Selenium Tutorial
Selenium IDE
Selenium WebDriver
selenium Misc
Selenium Python
Selenium C#
Selenium Maven
Selenium Interview Questions
Selenium Waits
Selenium Waits
You might have come across wait commands while writing your first Selenium program. In this article, you would be learning about what exactly Selenium Waits is. You would be covering various types and other necessary factors one needs to understand to get started with Selenium Waits.
What is Selenium Waits?
Waits in Selenium is one of the important pieces of code that executes a test case. It runs on certain commands called scripts that make a page load through it. Selenium Waits makes the pages less vigorous and reliable. It provides various types of wait options adequate and suitable under favorable conditions. This ensures you don't mess up and get ended into failed scripts while performing automation testing with it.
Elaborately, Selenium Waits helps the user to troubleshoot various issues while page redirection across different web pages. It is achieved by refreshing the entire web page and reloading it with new elements. At times, there's a call from Ajax as well. Thus, some time lag might exist while reloading pages and reflecting elements present on the web pages after refreshing.
Another instance to understand Selenium Waits is navigating web pages back and forth with the navigate() command. This navigate() method comes from WebDriver, whose main task is to simulate and manifest real-time scenarios like navigating between web pages concerning browsing history.
Why Do You Need Waits In Selenium?
Today, most of the modern application's front-end is built on either Ajax or JavaScript, followed by popular frameworks like Angular, React, or any other, which takes some time for loading elements on the web page. Hence, in such a case, Selenium throws an 'ElementNotVisibleException' message when you tend to locate an element present in your script which is still not loaded on the web page.
To clarify, you can look at the below code snippet where automation testing with Selenium is executed.
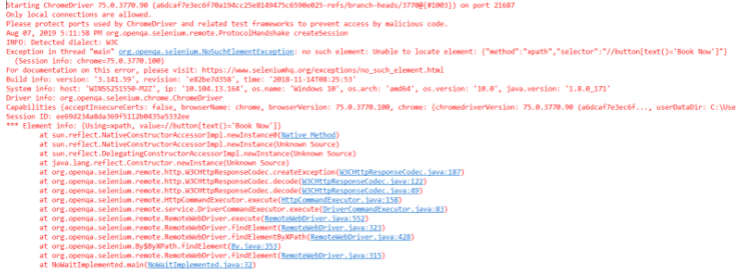
The given code will help you showcase the same problem as you execute automation testing with Selenium. An example of easemytrip.com is used, where the posting user selects the 'From' and 'To' destination with a date of journey. The web application takes a certain time to load the required flight details. In this case, without applying Wait, the user tends to book the first flight from the list. Since the page hasn't loaded yet, the script failed to find the 'book now button. It results in throwing a 'NoSuchElementException'. It is given below:
import org.open.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.JavascriptExecutor;
import org.openqa.selenium.Keys;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import
com.gargoylesoftware.htmlunit.javascript.background.JavaScriptExec
utor;
public class NoWaitImplemented {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver",
".\\Driver\\chromedriver.exe");
WebDriver driver=new ChromeDriver();
driver.manage().window().maximize();
driver.get("https://www.easemytrip.com/");
driver.findElement(By.id("FromSector_show")).sendKeys("Delhi",
Keys.ENTER);
driver.findElement(By.id("Editbox13_show")).sendKeys("Mumbai",
Keys.ENTER);
driver.findElement(By.id("ddate")).click();
driver.findElement(By.id("snd_4_08/08/2019")).click();
driver.findElement(By.className("src_btn")).click();
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//button[text()='Book Now']")).click();
}
}
The above code snippet depicts the same problem while executing automation testing with Selenium. In this code snippet, you can see an example of "easemytrip.com," where the user will select 'From' and 'To' destination selection with a journey date. The web application takes a certain loading time to load the available flights based on the selected input fields provided by the user. In this case, the user might select and book only the first flight from the list. Since the page is still loading, the script has failed to find the 'Book Now' button. This directly throws a 'NoSuchElementExpection' return status with the following output shown below.
Types of Waits in Selenium
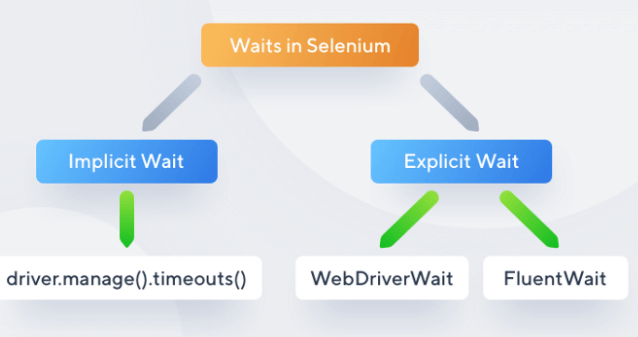
Implicit Waits
The main function of implicit Wait is to tell the web driver to wait for some time before throwing a "No Such Element Exception". Its default setting is knocked at zero. Once the time is set, the driver automatically will wait for the amount of time defined by you before throwing the above-given exception.
Syntax:
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(TimeOut,
TimeUnit.SECONDS);
To understand how implicit wait works, let's consider an example.
package Sachin;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
public class ImplicitWait{
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
{
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "C:Selenium-java-
javaTpointchromedriver_win32chromedriver.exe");
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.manage().window().maximize();
driver.manage().deleteAllCookies();
driver.manage().timeouts().pageLoadTimeout(40,
TimeUnit.SECONDS); // pageload timeout
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(20, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// Implicit Wait for 20 seconds
driver.get("https://login.google.com/");
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='login-
username']")).sendKeys("sachin"); //Finding element and
sending values
Thread.sleep(1000);
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='login-signin']")).click(); //Clicking on the next button if element is located
}
}
In the code snippet given above, the Implicit Wait is defined for only 20 seconds, implying that the output will load or arrive within the maximum waiting time of 20 seconds for the particular element.
Explicit Waits
Explicit Waits also known as Dynamic Waits because it is highly specific conditioned. It is implemented by WebDriverWait class. To understand why you need Explicit Wait in Selenium, you must go through the basic knowledge of the wait statements in a program. In simple terms, you must know some conditions. Such conditions have been created to give you a gist of the Explicit Waits and why they are important.
Condition 1:
Suppose you have a web page consisting of a login form that takes input and loads the Home or Main page content. This page is dynamic because of the time constraints and network frequency, sometimes taking 10 seconds or maybe 15 seconds to load completely. Explicit Wait comes in handy in such cases and allows you to wait until the page is not present to display.
Condition 2:
Consider that you are working on an application that is travel themed and users fill the web form and submit it using submit button. Now, you might need to wait until and unless the specific data is not displayed. In such a case, Explicit Wait becomes helpful by waiting until a specific period for the set of elements that are not displayed yet.
Syntax:
WebDriverWait wait=new
ebDriverWait(WebDriveReference,TimeOut);
The above syntax justifies an object of WebDriver Wait and is passed to the driver's preference, and the timeout is taken as a parameter. To understand this more broadly, consider the below sample application.
package Sacin;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
public class Locators {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "C:Selenium-java-
javatpointchromedriver_win32chromedriver.exe");
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.manage().window().maximize();
driver.manage().deleteAllCookies();
driver.manage().timeouts().pageLoadTimeout(40,
TimeUnit.SECONDS);
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
driver.get("https://www.facebook.com/");
WebElement firstname= driver.findElement(By.name("firstname"));
WebElement lastname= driver.findElement(By.name("lastname"));
sendKeys(driver, firstname, 10, "Edureka");
sendKeys(driver, lastname, 20, "Edureka");
WebElement forgotAccount=
driver.findElement(By.linkText("Forgotten account?"));
clickOn(driver,forgotAccount, 10);
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
public static void sendKeys(WebDriver driver1, WebElement element,
int timeout, String value){
new WebDriverWait(driver1,
timeout).until(ExpectedConditions.visibilityOf(element));
element.sendKeys(value);
}
public static void clickOn(WebDriver driver1, WebElement element,
int timeout)
{
new WebDriverWait(driver1,
timeout).until(ExpectedConditions.elementToBeClickable(element));
element.click();
}
}
In the sample snippet given above, you can see Facebook sign-up credentials using locators have been created. Further, a generic utility function is created to make all the elements available for the Explicit Wait. Also, sendKeys() method is defined for the particular text field that would internally provide explicit Wait. Inside the sendKeys() method, there are some expected conditions for the element. This means that the driver is being asked to wait for 20 seconds until and unless the expected condition of the element is visible. Furthermore, the main purpose of applying the sendKeys() method is to take the first name and the last name, and that will be passed to the driver. The timeout is defined to be 10 seconds for the first name and the last name.
When the above program is executed, the Chrome driver will launch Chrome, and it will navigate through facebook.com to take the mentioned values. It is, although not mandatory, to explicitly set the timeout for a particular value since it is changeable. Another advantage to adding up here is that once you define the timeout for 10 seconds, it becomes applicable for all the elements present on the web page, and then it cannot be modified. The same concept works with the onClick() method defined in the above program, but this method is constrained only to links. This is the best way to execute, understand and execute Explicit Wait.
Difference between Implicit and Explicit
- Implicit Wait applies to all the elements in the script, while Explicit Wait is applicable only for those values which are to be defined by the user.
- Implicit Wait needs specifying "ExpectedConditions" on the located element, while Explicit Wait doesn't need to be specified with this condition.
- Implicit Wait needs time frame specification in terms of methods like element visibility, clickable element, and the elements that are to be selected. In contrast, Explicit Wait is dynamic and needs no such specifications.
Fluent Wait
Fluent Wait is quite similar to explicit Wait. It is similar in terms of management and functioning. In Fluent Wait, you can perform wait for action for an element only when you are unaware of the time it might take to be clickable or visible. Few differential factors that Fluent offers are as follows:
The pooling frequency
The pooling frequency in the case of Explicit is 500 milliseconds. But, using Fluent Wait, this pooling frequency can be changed to any value based upon your need. This usually means telling the script to keep an eye on the element after every 'x' seconds.
Ignore Exception


