SQL Tutorial
SQL Database
SQL Table
SQL Select
SQL Order By
SQL Insert
SQL Update
SQL Delete
Difference
SQL Injection
SQL String Functions
Miscl
- SQL Formatter
- SQL group by
- SQL add/drop/update column operation
- SQL CAST Function
- SQL Comments
- SQL CONCAT Function
- CTE (Common Table Expression)SQL
- How to use distinct in SQL?
- Joining Three or More Tables in SQL
- What is Web SQL?
- How to create functions in SQL?
- How to run SQL Script?
- How to Delete Duplicate Rows in SQL?
- Nth Highest salary
- 12 Codd's Rules
- SQL EXCEPT
- Types of SQL JOIN
- Change datatype of column in SQL
- SQL Auto Increment
- SQL Like
- Commit and Rollback in SQL
- SQL Concatenate
- SQL get month from the date
- Savepoint in SQL
- SQL ORDER BY DATE
- TIME Datatype in SQL
- SQL BETWEEN
- CRUD Operations in SQL
- SQL INDEX
- Scalar Functions in SQL
- SET Operators in SQL
- Types of SQL Commands
- TCL Commands in SQL
- SQL Subquery
- SQL View
- Constraints in SQL
- Pattern Matching in SQL
- SQL Date Functions
- DDL Commands in SQL
- DML Commands in SQL
- SQL CASE
- SQL Inner Join
- SQL IN Operator
- Check Constraint in SQL
- SQL CLAUSES
- SQL LOGICAL OPERATORS
- Delete Column from Table
- Add Column in the Table
- Delete one row in SQL
- Change the Column Value
- How to Add Foreign Key in SQL
- Add a Primary Key
- Insert One or More rows
- How to Use LIKE in SQL
- Cursor in SQL
- Difference Between DROP and Truncate
- SQL Comparison Operators
- SQL COUNT WHERE
- SQL SELECT MIN
- SQL Stored Procedure
- SQL SELECT AVG
- SQL SELECT MAX
- SQL ADD COLUMN
- How to use Auto-Increment in SQL
- SQL Languages
- SQL Arithmetic Operators
- How to Use GROUP BY in SQL
- How to Use ORDER BY in SQL
- Trigger in SQL
- What is Race Condition
- SQL COUNT DISTINCT
PL/SQL Tutorial
Sql Interview Question
SQl Quiz
How to use distinct in SQL?
SQL DISTINCT clause is used to remove the duplicates columns from the result set.
The distinct keyword is used with select keyword in conjunction. It is helpful when we avoid duplicate values present in the specific columns/tables. The unique values are fetched when we use the distinct keyword.
- SELECT DISTINCT returns only distinct (different) values.
- DISTINCT eliminates duplicate records from the table.
- DISTINCT can be used with aggregates: COUNT, AVG, MAX, etc.
- DISTINCT operates on a single column.
- Multiple columns are not supported for DISTINCT.
Syntax:
FROM tables
[WHERE conditions];
Parameters:
Expressions: The columns or calculations that we want to retrieve are called expression.
Tables: The tables that we want to retrieve the records. There is only one table in the FROM clause.
WHERE conditions: The conditions may meet for the records which are selected and it is optional.
Note:
- When one expression is provided in the DISTINCT clause then the query will return the unique values of the expressions.
- The query will retrieve the unique combinations for the listed expressions if more than one expression is provided in the DISTINCT clause here.
- In SQL, the DISTINCT clause cannot ignore the NULL values. So when we use the DISTINCT clause in the SQL statement, our result set will include NULL as a distinct value.
Example:
Consider the following EMPLOYEES table.
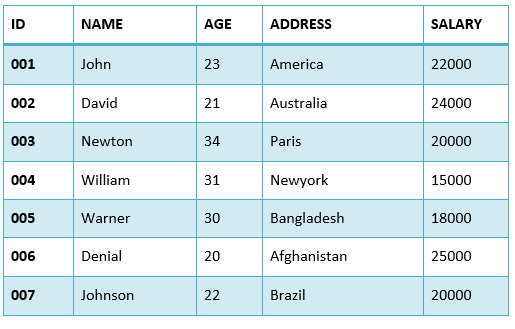
First, let us see the following SELECT query returns the duplicate salary records.
ORDER BY SALARY;
When we execute the above SQL query, it fetches all the records including the duplicate records. In the above table, salary of Newton and Johnson is same 20000.
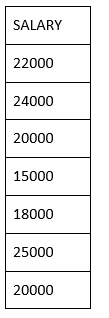
Now, let us use the DISTINCT keyword with the above SELECT query.
ORDER BY SALARY;
The above SQL query removes the duplicate records and shows the following result.
Example: Finding Unique Values in the Column
Look at the DISTINCT clause to find the unique values within one column in the table.
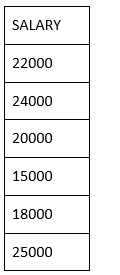
We have a table called suppliers with the following data:
From the above table, we are going to find the unique states.
FROM suppliers
ORDER BY state;
These are six the records.
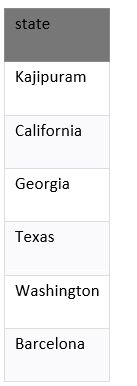
The example returns the unique state from suppliers table and removes the duplicate records from the result set.
Example: Finding Unique Values in Multiple Column
The SQL DISTINCT clause is used to remove the duplicate records from many fields in the SELECT statement.
Enter the SQL statement:
FROM suppliers
ORDER BY city, state;
Output:
These are 8 records:
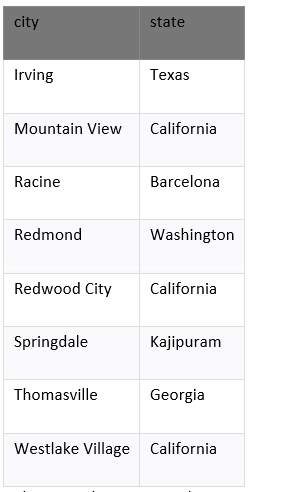
The example returns each unique city and state combination. We see the Redwood City and California, appears in the result set.
Example: DISTINCT Clause handles NULL Values
The DISTINCT clause considers NULL to the unique value in SQL. We have a table called products which contains the below data.
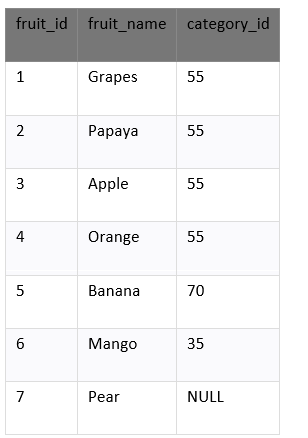
Select the unique values from the field fruit_id which contains the null value. Enter the below SQL syntax:
FROM fruits
ORDER BY category_id;
There are four records selected. These are the results which we see below:

In the above example, the query returns the unique values that are in the category_id column. We see by the first row in the result set, NULL is an exceptional value which is returned by the DISTINCT clause.


