Node.js Tutorial
- Node.js Tutorial
- Install Node.js on Windows
- Install Node.js on Linux/Ubuntu/CentOS
- Node.js First Example
- Node.js Console
- Node.js REPL
- Node.js Package Manager
- Node.js Command Line Options
- Node.js Global Objects
- Node.js OS
- Node.js Timer
- Node.js Errors
- Node.js DNS
- Node.js Net
- Node.js Crypto
- Node.js TLS/SSL
- Node.js Debugger
- Node.js Process
- Node.js Child Process
- Node.js Buffers
- Node.js Streams
- Node.js File System (FS)
- Node.js Path
- Node.js StringDecoder
- Node.js Query String
- Node.js ZLIB
- Node.js Assertion Testing
- Node.js V8
- Node.js Callbacks
- Node.js Events
- Node.js Punycode
- Node.js TTY
- Node.js Web Module
- NestJS
Node.js MySQL
Node.js MongoDB
Nodejs Difference
Node.js MCQ
Node.js Express
Nodejs Interview Questions
Node.js Command Line Options
There is a wide variety of command line options in Node.js. These options provide multiple ways to execute scripts and other helpful run-time options.
Let's see the list of Node.js command line options:
| Index | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | v, --version | It is used to print node's version. |
| 2. | -h, --help | It is used to print node command line options. |
| 3. | -e, --eval "script" | It evaluates the following argument as JavaScript. The modules which are predefined in the REPL can also be used in script. |
| 4. | -p, --print "script" | It is identical to -e but prints the result. |
| 5. | -c, --check | Syntax check the script without executing. |
| 6. | -i, --interactive | It opens the REPL even if stdin does not appear to be a terminal. |
| 7. | -r, --require module | It is used to preload the specified module at startup. It follows require()'s module resolution rules. Module may be either a path to a file, or a node module name. |
| 8. | --no-deprecation | Silence deprecation warnings. |
| 9. | --trace-deprecation | It is used to print stack traces for deprecations. |
| 10. | --throw-deprecation | It throws errors for deprecations. |
| 11. | --no-warnings | It silence all process warnings (including deprecations). |
| 12. | --trace-warnings | It prints stack traces for process warnings (including deprecations). |
| 13. | --trace-sync-io | It prints a stack trace whenever synchronous i/o is detected after the first turn of the event loop. |
| 14. | --zero-fill-buffers | Automatically zero-fills all newly allocated buffer and slowbuffer instances. |
| 15. | --track-heap-objects | It tracks heap object allocations for heap snapshots. |
| 16. | --prof-process | It processes V8 profiler output generated using the v8 option --prof. |
| 17. | --V8-options | It prints V8 command line options. |
| 18. | --tls-cipher-list=list | It specifies an alternative default tls cipher list. (requires node.js to be built with crypto support. (default)) |
| 19. | --enable-fips | It enables fips-compliant crypto at startup. (requires node.js to be built with ./configure --openssl-fips) |
| 20. | --force-fips | It forces fips-compliant crypto on startup. (cannot be disabled from script code.) (same requirements as --enable-fips) |
| 21. | --icu-data-dir=file | It specifies ICU data load path. (Overrides node_icu_data) |
Node.js Command Line Options Examples
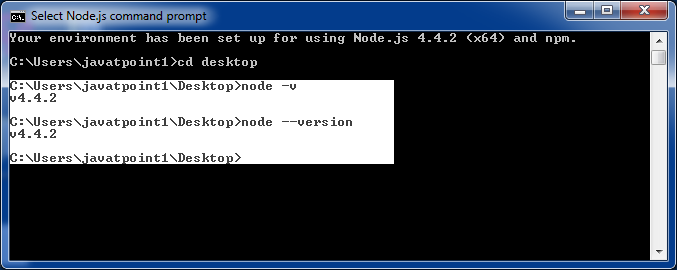
To see the version of the running Node:
Open Node.js command prompt and run command node -v or node --version
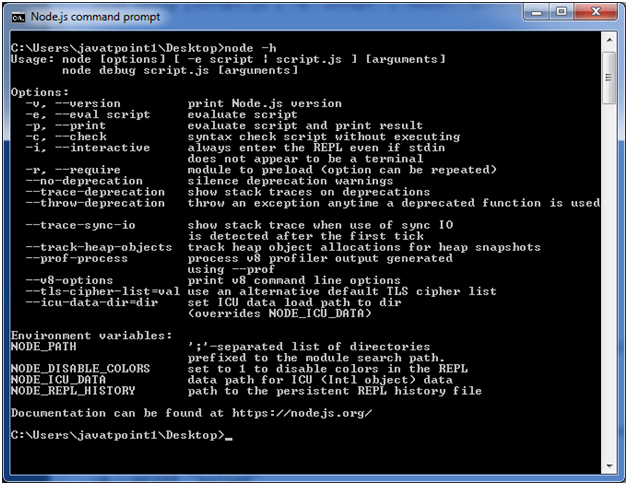
For Help:
Use command node ?h or node --help
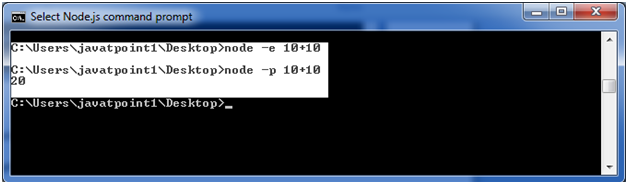
To evaluate an argument (but not print result):
Use command node -e, --eval "script"
To evaluate an argument and print result also:
Use command node -p "script"
To open REPL even if stdin doesn't appear:
Use command node -i, or node --interactive


