Node.js Tutorial
- Node.js Tutorial
- Install Node.js on Windows
- Install Node.js on Linux/Ubuntu/CentOS
- Node.js First Example
- Node.js Console
- Node.js REPL
- Node.js Package Manager
- Node.js Command Line Options
- Node.js Global Objects
- Node.js OS
- Node.js Timer
- Node.js Errors
- Node.js DNS
- Node.js Net
- Node.js Crypto
- Node.js TLS/SSL
- Node.js Debugger
- Node.js Process
- Node.js Child Process
- Node.js Buffers
- Node.js Streams
- Node.js File System (FS)
- Node.js Path
- Node.js StringDecoder
- Node.js Query String
- Node.js ZLIB
- Node.js Assertion Testing
- Node.js V8
- Node.js Callbacks
- Node.js Events
- Node.js Punycode
- Node.js TTY
- Node.js Web Module
- NestJS
Node.js MySQL
Node.js MongoDB
Nodejs Difference
Node.js MCQ
Node.js Express
Nodejs Interview Questions
Node.js OS
Node.js OS provides some basic operating-system related utility functions. Let's see the list generally used functions or methods.
| Index | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | os.arch() | This method is used to fetch the operating system CPU architecture. |
| 2. |
os.cpus() |
This method is used to fetch an array of objects containing information about each cpu/core installed: model, speed (in MHz), and times (an object containing the number of milliseconds the cpu/core spent in: user, nice, sys, idle, and irq). |
| 3. | os.endianness() | This method returns the endianness of the cpu. Its possible values are 'BE' for big endian or 'LE' for little endian. |
| 4. | os.freemem() | This methods returns the amount of free system memory in bytes. |
| 5. | os.homedir() | This method returns the home directory of the current user. |
| 6. |
os.hostname() |
This method is used to returns the hostname of the operating system. |
| 7. | os.loadavg() | This method returns an array containing the 1, 5, and 15 minute load averages. The load average is a time fraction taken by system activity, calculated by the operating system and expressed as a fractional number. |
| 8. | os.networkinterfaces() | This method returns a list of network interfaces. |
| 9. | os.platform() | This method returns the operating system platform of the running computer i.e.'darwin', 'win32','freebsd', 'linux', 'sunos' etc. |
| 10. | os.release() | This method returns the operating system release. |
| 11. | os.tmpdir() | This method returns the operating system's default directory for temporary files. |
| 12. | os.totalmem() | This method returns the total amount of system memory in bytes. |
| 13. | os.type() | This method returns the operating system name. For example 'linux' on linux, 'darwin' on os x and 'windows_nt' on windows. |
| 14. | os.uptime() | This method returns the system uptime in seconds. |
| 15. | os.userinfo([options]) | This method returns a subset of the password file entry for the current effective user. |
Node.js OS Example 1
In this example, we are including some basic functions. Create a file named os_example1.js having the following code:
File: os_example1.js
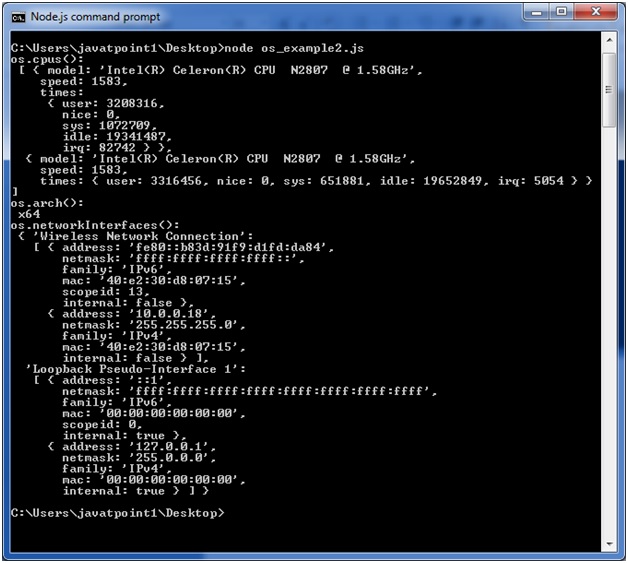
- const os=require('os');
- console.log("os.freemem(): \n",os.freemem());
- console.log("os.homedir(): \n",os.homedir());
- console.log("os.hostname(): \n",os.hostname());
- console.log("os.endianness(): \n",os.endianness());
- console.log("os.loadavg(): \n",os.loadavg());
- console.log("os.platform(): \n",os.platform());
- console.log("os.release(): \n",os.release());
- console.log("os.tmpdir(): \n",os.tmpdir());
- console.log("os.totalmem(): \n",os.totalmem());
- console.log("os.type(): \n",os.type());
- console.log("os.uptime(): \n",os.uptime());
Open Node.js command prompt and run the following code:
- node os_example1.js
Node.js OS Example 2
In this example, we are including remaining functions. Create a file named os_example2.js having the following code:
File: os_example2.js
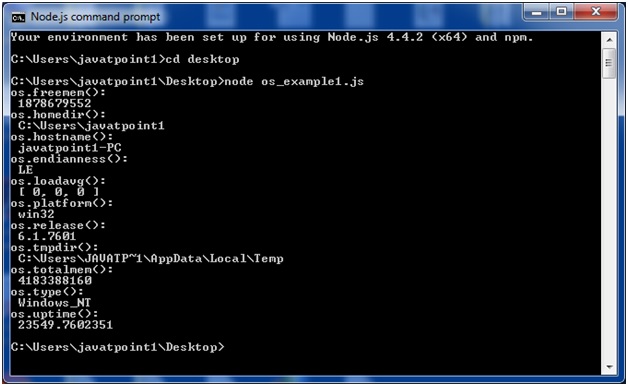
- const os=require('os');
- console.log("os.cpus(): \n",os.cpus());
- console.log("os.arch(): \n",os.arch());
- console.log("os.networkInterfaces(): \n",os.networkInterfaces());
Open Node.js command prompt and run the following code:
- node os_example2.js