Azure Tutorial
Azure Storage Service
Network Services
Compute Services
App Services
Database Service
Azure Misc
- What is MS Azure Functions
- What is ETL
- What is Microsoft Azure Instance
- What is Databrick
- Why is PowerShell Used
- What is a Notebook in Ms Azure
- What is Azure Resource Manager
- What is a container group In Microsoft Azure
- What is Microsoft Azure Functions Premium plan
- What is Microsoft Azure Subscription
- What is Azure Lighthouse
- Active Directory Identity in Azure and access management operations
- What is Privileged Access Management for Active Directory Domain Services in Azure
- What is the difference between Azure DevOps Server and Azure DevOps Services
- Azure Fundamentals
Azure Interview Questions
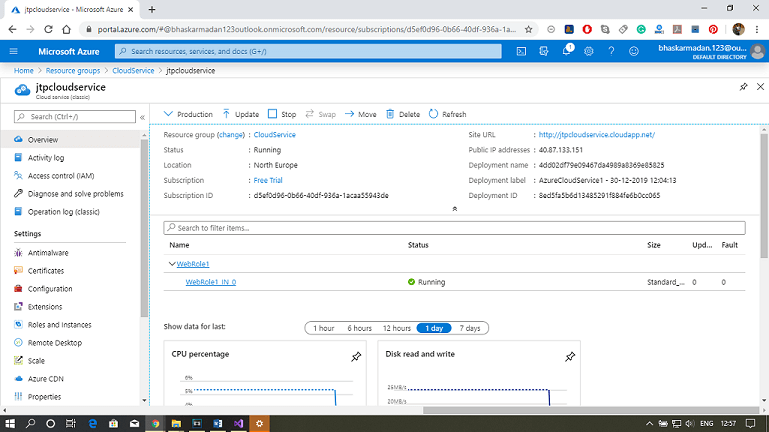
Azure Cloud Service
Cloud Service is a Platform as a Service that is designed to support web applications that are scalable, reliable, and cheaper to operate. Using cloud service, we can deploy a web application into Azure. We have more control over Virtual Machines. We can install custom software on VMs that uses Azure Cloud Service, and we can access them remotely.
Using cloud service, we don't create virtual machines. Instead, we provide a configuration file that tells Azure how many instances we would like to create, the size of the instance, and the platform will create them for us.
Cloud service is able to detect any failed VMs and applications and ready to start new VMs or application instances when a failure occurs. Cloud service applications shouldn't maintain state in the file system of its own VMs.
Cloud Service Roles
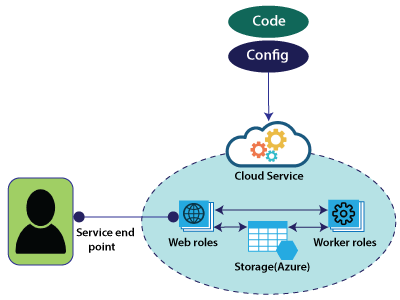
Web role: It automatically deploys and hosts our app through IIS.
Work role: It does not use IIS and runs our app standalone. If we want to run any continuous bathes, then we can use worker roles, and both the Web role and Worker role will interact with storage to get an application package, etc.
To deploy these Web roles and Worker roles, we will provide configuration and code associated with these web applications.
Cloud Service Components
Three key components constitute a cloud service.
- ServiceDefenition.csdef file specifies the settings that are used by Azure to configure the cloud service. For example - sites, endpoints, certificates, etc.
- ServiceConfiguration.cscfg contains the values that will be used to determine the configuration of settings for the cloud service. For example - number of instances, types of instances, ports, etc.
- Service package.cspkg used to deploy the application as a cloud service. First, it needs to be packaged using the CSPacK command-line tool. CSPacK generates an application package file that can be uploaded into Azure using the portal.
Creating cloud service using the Azure portal
Step 1: Click on create a resource and then type-in Cloud Service.
Step 2: After that, click on it and then click on create.
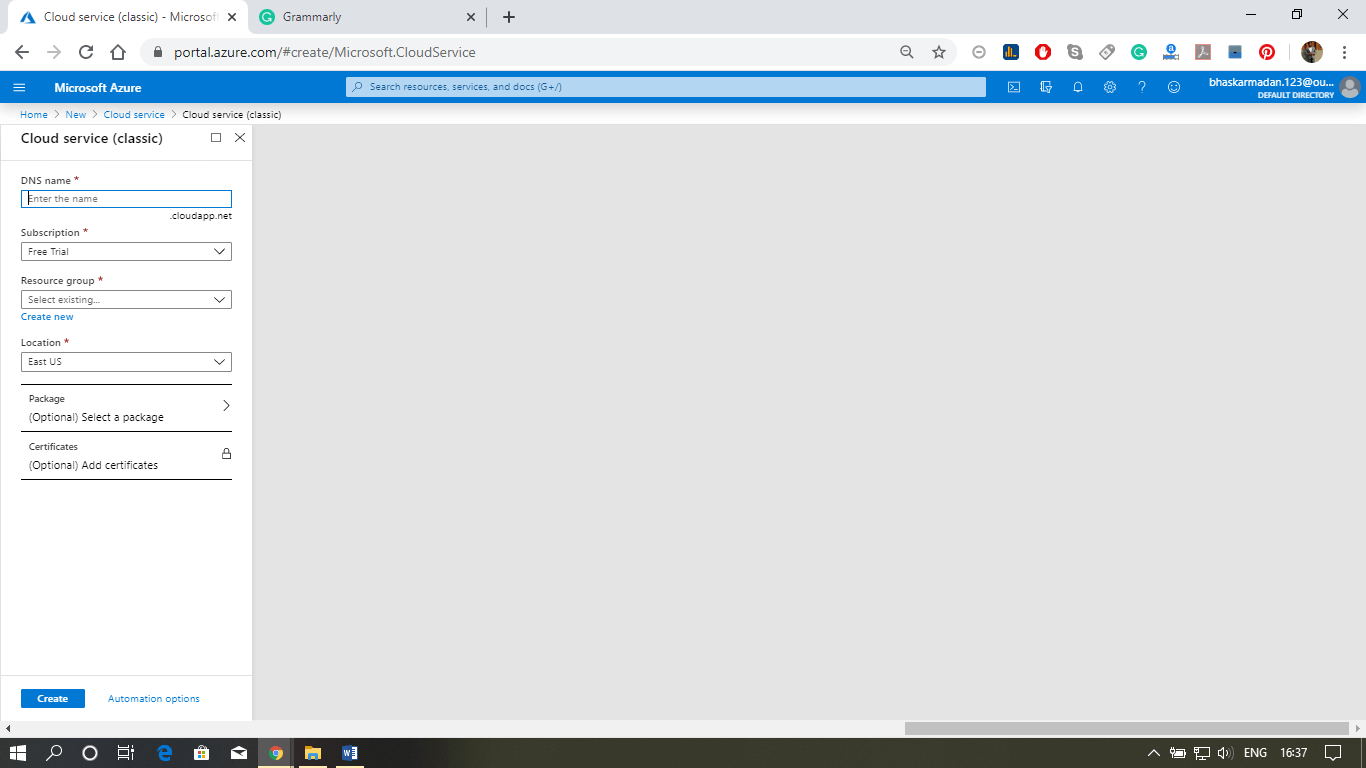
Step 3: Fill-in the DNS name, select the resource group, and location.
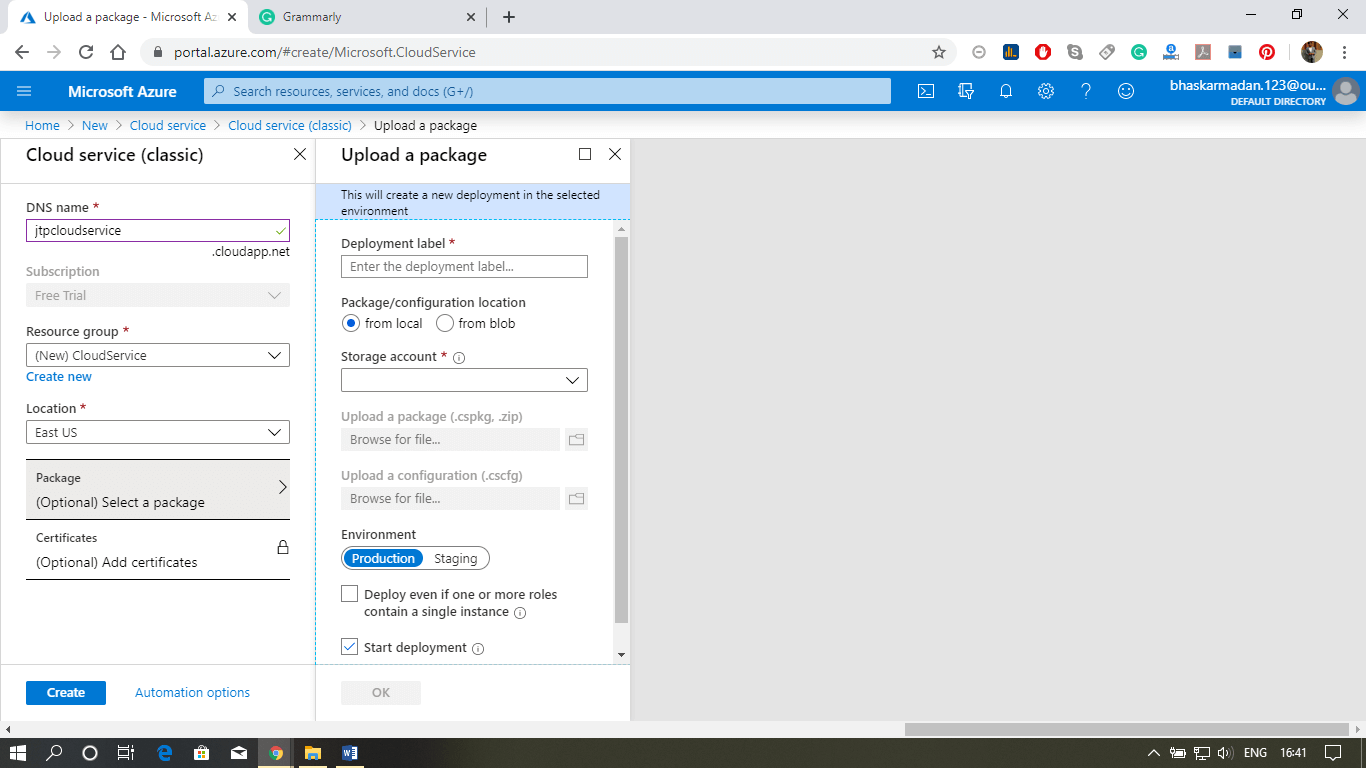
Step 4: Now, Click on create. Your cloud service will be created.
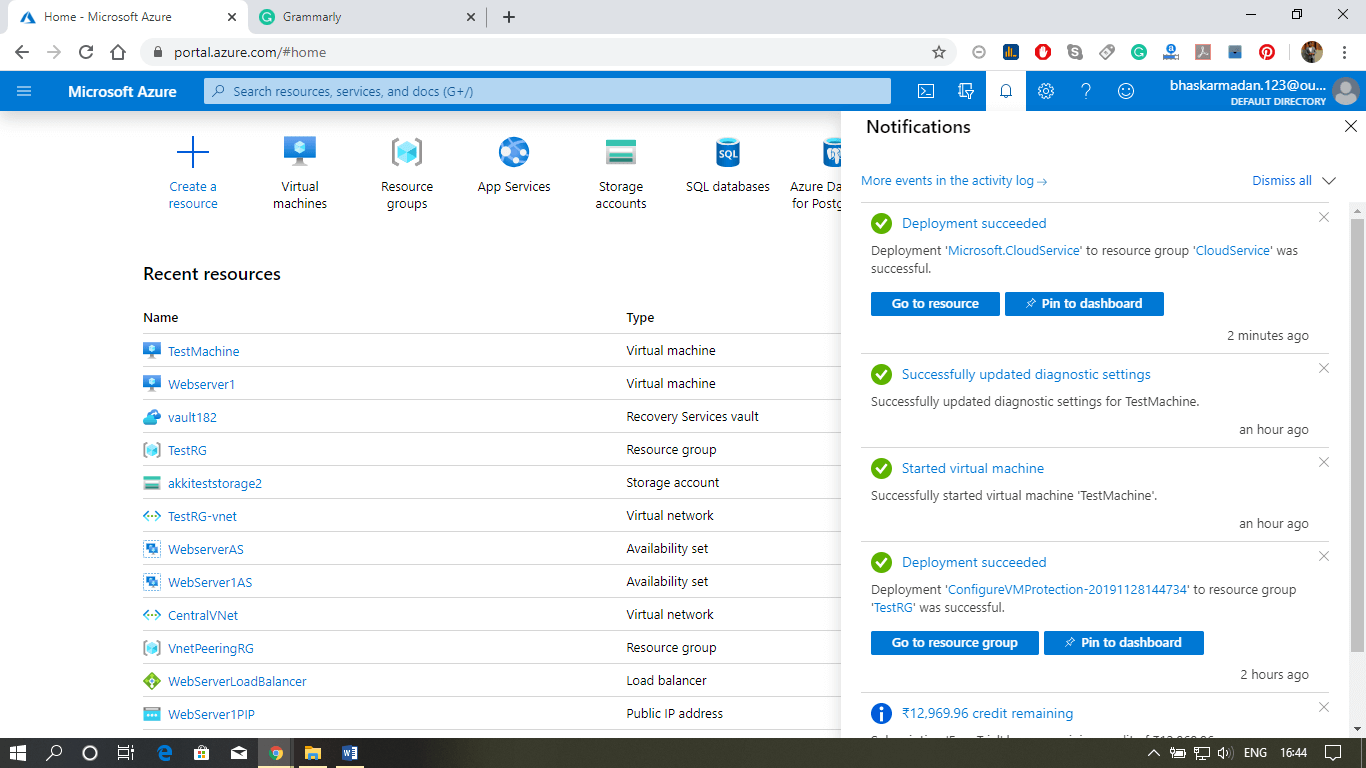
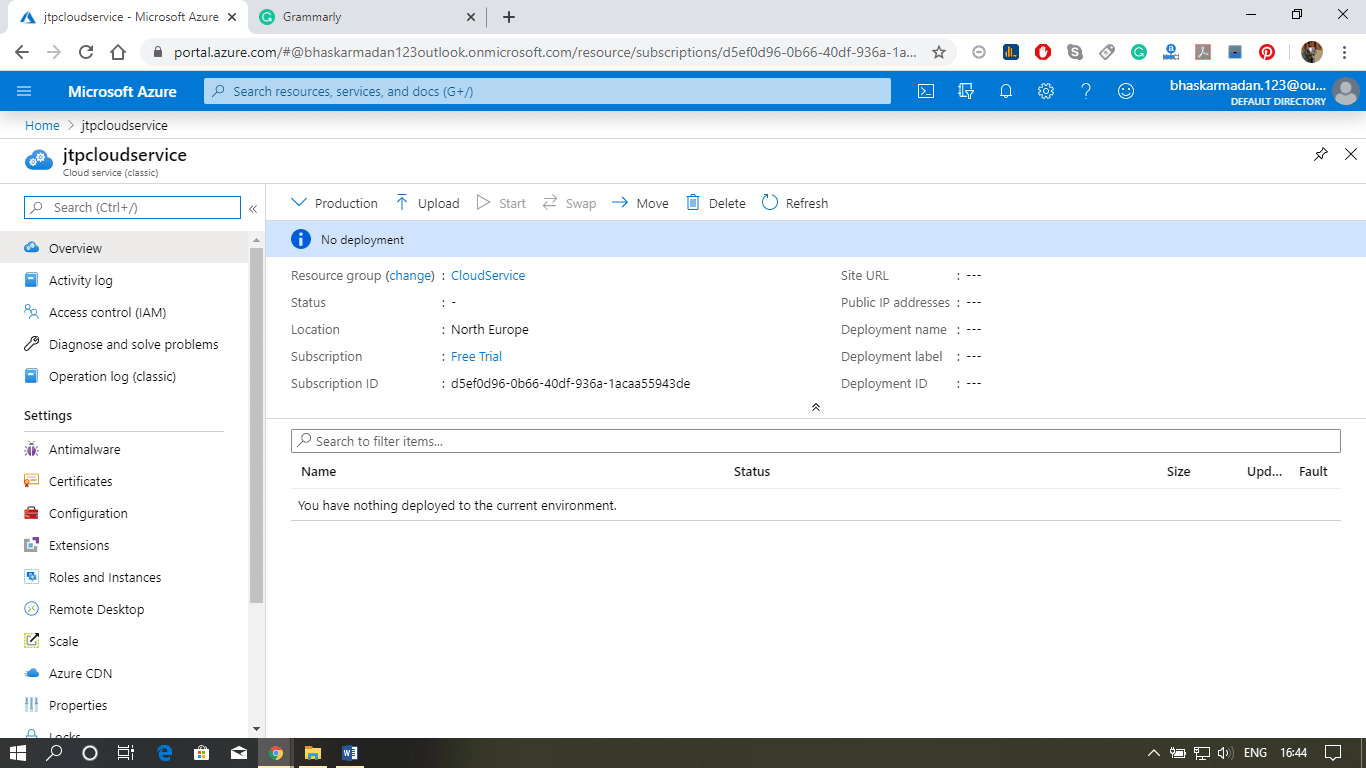
Step 5: To view the cloud service, click on go-to resources.
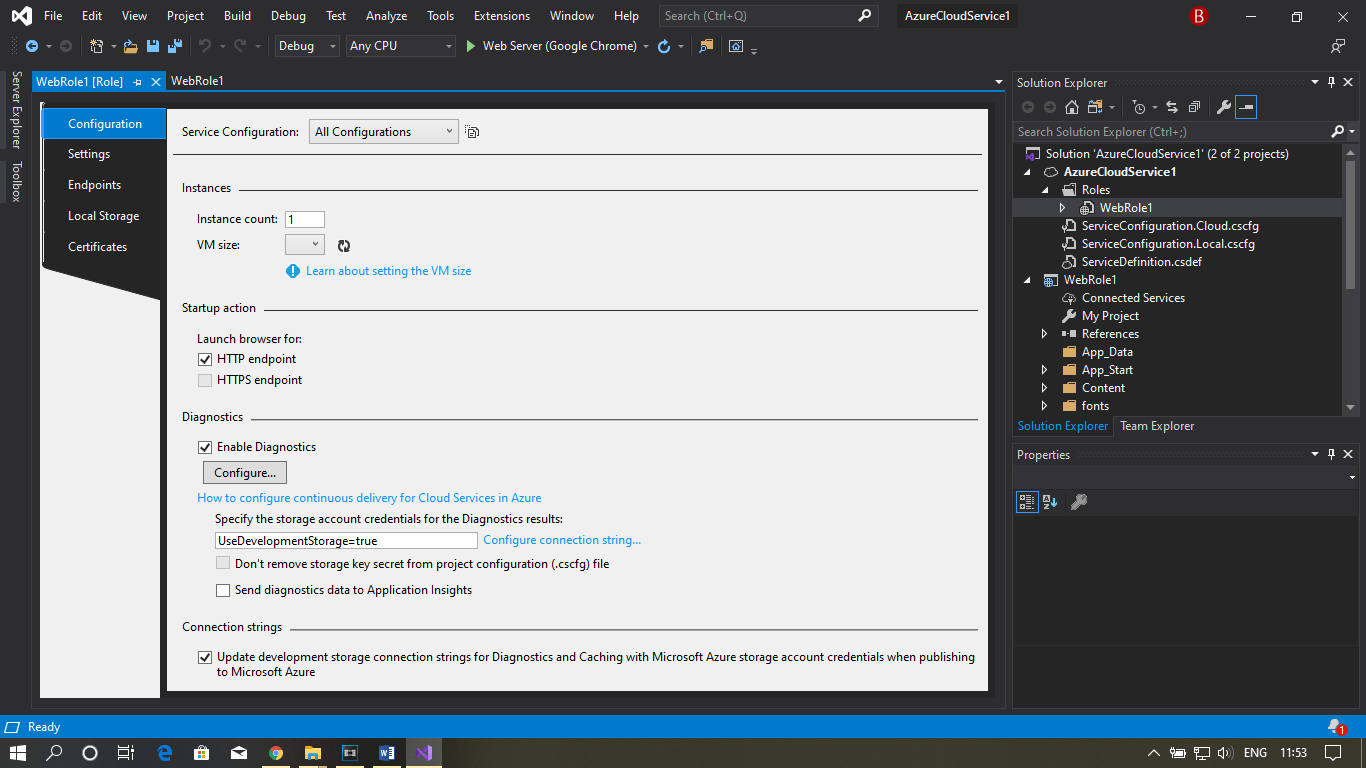
Step 6: Now, go to Visual Studio and create a new cloud service project. Here you can see the basic configuration setting, as shown in the image below.
Step 7: To publish this cloud service into Azure, right-click on the file name. Then click on publish.
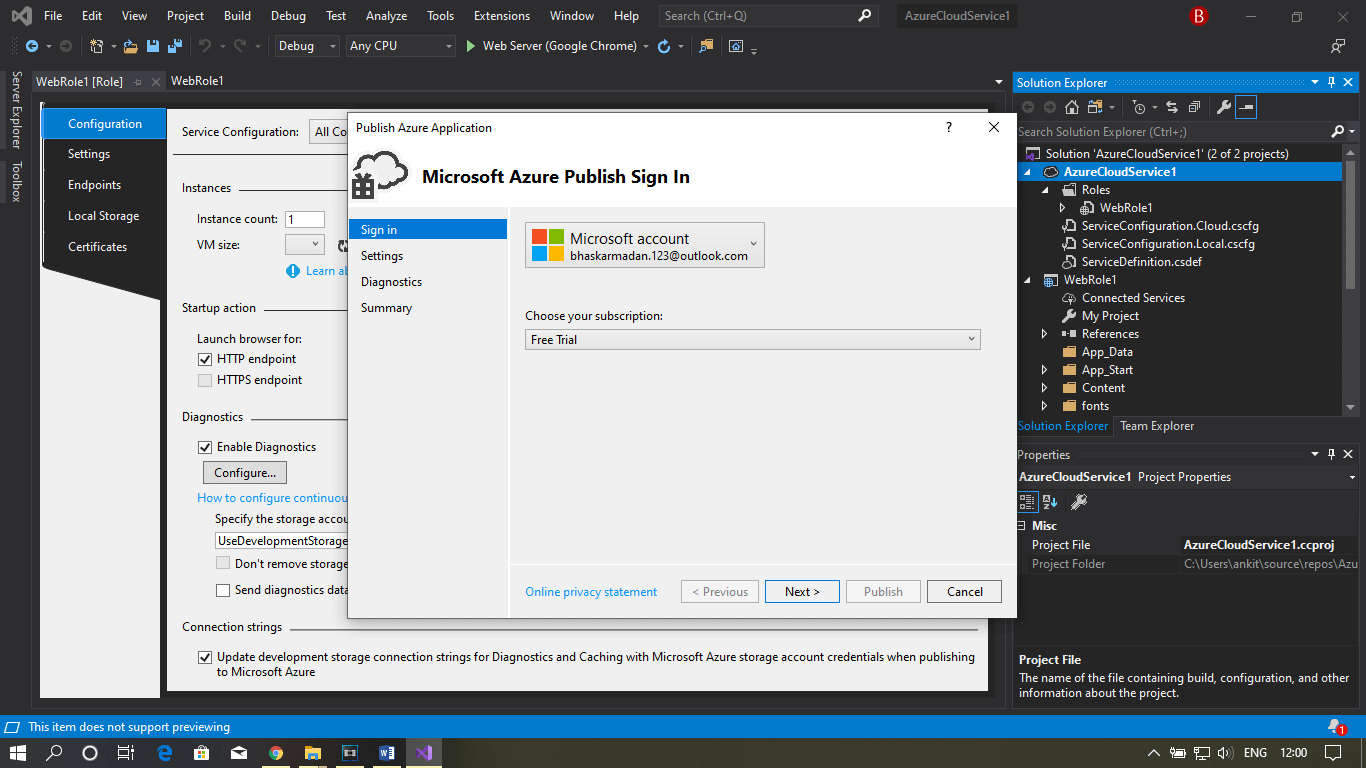
Step 8: Select your subscription and click next.
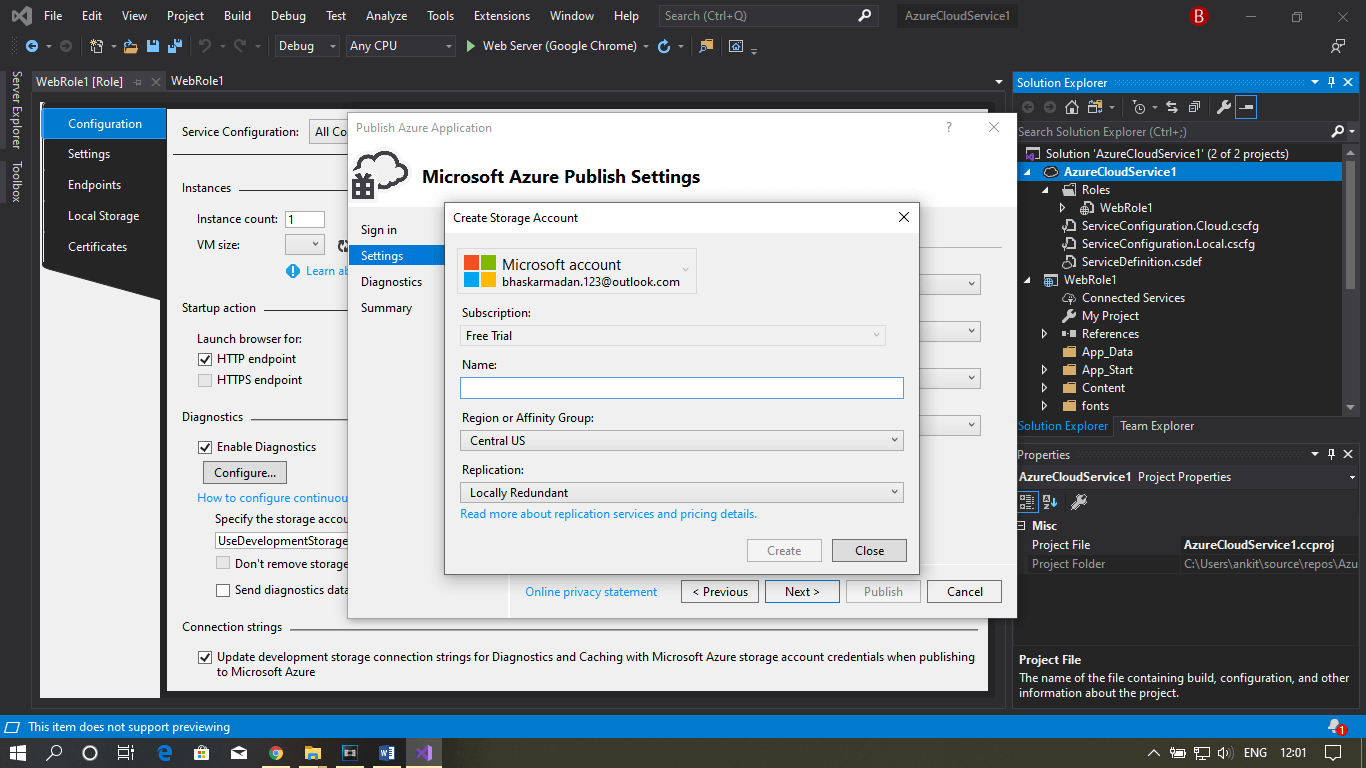
Step 9: Fill all the required details and then click on publish.
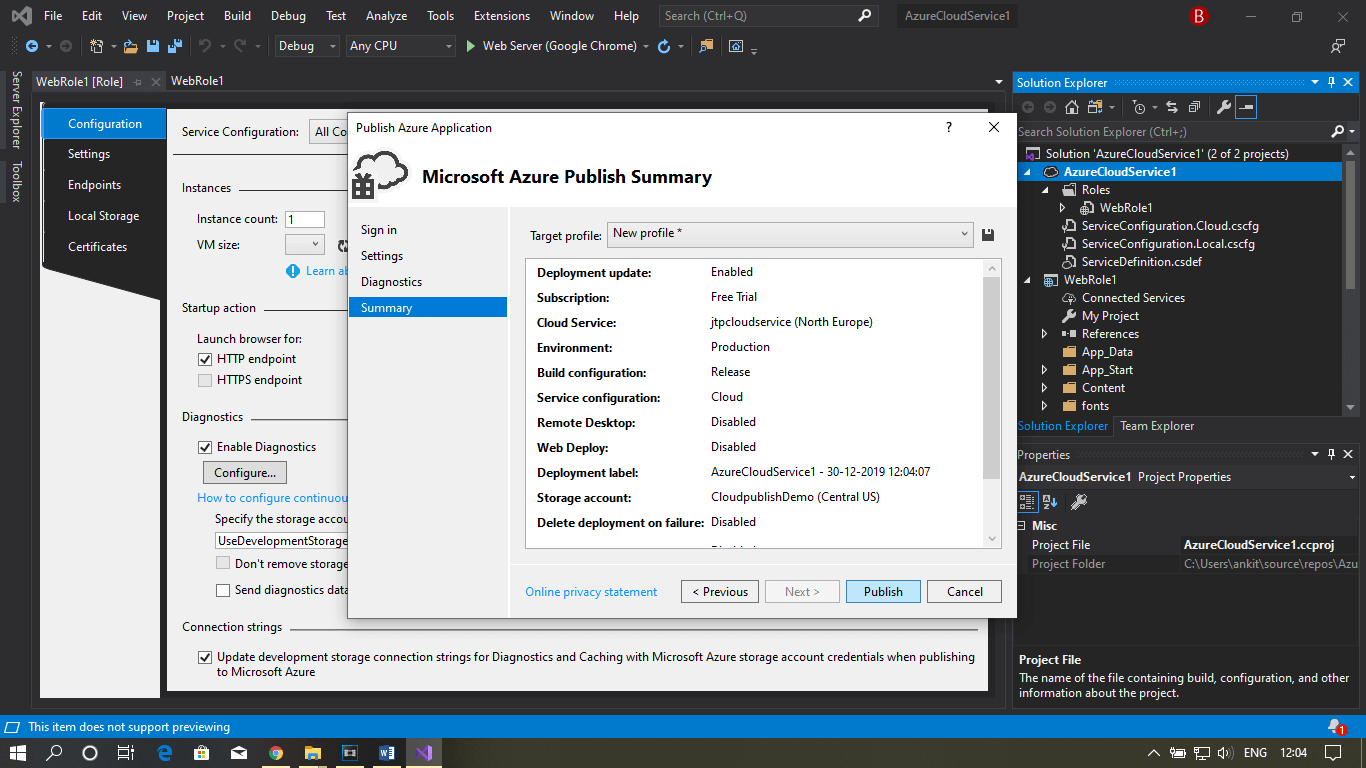
Step 10: Now, go to the Azure portal and click on the Resource group that you have created. You can now see your web role published, as shown in the figure below.