Java
JSP
JSTL
Java Tutorial
Control Statements
Java Object Class
Java Inheritance
Java Polymorphism
Java Abstraction
Java Encapsulation
Java Array
Java OOPs Misc
Hibernet
Inheritance in Java
Inheritance in Java
- Inheritance
- Types of Inheritance
- Why multiple inheritance is not possible in Java in case of class?
Inheritance in Java is a mechanism in which one object acquires all the properties and behaviors of a parent object. It is an important part of OOPs (Object Oriented programming system).
The idea behind inheritance in Java is that you can create new classes that are built upon existing classes. When you inherit from an existing class, you can reuse methods and fields of the parent class. Moreover, you can add new methods and fields in your current class also.
Inheritance represents the IS-A relationship which is also known as a parent-child relationship.
Why use inheritance in java
- For Method Overriding (so runtime polymorphism can be achieved).
- For Code Reusability.
Terms used in Inheritance
- Class: A class is a group of objects which have common properties. It is a template or blueprint from which objects are created.
- Sub Class/Child Class: Subclass is a class which inherits the other class. It is also called a derived class, extended class, or child class.
- Super Class/Parent Class: Superclass is the class from where a subclass inherits the features. It is also called a base class or a parent class.
- Reusability: As the name specifies, reusability is a mechanism which facilitates you to reuse the fields and methods of the existing class when you create a new class. You can use the same fields and methods already defined in the previous class.
The syntax of Java Inheritance
class Subclass-name extends Superclass-name
{
//methods and fields
}
The extends keyword indicates that you are making a new class that derives from an existing class. The meaning of "extends" is to increase the functionality.
java Inheritance Example
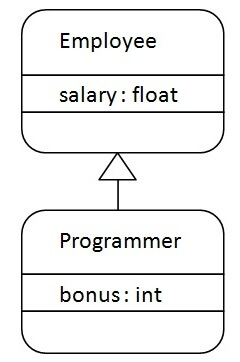

class Employee{
float salary=40000;
}
class Programmer extends Employee{
int bonus=10000;
public static void main(String args[]){
Programmer p=new Programmer();
System.out.println("Programmer salary is:"+p.salary);
System.out.println("Bonus of Programmer is:"+p.bonus);
}
}
class Employee{
float salary=40000;
}
class Programmer extends Employee{
int bonus=10000;
public static void main(String args[]){
Programmer p=new Programmer();
System.out.println("Programmer salary is:"+p.salary);
System.out.println("Bonus of Programmer is:"+p.bonus);
}
}
The relationship between the two classes is Programmer IS-A Employee. It means that Programmer is a type of Employee.

