Cassandra Tutorial
Cassandra Keyspace
Cassandra Table Index
Cassandra Query (CQL)
Cassandra Collections
Cassandra Interview
Cassandra Collections
Cassandra collections are used to handle tasks. You can store multiple elements in collection. There are three types of collection supported by Cassandra:
- Set
- List
- Map
Set Collection
A set collection stores group of elements that returns sorted elements when querying.
Syntax:
Java Collection MCQ Set 1
(
id int,
Name text,
Email set,
Primary key(id)
);
Example:
Let's take an example to demonstrate set collection. Create a table "employee" having the three columns id, name and email.
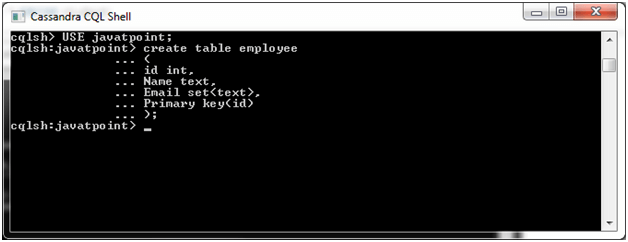
The table is created like this:
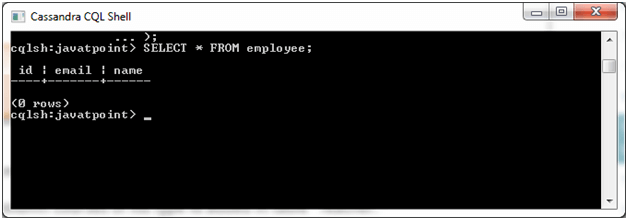
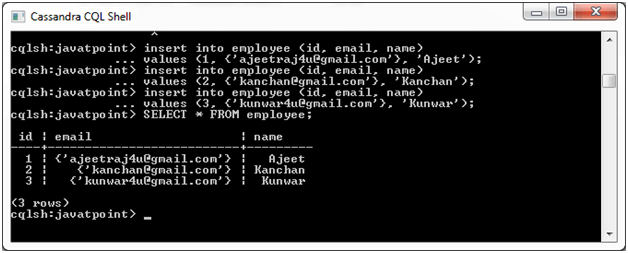
Insert values in the table:
VALUES(1, {'ajeetraj4u@gmail.com'}, 'Ajeet');
INSERT INTO employee (id, email, name)
VALUES(2,{'kanchan@gmail.com'}, 'Kanchan');
INSERT INTO employee (id, email, name)
VALUES(3, {'kunwar4u@gmail.com'}, 'Kunwar');
Output:
List Collection
The list collection is used when the order of elements matters.
Let's take the above example of "employee" table and a new column name "department" in the table employee.
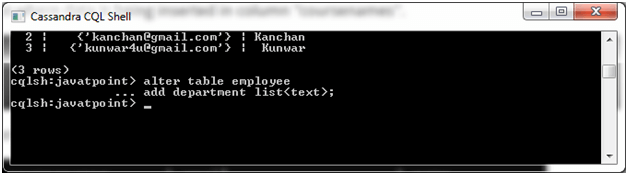
Now the new column is added. Insert some value in the new column "department".
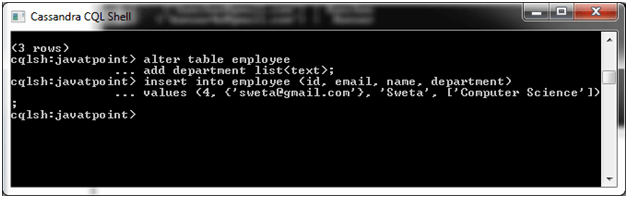
Output:
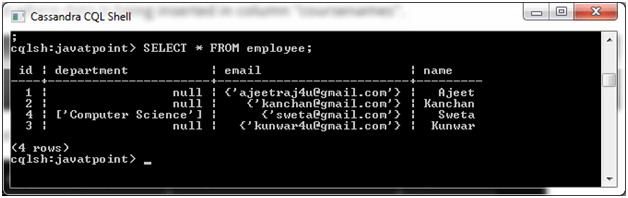
Map Collection
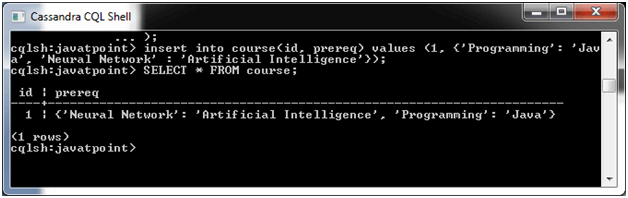
The map collection is used to store key value pairs. It maps one thing to another. For example, if you want to save course name with its prerequisite course name, you can use map collection.
See this example:
Create a table named "course".
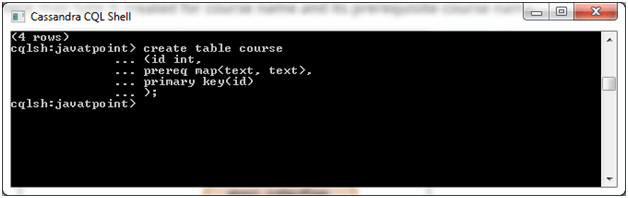
Now table is created. Insert some data in map collection type.
Output: