Flutter Tutorial
Dart Programming
Flutter Basics
Flutter Widgets
- Flutter Scaffold
- Flutter Container
- Flutter Row and Column
- Flutter Text
- Flutter TextField
- Flutter Buttons
- Flutter Stack
- Flutter Forms
- Flutter Alert Dialogs
- Flutter Icons
- Flutter Images
- Flutter Card
- Flutter Tabbar
- Flutter Drawer
- Flutter Lists
- Flutter GridView
- Flutter Toast Notification
- Flutter Checkbox
- Flutter Radio Button
- Flutter Progress Bar
- Flutter Snackbar
- Flutter Tooltip
- Flutter Slider
- Flutter Switch
- Flutter Charts
- Flutter Bottom Navigation Bar
- Flutter Themes
- Flutter Table
- Flutter Calendar
- Flutter Animation
Flutter Routing
Advanced Concepts
Flutter Differences
Flutter Interview Questions
Flutter Creating Android Platform-Specific Code
In this section, we are going to see how we can write custom platform-specific code in Flutter. Flutter is an excellent framework, which provides a mechanism to handle/access platform-specific features. This feature allows the developer to extend the functionality of the Flutter framework. Some of the essential platform-specific functionality that can be accessed easily through the framework are camera, battery level, browser, etc.
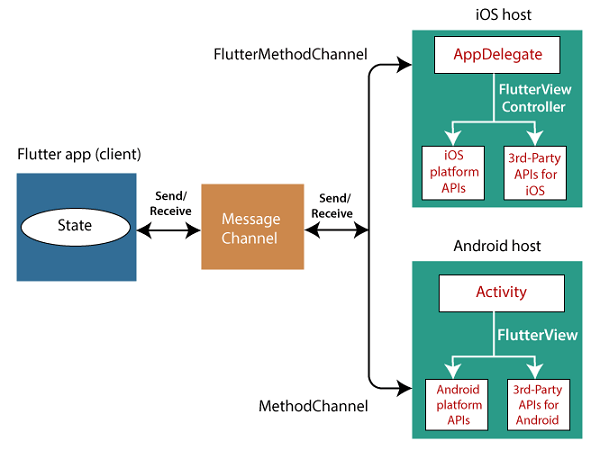
Flutter uses a flexible system to call platform-specific API either available on Android in Java or Kotlin code, or in Objective-C or Swift code on iOS. The general idea of accessing the platform-specific code in Flutter is through the messaging protocol. The messages are passed between the client (UI) and Host (Platform) using the common message channel. It means the clients sends a message to the Host by using this message channel. Next, the Host listens on that message channel, receives the message, does the appropriate functionality, and finally returns the result to the client.
The following block diagram shows the appropriate platform-specific code architecture.
The messaging channel uses a standard message codec (StandardMessageCodec class), which supports efficient binary serialization of JSON like values, such as string, Boolean, numbers, byte buffers, and List and Maps, etc. The serialization and deserialization of these values work automatically between clients and hosts when you send and receive values.
The following table shows how dart values are received on Android and iOS platform and vice-versa:
| Dart | Android | iOS |
|---|---|---|
| null | null | nil (NSNull when nested) |
| bool | java.lang.Boolean | NSNumber numberWithBool: |
| int | java.lang.Integer | NSNumber numberWithInt: |
| double | java.lang.Double | NSNumber numberWithDouble: |
| String | java.lang.String | NSString: |
| Uint8List | byte[] | FlutterStandardTypedData typedDataWithBytes: |
| Int32List | int[] | FlutterStandardTypedData typedDataWithInt32: |
| Int64List | long[] | FlutterStandardTypedData typedDataWithInt64: |
| Float64List | double[] | FlutterStandardTypedData typedDataWithFloat64: |
| List | java.util.ArrayList | NSArray |
| Map | java.util.HashMAp | NSDictionary |
Let us create a simple application to demonstrate how to call a platform-specific API to open a browser. To do this, we need to create a Flutter project in Android Studio and insert the following code in the main.dart file.
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter DemoApplication',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.green,
),
home: MyHomePage(
title: 'Flutter Platform Specific Page'
),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
static const platform = const MethodChannel('flutterplugins.javatpoint.com/browser');
Future<void> _openBrowser() async {
try {
final int result = await platform.invokeMethod('openBrowser', <String, String>{
'url': "https://www.javatpoint.com"
});
}
on PlatformException catch (e) {
// Unable to open the browser
print(e);
}
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(this.title),
),
body: Center(
child: RaisedButton(
child: Text('Click Here'),
onPressed: _openBrowser,
),
),
);
}
}
In the above file, we have imported a service.dart file, which includes the functionality to invoke the platform-specific code. In the MyHomePage widget, we have created a message channel and write a method _openBrowser to invoke the platform-specific code.
try {
final int result = await platform.invokeMethod('openBrowser', <String, String>{
'url': "https://www.javatpoint.com"
});
}
on PlatformException catch (e) {
// Unable to open the browser
print(e);
}
}
Finally, we have created a button to open the browser.
Now, we need to provide the custom platform-specific implementation. To do this, navigate to the Android folder of your Flutter project and select the Java or Kotlin file and insert the following code into the MainActivity file. This code might change according to the Java or Kotlin language.
import android.app.Activity
import android.content.Intent
import android.net.Uri
import android.os.Bundle
import io.flutter.app.FlutterActivity
import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodCall
import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel
import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel.MethodCallHandler
import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel.Result
import io.flutter.plugins.GeneratedPluginRegistrant
class MainActivity:FlutterActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState:Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
GeneratedPluginRegistrant.registerWith(this)
MethodChannel(flutterView, CHANNEL).setMethodCallHandler { call, result ->
val url = call.argument<String>("url")
if (call.method == "openBrowser") {
openBrowser(call, result, url)
} else {
result.notImplemented()
}
}
}
private fun openBrowser(call:MethodCall, result:Result, url:String?) {
val activity = this
if (activity == null)
{
result.error("UNAVAILABLE", "It cannot open the browser without foreground activity", null)
return
}
val intent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW)
intent.data = Uri.parse(url)
activity!!.startActivity(intent)
result.success(true as Any)
}
companion object {
private val CHANNEL = "flutterplugins.javatpoint.com/browser"
}
}
In the MainActivity.kt file, we have created a method openBrowser() to open the browser.
val activity = this
if (activity == null)
{
result.error("UNAVAILABLE", "It cannot open the browser without foreground activity", null)
return
}
val intent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW)
intent.data = Uri.parse(url)
activity!!.startActivity(intent)
result.success(true as Any)
}
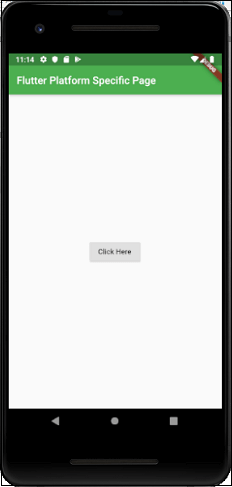
Output
Now, run the app in your android studio, you will get the following output. When you click on the button Click Here, you can see that the browser home page screen is launched.