Node.js Tutorial
- Node.js Tutorial
- Install Node.js on Windows
- Install Node.js on Linux/Ubuntu/CentOS
- Node.js First Example
- Node.js Console
- Node.js REPL
- Node.js Package Manager
- Node.js Command Line Options
- Node.js Global Objects
- Node.js OS
- Node.js Timer
- Node.js Errors
- Node.js DNS
- Node.js Net
- Node.js Crypto
- Node.js TLS/SSL
- Node.js Debugger
- Node.js Process
- Node.js Child Process
- Node.js Buffers
- Node.js Streams
- Node.js File System (FS)
- Node.js Path
- Node.js StringDecoder
- Node.js Query String
- Node.js ZLIB
- Node.js Assertion Testing
- Node.js V8
- Node.js Callbacks
- Node.js Events
- Node.js Punycode
- Node.js TTY
- Node.js Web Module
- NestJS
Node.js MySQL
Node.js MongoDB
Nodejs Difference
Node.js MCQ
Node.js Express
Nodejs Interview Questions
Node.js Errors
The Node.js applications generally face four types of errors:
- Standard JavaScript errors i.e. <EvalError>, <SyntaxError>, <RangeError>, <ReferenceError>, <TypeError>, <URIError> etc.
- System errors
- User-specified errors
- Assertion errors
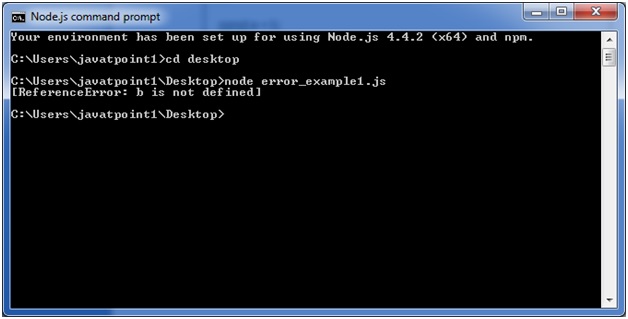
Node.js Errors Example 1
Let's take an example to deploy standard JavaScript error - ReferenceError.
File: error_example1.js
- // Throws with a ReferenceError because b is undefined
- try {
- const a = 1;
- const c = a + b;
- } catch (err) {
- console.log(err);
- }
Open Node.js command prompt and run the following code:
- node error_example1.js
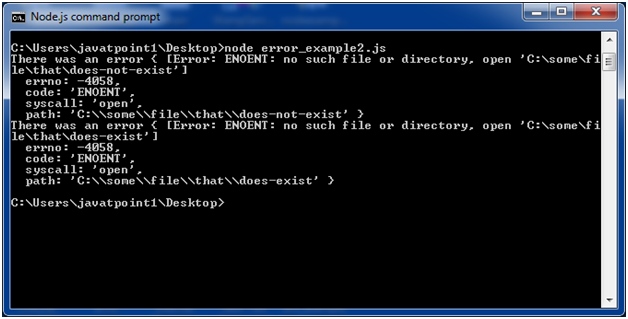
Node.js Errors Example 2
File: timer2.js
- const fs = require('fs');
- function nodeStyleCallback(err, data) {
- if (err) {
- console.error('There was an error', err);
- return;
- }
- console.log(data);
- }
- fs.readFile('/some/file/that/does-not-exist', nodeStyleCallback);
- fs.readFile('/some/file/that/does-exist', nodeStyleCallback);
Open Node.js command prompt and run the following code:
- node error_example2.js