaches to join three or more tables in SQL.
Example:
We are creating three tables, as follows:
- student
- marks
- details
Table 1: student
insert into student values(1, 'Jack');
insert into student values(2, 'Rithvik');
insert into student values(3, 'Jaspreet');
insert into student values(4, 'Praveen');
insert into student values(5, 'Bisa');
insert into student values(6, 'Suraj');
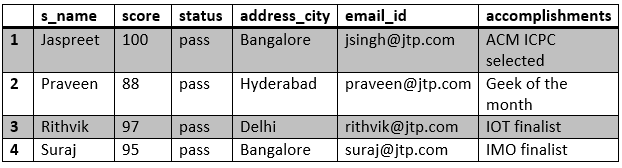
STUDENT TABLE
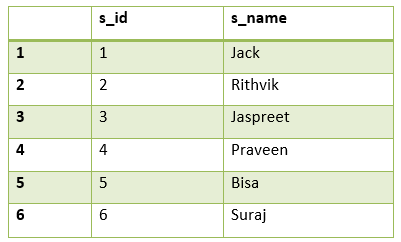
In the above table s_id is the primary key.
Table 2: marks
insert into marks values(1004, 1, 23, 'fail');
insert into marks values(1008, 6, 95, 'pass');
insert into marks values(1012, 2, 97, 'pass');
insert into marks values(1016, 7, 67, 'pass');
insert into marks values(1020, 3, 100, 'pass');
insert into marks values(1025, 8, 73, 'pass');
insert into marks values(1030, 4, 88, 'pass');
insert into marks values(1035, 9, 13, 'fail');
insert into marks values(1040, 5, 16, 'fail');
insert into marks values(1050, 10, 53, 'pass');
MARKS TABLE
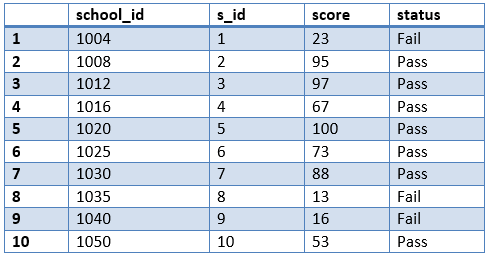
In the above table, school_id is primary key and s_id is the foreign key.
Table 3: details
insert into details values('Bangalore', 'jsingh@jtp.com',
1020, 'ACM ICPC selected');
insert into details values('Hyderabad', 'praveen@jtp.com',
1030, 'Geek of the month');
insert into details values('Delhi', 'rithvik@jtp.com',
1012, 'IOI finalist');
insert into details values('Chennai', 'om@jtp.com',
1111, 'Geek of the year');
insert into details values('Banglore', ' suraj@jtp.com',
1008, 'IMO finalist');
insert into details values('Mumbai', 'sasukeh@jtp.com',
2211, 'Made a robot');
insert into details values('Ahmedabad', 'itachi@jtp.com',
1172, 'Code Jam finalist');
insert into details values('Jaipur', 'kumar@jtp.com',
1972, 'KVPY finalist');
Output:
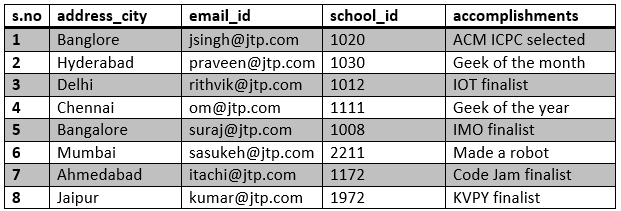
In the above table, school_id is the foreign key.
There are two approaches to join three or more tables in SQL:
1. Using JOINS in SQL:
The same logic is applied here which is used to join two tables i.e., the minimum number of join statements to join n tables are (n-1).
accomplishments from student s inner join mark m on
s.s_id = m.s_id inner join details d on
d.school_id = m.school_id;
Output:
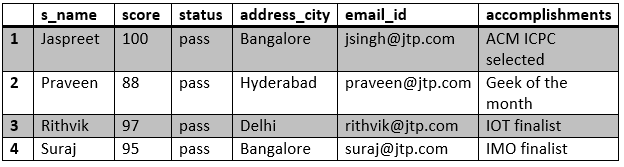
2. Using the Parent-child Relationship:
In the parent-child relationship, we use where clause to join two or more tables. Create column X as a primary key in one table and a foreign key in another table
Look at the tables which are created:
s_id is the primary key in the student table and foreign key in the marks table. (student (parent) - marks(child)).
school_id is the primary key in the marks table and foreign key in the student table. (marks(parent) - details(child)).
Query:
email_id, accomplishments from student s,
marks m, details d where s.s_id = m.s_id and
m.school_id = d.school_id;
Output: