Node.js Tutorial
- Node.js Tutorial
- Install Node.js on Windows
- Install Node.js on Linux/Ubuntu/CentOS
- Node.js First Example
- Node.js Console
- Node.js REPL
- Node.js Package Manager
- Node.js Command Line Options
- Node.js Global Objects
- Node.js OS
- Node.js Timer
- Node.js Errors
- Node.js DNS
- Node.js Net
- Node.js Crypto
- Node.js TLS/SSL
- Node.js Debugger
- Node.js Process
- Node.js Child Process
- Node.js Buffers
- Node.js Streams
- Node.js File System (FS)
- Node.js Path
- Node.js StringDecoder
- Node.js Query String
- Node.js ZLIB
- Node.js Assertion Testing
- Node.js V8
- Node.js Callbacks
- Node.js Events
- Node.js Punycode
- Node.js TTY
- Node.js Web Module
- NestJS
Node.js MySQL
Node.js MongoDB
Nodejs Difference
Node.js MCQ
Node.js Express
Nodejs Interview Questions
Node.js Callbacks
Callback is an asynchronous equivalent for a function. It is called at the completion of each task. In Node.js, callbacks are generally used. All APIs of Node are written in a way to supports callbacks. For example: when a function start reading file, it returns the control to execution environment immediately so that the next instruction can be executed.
In Node.js, once file I/O is complete, it will call the callback function. So there is no blocking or wait for File I/O. This makes Node.js highly scalable, as it can process high number of request without waiting for any function to return result.
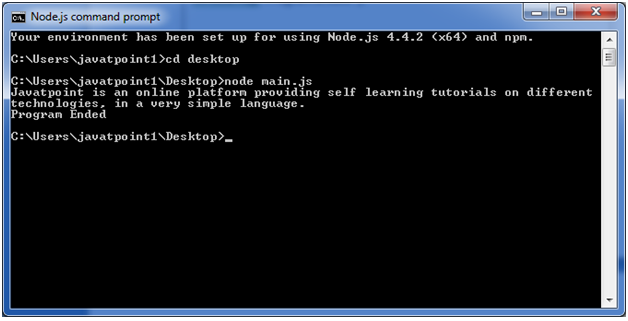
Blocking Code Example
Follow these steps:
- Javatpoint is an online platform providing self learning tutorials on
- different technologies, in a very simple language.
- var fs = require("fs");
- var data = fs.readFileSync('input.txt');
- console.log(data.toString());
- console.log("Program Ended");
- node main.js
- Create a text file named input.txt having the following content:
- Create a JavaScript file named main.js having the following code:
- Open the Node.js command prompt and execute the following code.
Non Blocking Code Example
Follow these steps:
- Javatpoint is an online platform providing self learning tutorials on
- different technologies, in a very simple language.
- var fs = require("fs");
- fs.readFile('input.txt', function (err, data) {
- if (err) return console.error(err);
- console.log(data.toString());
- });
- console.log("Program Ended");
- node main.js
- Create a text file named input.txt having the following content:
- Create a JavaScript file named main.js having the following code:
- Open the Node.js command prompt and execute the following code.
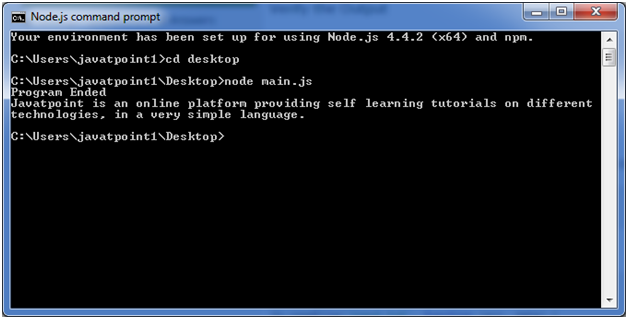
You can see that above two examples explain the concept of blocking and non-blocking calls. The first example shows that program blocks until it reads the file and then only it proceeds to end the program on the other hand in second example, program does not wait for file reading but it just proceeded to print "Program Ended" and same time program without blocking continues reading the file.
So we can say that, a blocking program executes very much in sequence. It is also easier to implement the logic from programming point of view in block programs. But non-blocking programs does not execute in sequence, so in case a program needs to use any data to be processed, it should be kept with-in the same block to make it sequential execution.


